Abstract
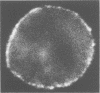
During the winter of 1977-1978 three influenza A virus serotypes (A/Vic/3/75, A/Texas/1/77 [both H3N2], and A/USSR/90/77 [H1N1]) circulated in Denver, offering us the opportunity to apply fluorescent antibody techniques to the specific identification of these viruses. Surface antigens of infected, unfixed primary monkey kidney cells were stained in suspension by an indirect immunofluorescence technique with anti-H3N2 and anti-H1N1 antisera. In tests of cells infected with known viruses, the members of the H3N2 family could not be distinguished from one another, but were easily distinguished from H1N1 strains. A total of 101 hemadsorption-positive clinical specimens were evaluated over a 6-month period. Forty-five of 48 influenza A H3N2 and 24 of 29 H1N1 specimens confirmed by hemagglutination inhibition were correctly identified by membrane fluorescence of cultured cells, with no misidentifications among influenza strains and with 1 false positive among 24 non-influenza isolates. The average time to identification by this technique was 4 days compared to 7 days by hemagglutination inhibition. Live cell membrane fluorescence is a simple, rapid, and accurate method for identifying and grouping influenza A viruses.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bjorvatn B., Wolontis S. The use of immunofluorescence in the laboratory diagnosis of influenza type B. Scand J Infect Dis. 1972;4(3):177–182. doi: 10.3109/inf.1972.4.issue-3.02. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braciale T. J. Immunologic recognition of influenza virus-infected cells. II. Expression of influenza A matrix protein on the infected cell surface and its role in recognition by cross-reactive cytotoxic T cells. J Exp Med. 1977 Sep 1;146(3):673–689. doi: 10.1084/jem.146.3.673. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brocklebank J. T., Court S. D., McQuillin J., Gardner P. S. Influenza-A infection in children. Lancet. 1972 Sep 9;2(7776):497–500. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(72)91902-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardner P. S., McQuillin J., McGuckin R., Ditchburn R. K. Observations on clinical and immunofluorescent diagnosis of parainfluenza virus infections. Br Med J. 1971 Apr 3;2(5752):7–12. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5752.7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hers J. F., van der Kuip L., Masurel N. Rapid diagnosis of influenza. Lancet. 1968 Mar 9;1(7541):510–511. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(68)91470-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ISAACS A., ANDREWES C. H. The spread of influenza; evidence from 1950-1951. Br Med J. 1951 Oct 20;2(4737):921–927. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.4737.921. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joseph B. S., Oldstone M. B. Antibody-induced redistribution of measles virus antigens on the cell surface. J Immunol. 1974 Oct;113(4):1205–1209. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KLEIN E., KLEIN G. ANTIGENIC PROPERTIES OF LYMPHOMAS INDUCED BY THE MOLONEY AGENT. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1964 Mar;32:547–568. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein G., Pearson G., Nadkarni J. S., Nadkarni J. J., Klein E., Henle G., Henle W., Clifford P. Relation between Epstein-Barr viral and cell membrane immunofluorescence of Burkitt tumor cells. I. Dependence of cell membrane immunofluorescence on presence of EB virus. J Exp Med. 1968 Nov 1;128(5):1011–1020. doi: 10.1084/jem.128.5.1011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LIU C. Rapid diagnosis of human influenza infection from nasal smears by means of fluorescein-labeled antibody. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1956 Aug-Sep;92(4):883–887. doi: 10.3181/00379727-92-22642. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maeno K., Kilbourne E. D. Developmental sequence and intracellular sites of synthesis of three structural protein antigens of influenza A2 virus. J Virol. 1970 Feb;5(2):153–164. doi: 10.1128/jvi.5.2.153-164.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malmgren R. A., Takemoto K. K., Carney P. G. Immunofluorescent studies of mouse and hamster cell surface antigens induced by polyoma virus. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1968 Feb;40(2):263–268. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nahmias A., DelBuono I., Pipkin J., Hutton R., Wickliffe C. Rapid identification and typing of herpes simplex virus types 1 and 2 by a direct immunofluorescence technique. Appl Microbiol. 1971 Sep;22(3):455–458. doi: 10.1128/am.22.3.455-458.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakajima K., Desselberger U., Palese P. Recent human influenza A (H1N1) viruses are closely related genetically to strains isolated in 1950. Nature. 1978 Jul 27;274(5669):334–339. doi: 10.1038/274334a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olding-Stenkvist E., Grandien M. Rapid diagnosis of influenza A infection by immunofluorescence. Methodological problems and clinical material. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B. 1977 Oct;85B(5):296–302. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1977.tb01978.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott R., De Landazuri M. O., Gardner P. S., Owen J. J. Detection of antibody to respiratory syncytial virus by membrane fluorescence. Clin Exp Immunol. 1976 Oct;26(1):78–85. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tateno I., Kitamoto O., Kawamura A., Jr Diverse immunocytologic findings of nasal smears in influenza. N Engl J Med. 1966 Feb 3;274(5):237–242. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196602032740502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WATSON B. K., COONS A. H. Studies of influenza virus infection in the chick embryo using fluorescent antibody. J Exp Med. 1954 May 1;99(5):419–428. doi: 10.1084/jem.99.5.419. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams V., Gershon A., Brunell P. A. Serologic response to varicella-zoster membrane antigens measured by direct immunofluorescence. J Infect Dis. 1974 Dec;130(6):669–672. doi: 10.1093/infdis/130.6.669. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]