Abstract
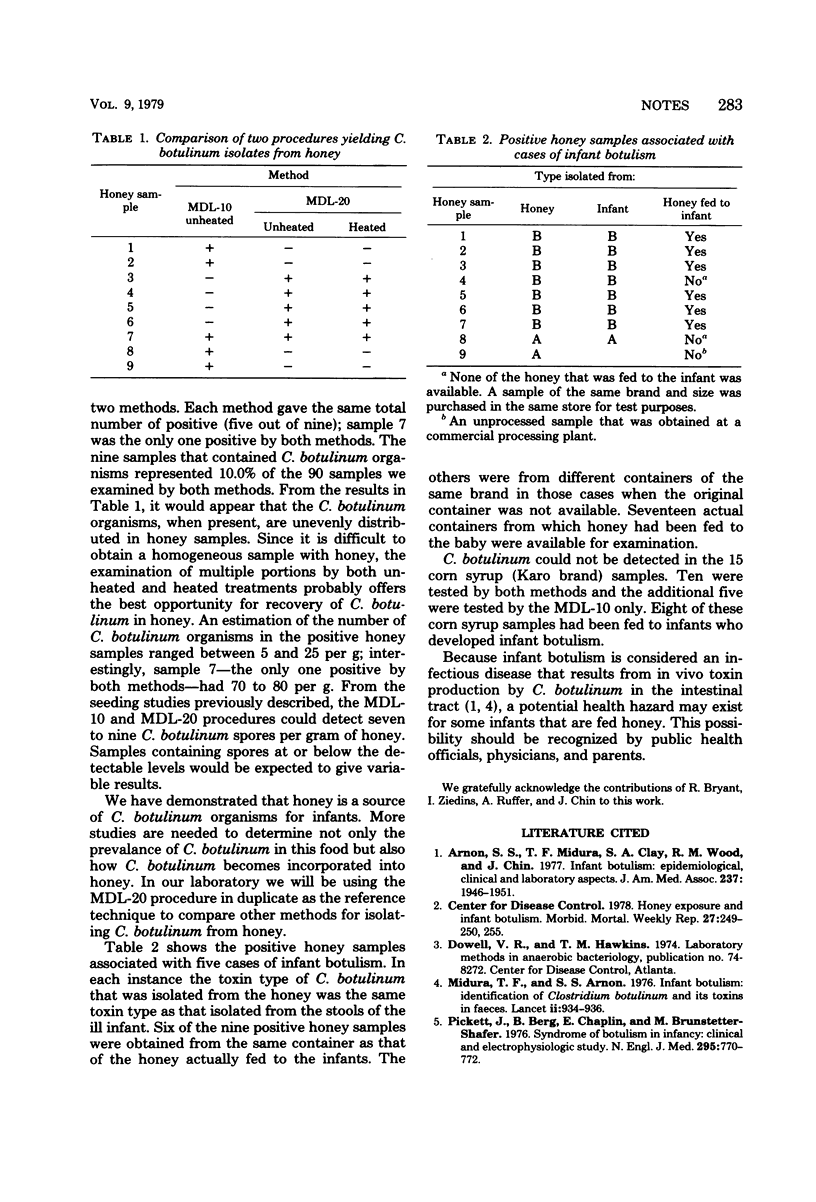
Methods for the isolation of Clostridium botulinum from honey samples are described. A total of 9 of 90 honey samples were positive for C. botulinum; 6 of the positive samples had been fed to babies who developed infant botulism.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arnon S. S., Midura T. F., Clay S. A., Wood R. M., Chin J. Infant botulism. Epidemiological, clinical, and laboratory aspects. JAMA. 1977 May 2;237(18):1946–1951. doi: 10.1001/jama.237.18.1946. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Midura T. F., Arnon S. S. Infant botulism. Identification of Clostridium botulinum and its toxins in faeces. Lancet. 1976 Oct 30;2(7992):934–936. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(76)90894-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pickett J., Berg B., Chaplin E., Brunstetter-Shafer M. A. Syndrome of botulism in infancy: clinical and electrophysiologic study. N Engl J Med. 1976 Sep 30;295(14):770–772. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197609302951407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


