Abstract
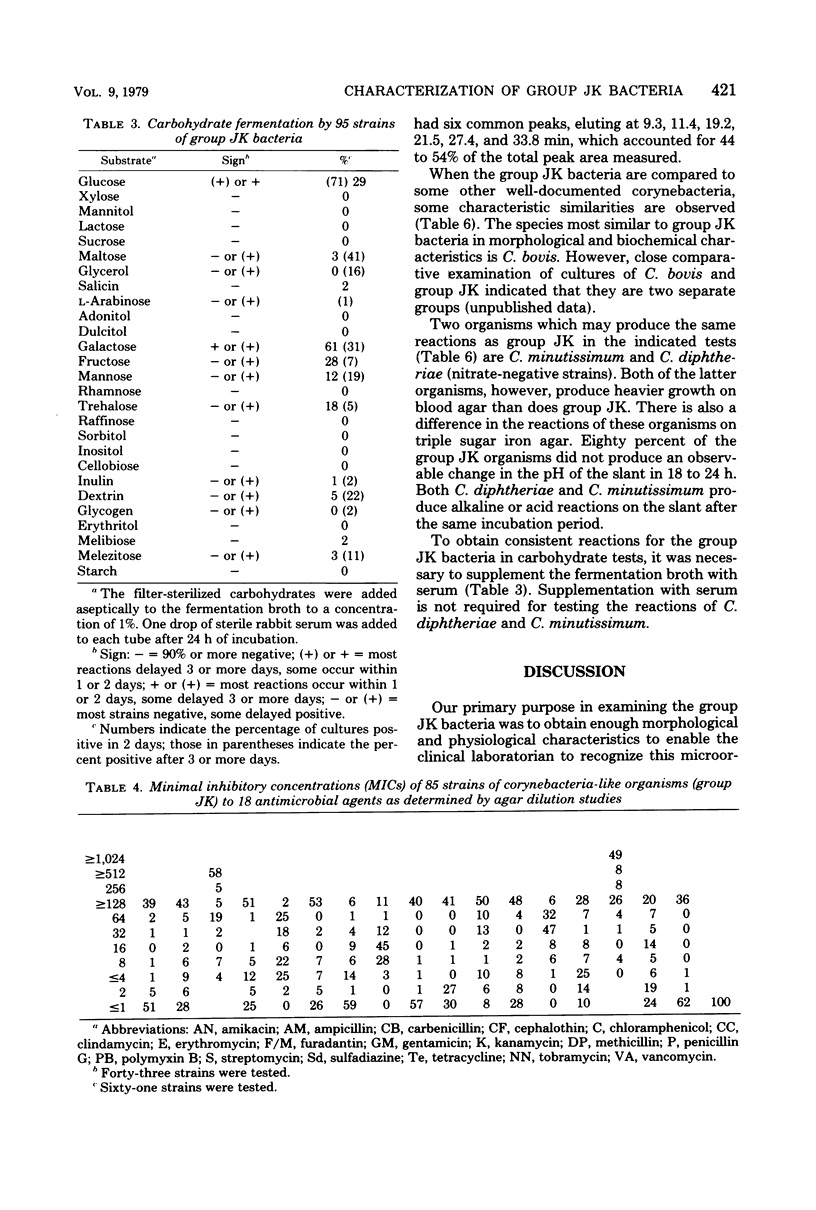
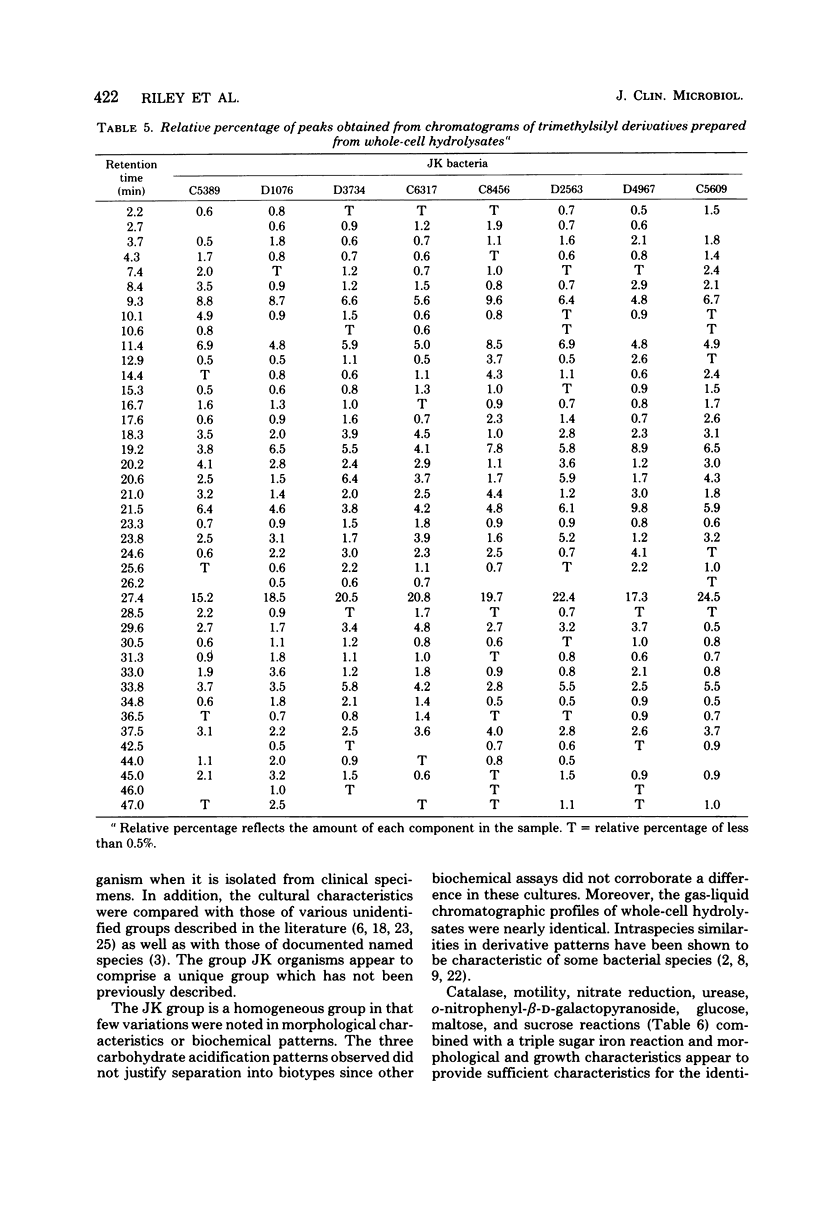
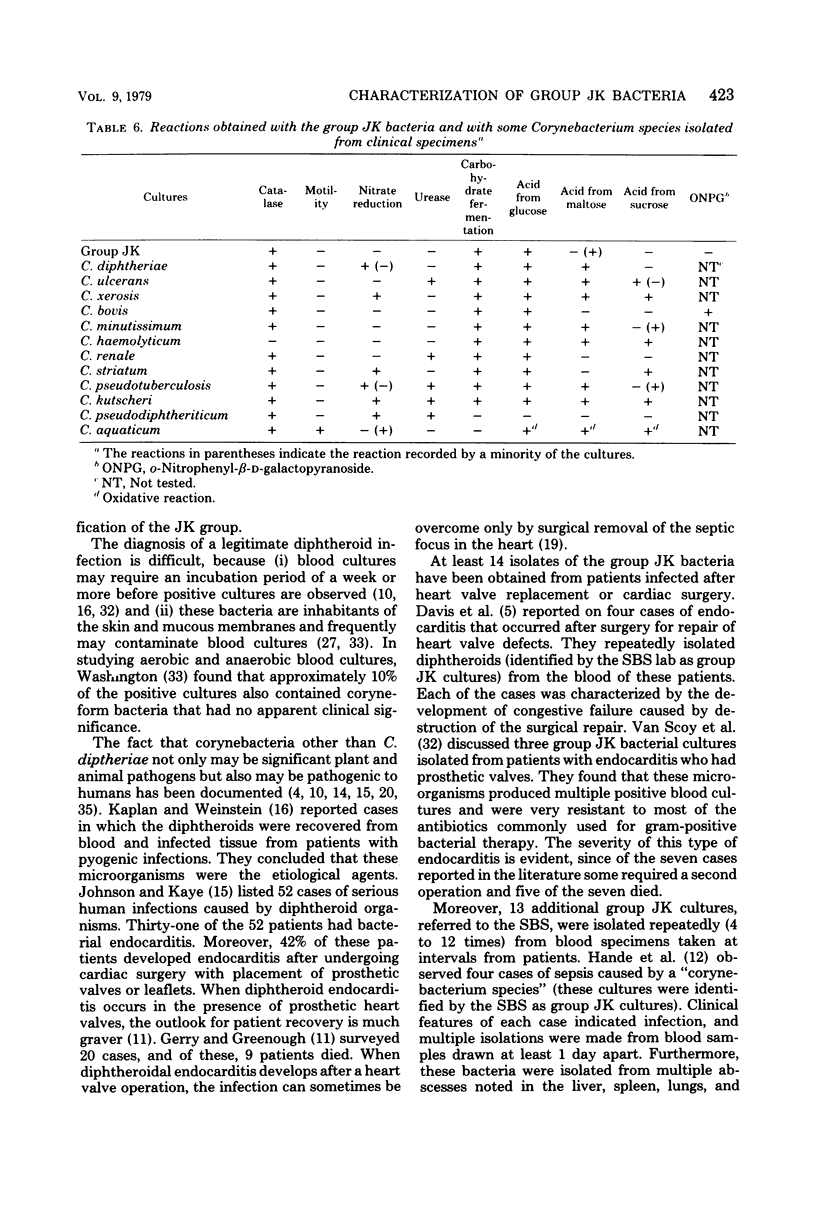
Ninety-five cultures of group JK bacteria isolated from clinical specimens were characterized morphologically and biochemically. The microorganisms were isolated primarily from blood cultures. The bacterial cultures produced positive reactions when tested for catalase, Tween hydrolysis, and carbohydrate fermentation. Glucose and galactose were fermented by more than 90% of the organisms. Gas-liquid chromatography of trimethylsilyl derivatives of whole-cell hydrolysates of some of the group JK cultures yielded nearly identical elution profiles. The group JK microorganisms were susceptible to vancomycin but were resistant to most of the other 17 antimicrobial agents tested. A method is presented for differentiating the group JK microorganisms from other similar bacteria encountered in clinical specimens. Although these bacteria rarely occur in clinical specimens, they are capable of producing fatal infections (endocarditis and sepsis) in humans.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bovre K., Hytta R., Jantzen E., Froholm L. O. Gas chromatography of bacterial whole cell methanolysates. 3. Group relations of Neisseriae and Moraxellae. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B Microbiol Immunol. 1972;80(5):683–689. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1972.tb00194.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chlosta E. M., Richards G. K., Wagner E., Holland J. F. An opportunistic infection with Corynebacterium pyogenes producing empyema. Am J Clin Pathol. 1970 Feb;53(2):167–170. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/53.2.167. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans N. M. The classification of aerobic diphtheroids from human skin. Br J Dermatol. 1968 Feb;80(2):81–83. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2133.1968.tb12264.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farshy D. C., Moss C. W. Characterization of clostridia by gas chromatography differentiation of species by trimethylsilyl derivatives of whole-cell hydrolysates. Appl Microbiol. 1970 Jul;20(1):78–84. doi: 10.1128/am.20.1.78-84.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Froholm L. O., Jantzen E., Hytta R., Bovre K. Gas chromatography of bacterial whole cell methanolysates. II. A taxonomic evaluation of the method for species of Moraxella. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B Microbiol Immunol. 1972;80(5):672–682. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geraci J. E., Forth R. J., Ellis F. H., Jr Postoperative prosthetic valve bacterial endocarditis due to Corynebacterium xerosis. Mayo Clin Proc. 1967 Nov;42(11):736–743. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerry J. L., Greenough W. B., 3rd Diphtheroid endocarditis. Report of nine cases and review of the literature. Johns Hopkins Med J. 1976 Aug;139(2):61–68. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hande K. R., Witebsky F. G., Brown M. S., Schulman C. B., Anderson S. E., Jr, Levine A. S., MacLowery J. D., Chabner B. A. Sepsis with a new species of Corynebacterium. Ann Intern Med. 1976 Oct;85(4):423–426. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-85-4-423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jobanputra R. S., Swain C. P. Septicaemia due to Corynebacterium haemolyticum. J Clin Pathol. 1975 Oct;28(10):798–800. doi: 10.1136/jcp.28.10.798. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson W. D., Kaye D. Serious infections caused by diphtheroids. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1970 Oct 30;174(2):568–576. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1970.tb45582.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan K., Weinstein L. Diphtheroid infections of man. Ann Intern Med. 1969 May;70(5):919–929. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-70-5-919. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marples R. R. Diphtheroids of normal human skin. Br J Dermatol. 1969;81(Suppl):47+–47+. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2133.1969.tb12833.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller H. E., Siepe O. Uber die durch aerobe Corynebakterien bedingte Endokarditis. Dtsch Med Wochenschr. 1973 Sep 21;98(38):1765–1767. doi: 10.1055/s-0028-1107124. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PROCEK J., HLAVA H. [Pyogenic Corynebacterium as a pathogen in osteomyelitis following a fracture]. Acta Chir Orthop Traumatol Cech. 1961 Dec;28:546–548. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reid J. D., Greenwood L. Corynebacterial endocarditis. A report of two cases with review. Arch Intern Med. 1967 Jan;119(1):106–110. doi: 10.1001/archinte.119.1.106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riley P. S., Weaver R. E. Recognition of Pseudomonas pickettii in the clinical laboratory: biochemical characterization of 62 strains. J Clin Microbiol. 1975 Jan;1(1):61–64. doi: 10.1128/jcm.1.1.61-64.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith R. F., Blasi D., Dayton S. L. Isolation and characterization of corynebacteria from burned children. Appl Microbiol. 1973 Oct;26(4):554–559. doi: 10.1128/am.26.4.554-559.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith R. F. Characterization of human cutaneous lipophilic diphtheroids. J Gen Microbiol. 1969 Mar;55(3):433–443. doi: 10.1099/00221287-55-3-433. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torregrosa M. V. Infrequently encountered infections with gram-positive bacilli. Am J Clin Pathol. 1968 Dec;50(6):689–691. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/50.6.689. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Scoy R. E., Cohen S. N., Geraci J. E., Washington J. A., 2nd Coryneform bacterial endocarditis: difficulties in diagnosis and treatment, presentation of three cases, and review of literature. Mayo Clin Proc. 1977 Apr;52(4):216–219. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vanderzant C., Judkins P. W., Nickelson R., Fitzhugh H. A., Jr Numerical taxonomy of coryneform bacteria isolated from pond-reared shrimp (Penaeus aztecus) and pond water. Appl Microbiol. 1972 Jan;23(1):38–45. doi: 10.1128/am.23.1.38-45.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Washington J. A., 2nd Comparison of two commercially available media for detection of bacteremia. Appl Microbiol. 1971 Oct;22(4):604–607. doi: 10.1128/am.22.4.604-607.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiner M., Werthamer S. Corynebacterium aquaticum septicemia. Characterization of the microorganisms. Am J Clin Pathol. 1975 Sep;64(3):378–381. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/64.3.378. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]