Abstract
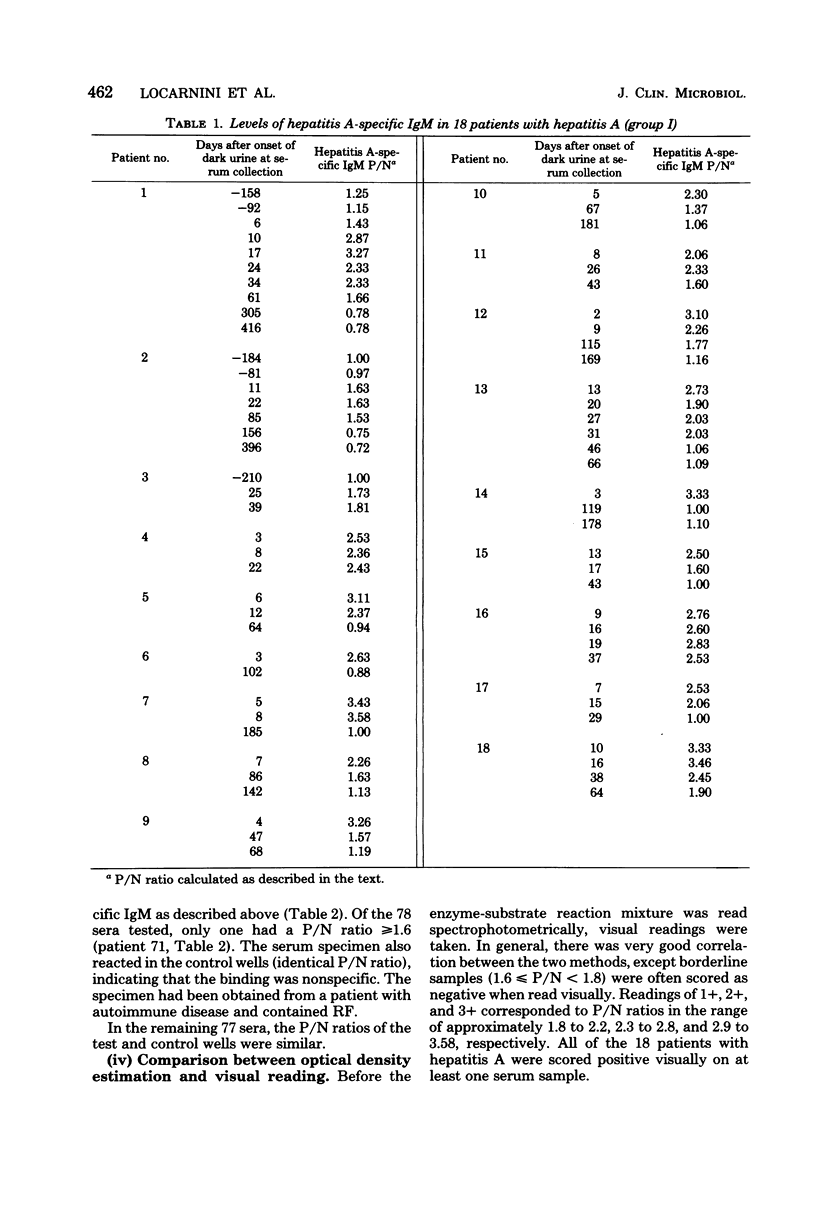
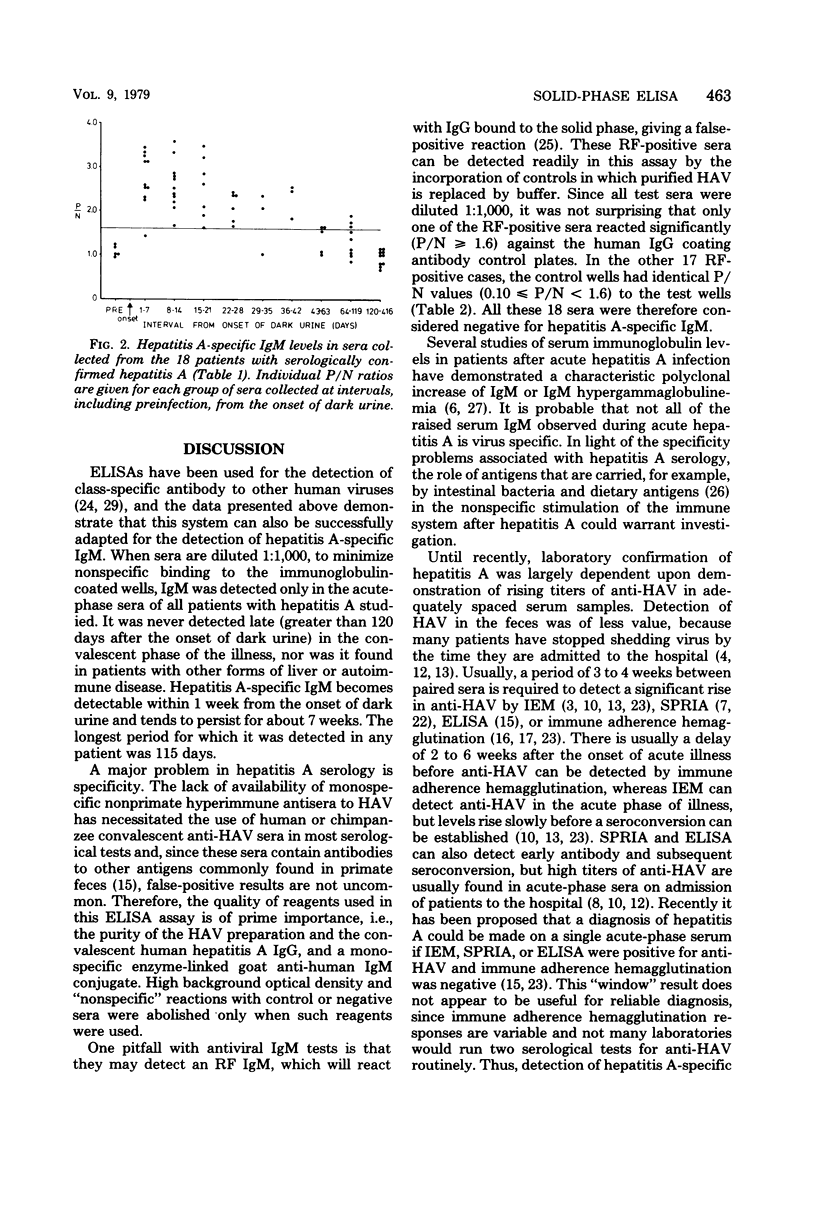
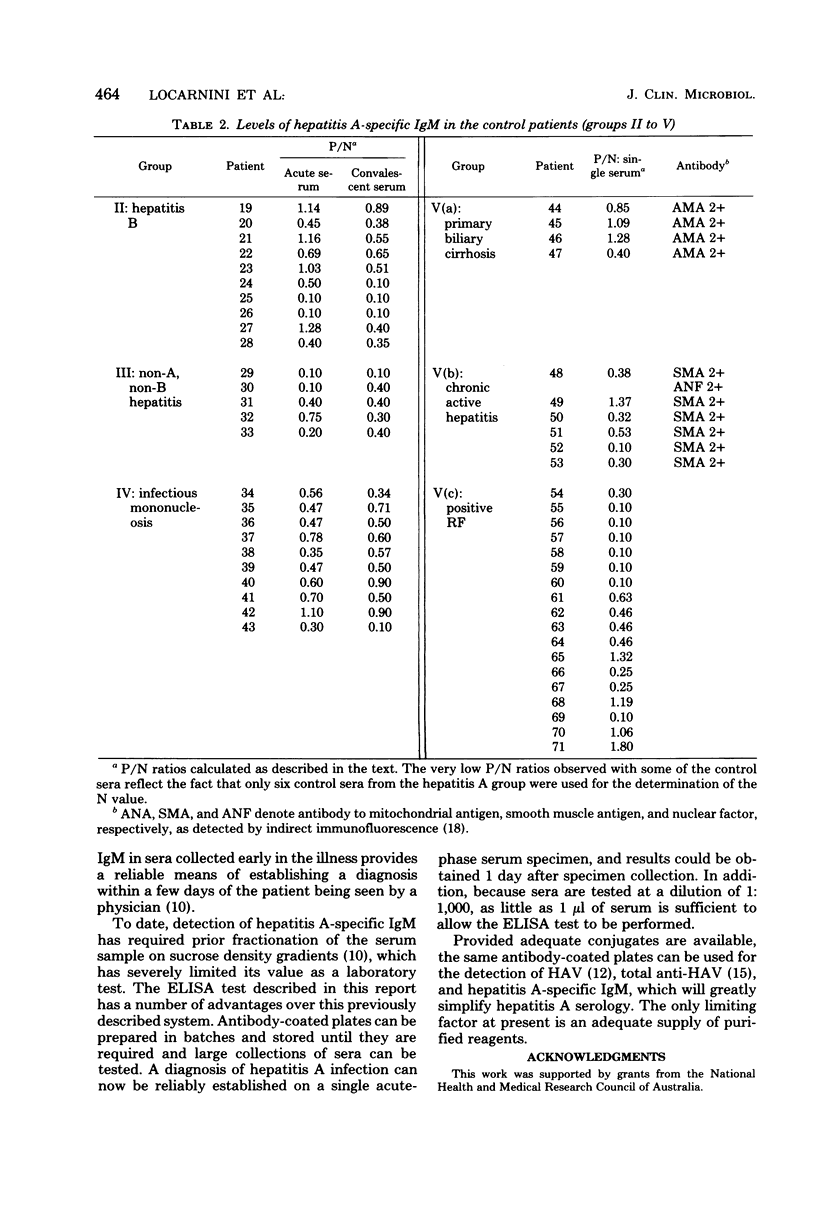
A solid-phase enzyme linked immunosorbent assay was developed for the detection of immunoglobulin M antibody to hepatitis A virus. The system was capable of detecting hepatitis A-specific immunoglobulin M in a single dilution of serum and appears to be a reliable and rapid means of establishing a diagnosis of hepatitis A infection. Specific immunoglobulin M was only detected in patients with serologically confirmed hepatitis A and not in patients with other forms of hepatitis, chronic liver disease, or autoimmune disease. In patients with hepatitis A, specific immunoglobulin M was usually detectable for 6 weeks after the onset of dark urine, and the longest period for which it was present in any patient was 115 days. This enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay is rapid, simple to perform, and does not require complicated equipment. Provided adequate supplies of purified reagents can be obtained, this enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay procedure is likely to simplify hepatitis A serology, because the same antibody-coated plates can be utilized to detect hepatitis A virus, anti-hepatitis A virus, and hepatitis A-specific immunoglobulin M.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Avrameas S., Ternynck T. The cross-linking of proteins with glutaraldehyde and its use for the preparation of immunoadsorbents. Immunochemistry. 1969 Jan;6(1):53–66. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(69)90178-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coulepis A. G., Locarnini S. A., Ferris A. A., Lehmann N. I., Gust I. D. The polypeptides of hepatitis A virus. Intervirology. 1978;10(1):24–31. doi: 10.1159/000148964. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dienstag J. L., Alling D. W., Purcell R. H. Quantitation of antibody to hepatitis A antigen by immune electron microscopy. Infect Immun. 1976 Apr;13(4):1209–1213. doi: 10.1128/iai.13.4.1209-1213.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dienstag J. L., Feinstone S. M., Kapikian A. Z., Purcell R. H. Faecal shedding of hepatitis-A antigen. Lancet. 1975 Apr 5;1(7910):765–767. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(75)92434-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinstone S. M., Kapikian A. Z., Purceli R. H. Hepatitis A: detection by immune electron microscopy of a viruslike antigen associated with acute illness. Science. 1973 Dec 7;182(4116):1026–1028. doi: 10.1126/science.182.4116.1026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giles J. P., Krugman S. Viral hepatitis. Immunoglobulin response during the course of the disease. JAMA. 1969 Apr 21;208(3):497–503. doi: 10.1001/jama.208.3.497. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollinger F. B., Bradley D. W., Maynard J. E., Dreesman G. R., Melnick J. L. Detection of hepatitis A viral antigen by radioimmunoassay. J Immunol. 1975 Nov;115(5):1464–1466. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehmann N. I., Gust I. D. The prevalence of antibody to hepatitis A virus in two populations in Victoria. Med J Aust. 1977 Nov 26;2(22):731–732. doi: 10.5694/j.1326-5377.1977.tb99252.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Locarnini S. A., Coulepis A. G., Ferris A. A., Lehmann N. I., Gust I. D. Purification of hepatitis A virus from human feces. Intervirology. 1978;10(5):300–308. doi: 10.1159/000148992. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Locarnini S. A., Ferris A. A., Lehmann N. I., Gust I. D. The antibody response following hepatitis A infection. Intervirology. 1977;8(5):309–318. doi: 10.1159/000148905. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Locarnini S. A., Ferris A. A., Stott A. C., Gust I. D. The relationship between a 27-nm virus-like particle and hepatitis A as demonstrated by immune electron microscopy. Intervirology. 1974;4(2):110–118. doi: 10.1159/000149849. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Locarnini S. A., Garland S. M., Lehmann N. I., Pringle R. C., Gust I. D. Solid-phase enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for detection of hepatitis A virus. J Clin Microbiol. 1978 Sep;8(3):277–282. doi: 10.1128/jcm.8.3.277-282.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Locarnini S. A., Gust I. D., Ferris A. A., Stott A. C., Wong M. L. A prospective study of acute viral hepatitis with particular reference to hepatitis A. Bull World Health Organ. 1976;54(2):199–206. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathiesen L. R., Feinstone S. M., Wong D. C., Skinhoej P., Purcell R. H. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for detection of hepatitis A antigen in stool and antibody to hepatitis A antigen in sera: comparison with solid-phase radioimmunoassay, immune electron microscopy, and immune adherence hemagglutination assay. J Clin Microbiol. 1978 Feb;7(2):184–193. doi: 10.1128/jcm.7.2.184-193.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKinnon G. T., Pringle R. C. A serological study of antibody to Epstein-Barr virus in an Australian population. Med J Aust. 1974 Aug 17;2(7):243–246. doi: 10.5694/j.1326-5377.1974.tb70741.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller W. J., Provost P. J., McAleer W. J., Ittensohn O. L., Villarejos V. M., Hilleman M. R. Specific immune adherence assay for human hepatitis A antibody application to diagnostic and epidemiologic investigations. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1975 May;149(1):254–261. doi: 10.3181/00379727-149-38783. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moritsugu Y., Dienstag J. L., Valdesuso J., Wong D. C., Wagner J., Routenberg J. A., Purcell R. H. Purification of hepatitis A antigen from feces and detection of antigen and antibody by immune adherence hemagglutination. Infect Immun. 1976 Mar;13(3):898–908. doi: 10.1128/iai.13.3.898-908.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakane P. K., Kawaoi A. Peroxidase-labeled antibody. A new method of conjugation. J Histochem Cytochem. 1974 Dec;22(12):1084–1091. doi: 10.1177/22.12.1084. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Provost P. J., Ittensohn O. L., Villarejos V. M., Hilleman M. R. A specific complement-fixation test for human hepatitis a employing CR326 virus antigen. Diagnosis and epidemiology. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1975 Apr;148(4):962–969. doi: 10.3181/00379727-148-38669. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purcell R. H., Wong D. C., Alter H. J., Holland P. V. Microtiter solid-phase radioimmunoassay for hepatitis B antigen. Appl Microbiol. 1973 Oct;26(4):478–484. doi: 10.1128/am.26.4.478-484.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purcell R. H., Wong D. C., Moritsugu Y., Dienstag J. L., Routenberg J. A., Boggs J. D. A microtiter solid-phase radioimmunoassay for hepatitis A antigen and antibody. J Immunol. 1976 Feb;116(2):349–356. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rakela J., Stevenson D., Edwards V. M., Gordon I., Mosley J. W. Antibodies to hepatitis A virus: patterns by two procedures. J Clin Microbiol. 1977 Jan;5(1):110–111. doi: 10.1128/jcm.5.1.110-111.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmitz H., Doerr H. W., Kampa D., Vogt A. Solid-phase enzyme immunoassay for immunoglobulin M antibodies to cytomegalovirus. J Clin Microbiol. 1977 Jun;5(6):629–634. doi: 10.1128/jcm.5.6.629-634.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shirodaria P. V., Fraser K. B., Stanford F. Secondary fluorescent staining of virus antigens by rheumatoid factor and fluorescein-conjugated anti-IgM. Ann Rheum Dis. 1973 Jan;32(1):53–57. doi: 10.1136/ard.32.1.53. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Triger D. R., Alp M. H., Wright R. Bacterial and dietary antibodies in liver disease. Lancet. 1972 Jan 8;1(7741):60–63. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(72)90061-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wollheim F. A. Immunoglobulins in the course of viral hepatitis and in cholestatic and obstructive jaundice. Acta Med Scand. 1968 May;183(5):473–479. doi: 10.1111/j.0954-6820.1968.tb10510.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolters G., Kuijpers L. P., Kacaki J., Schuurs A. H. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for hepatitis B surface antigen. J Infect Dis. 1977 Oct;136 (Suppl):S311–S317. doi: 10.1093/infdis/136.supplement_2.s311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yolken R. H., Wyatt R. G., Kim H. W., Kapikian A. Z., Chanock R. M. Immunological response to infection with human reovirus-like agent: measurement of anti-human reovirus-like agent immunoglobulin G and M levels by the method of enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Infect Immun. 1978 Feb;19(2):540–546. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.2.540-546.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


