Abstract
A grapelike odor is often of diagnostic importance in detecting the growth of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in culture and in burn wounds. The compound responsible for the odor has been identified as 2-aminoacetophenone by mass spectroscopy. Although the grape odor is sometimes difficult to detect in culture media, gas chromatographic, fluorometric, and colorimetric methods can be utilized to assay 2-aminoacetophenone production in a variety of media. Its synthesis occurs relatively early in the growth cycle. It has proved easy and convenient to detect 2-aminoacetophenone excretion by P. aeruginosa after 24 h of incubation on blood agar plates employing a fluorometric assay of ether extracts of the agar medium.
Full text
PDF

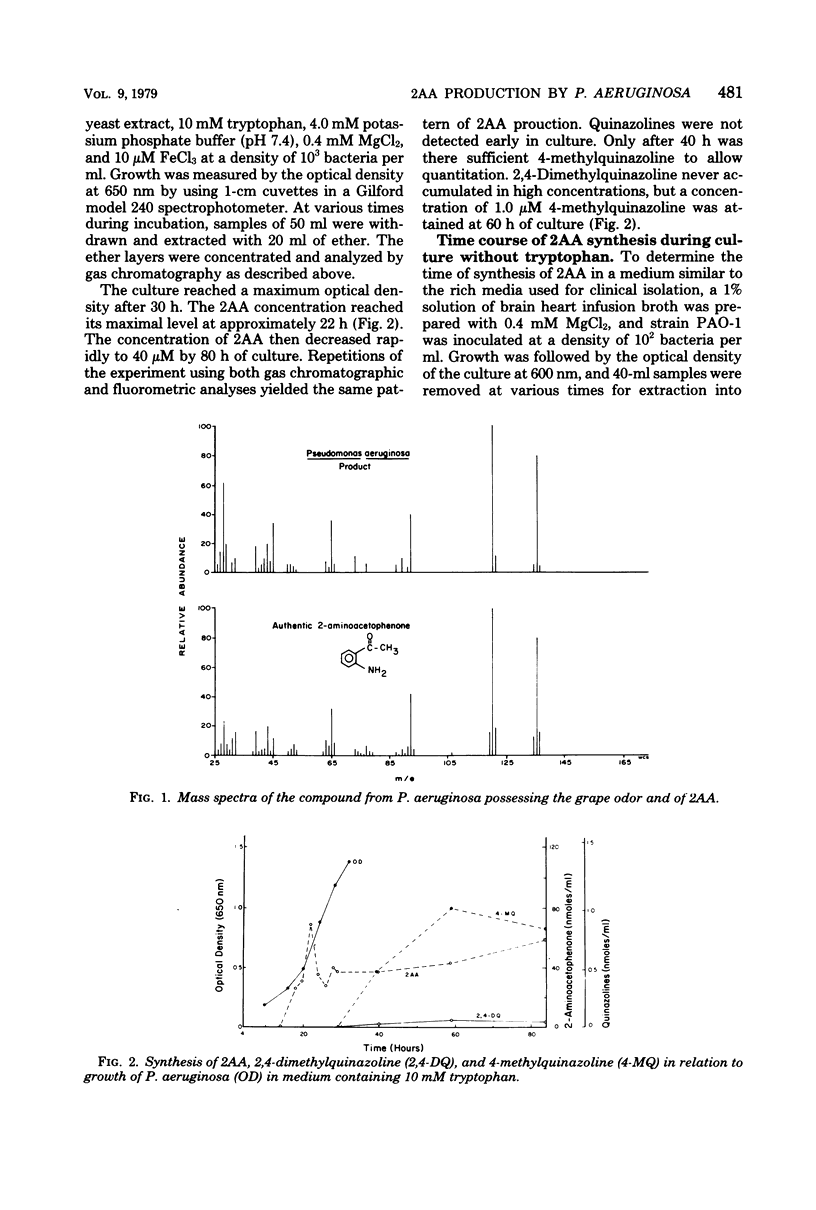


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Habs H., Mann S. Die Bildung von ortho-Aminoacetophenon durch apyocyaninogene Stämme von P. aeruginosa. Zentralbl Bakteriol Orig. 1967;203(4):473–477. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones L. F., Zakanycz J. P., Thomas E. T., Farmer J. J., 3rd Pyocin typing of Pseudomonas aeruginosa: a simplified method. Appl Microbiol. 1974 Feb;27(2):400–406. doi: 10.1128/am.27.2.400-406.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mann S. Besonderheiten im Tryptophanstoffwechsel von Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Arch Hyg Bakteriol. 1967 Oct;151(5):474–491. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mann S. Chinazolinderivate bei Pseudomonaden. Arch Mikrobiol. 1967 Apr 17;56(4):324–329. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


