Abstract
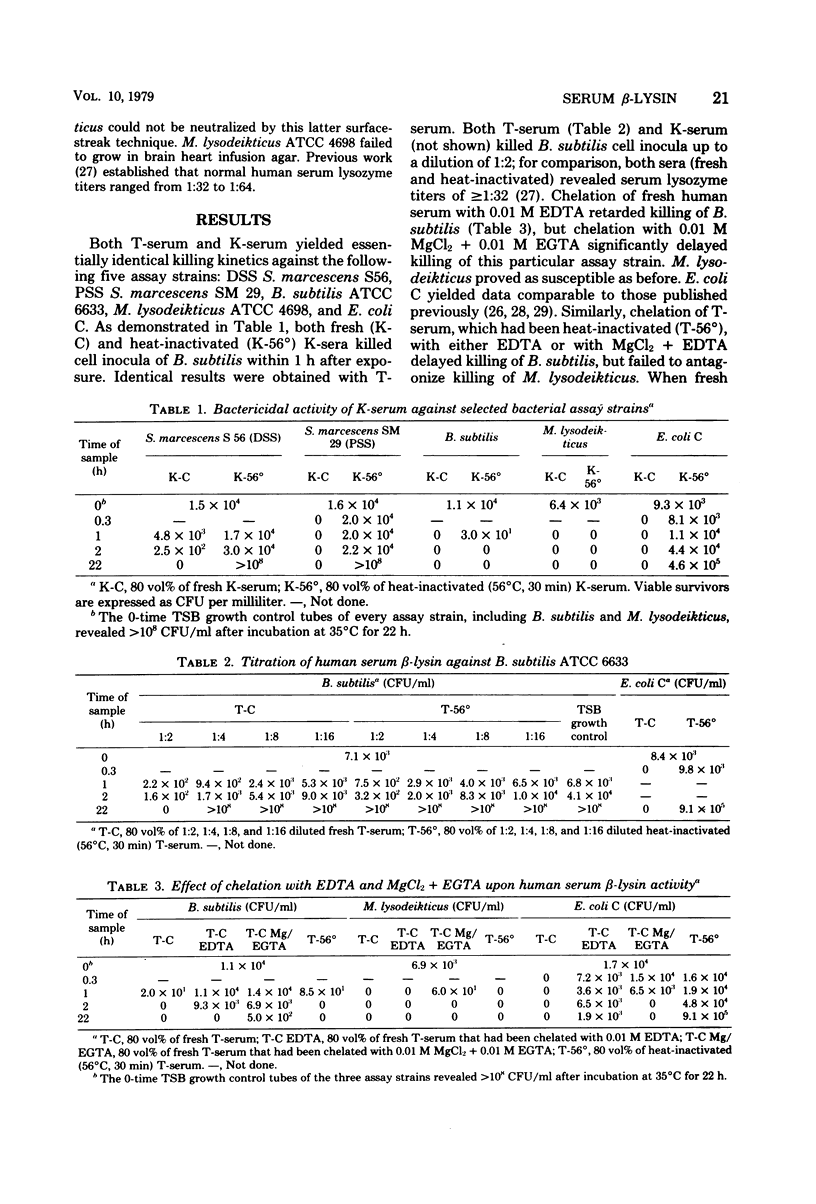
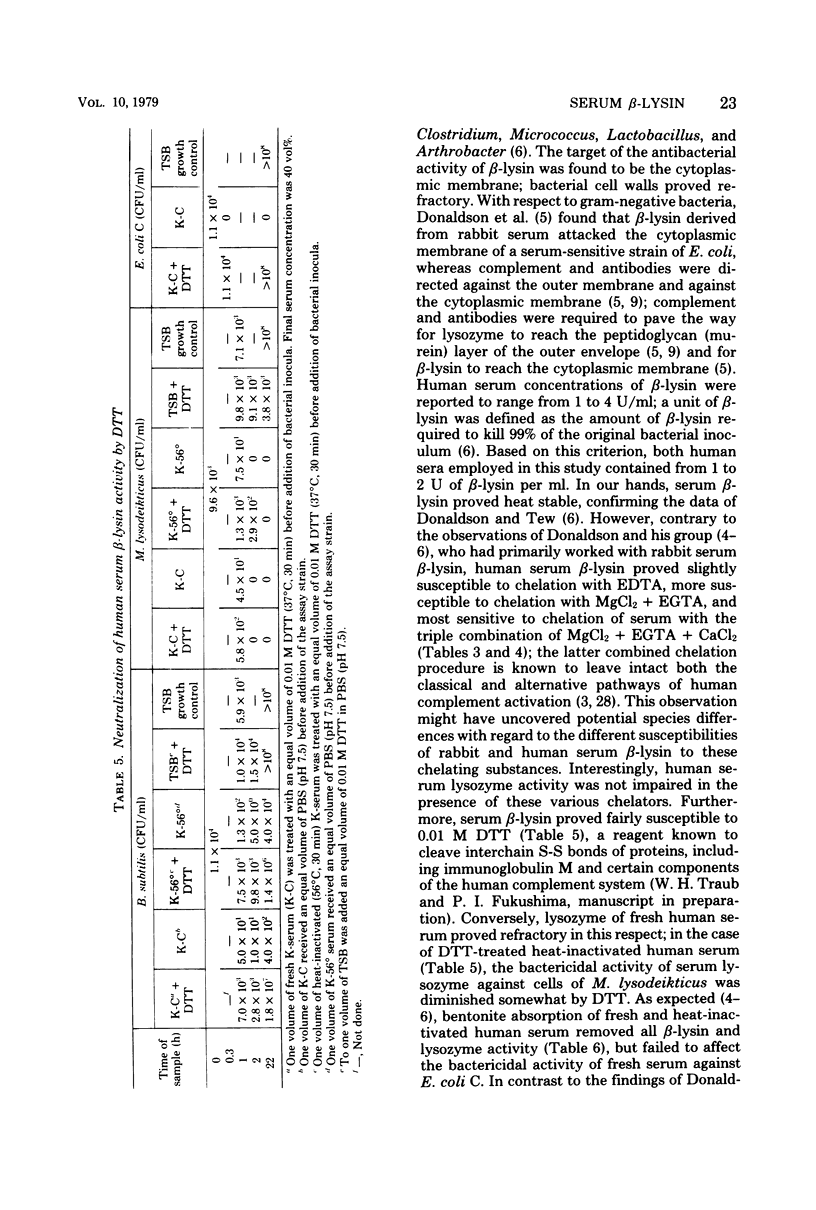
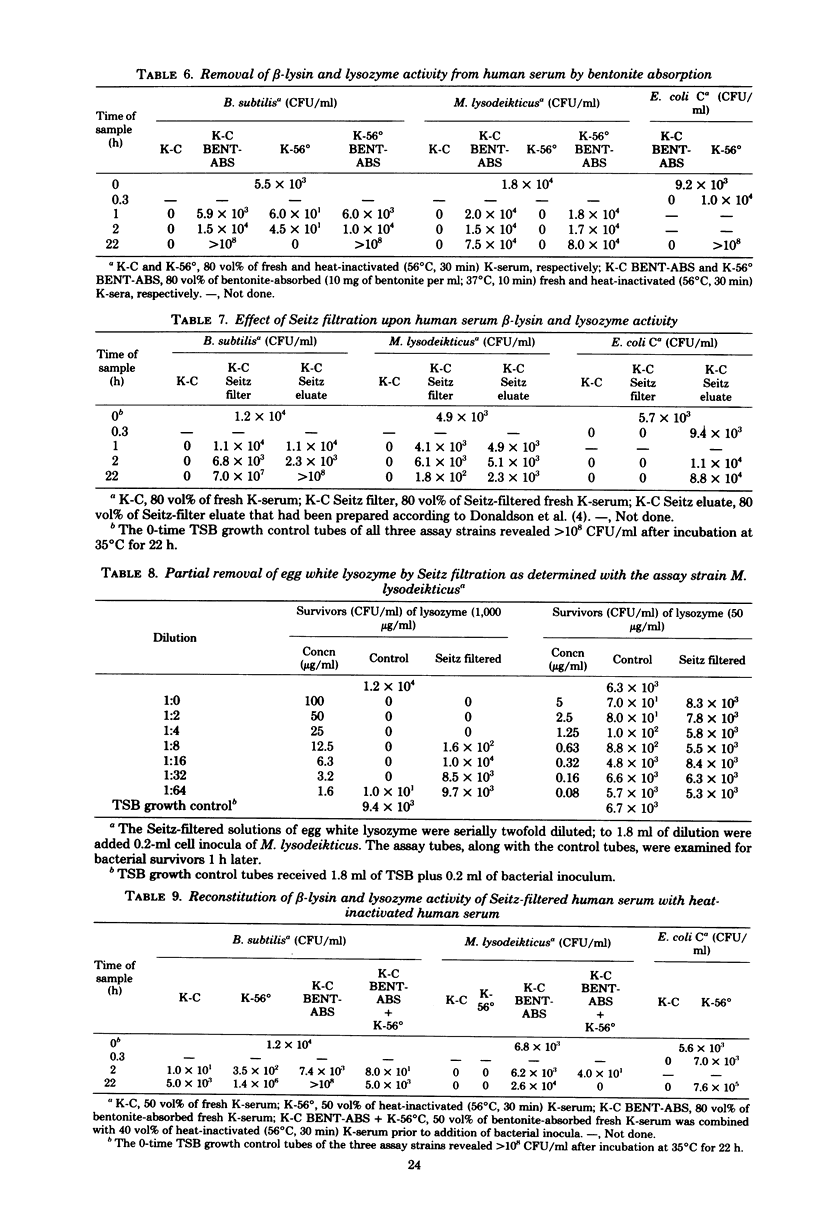
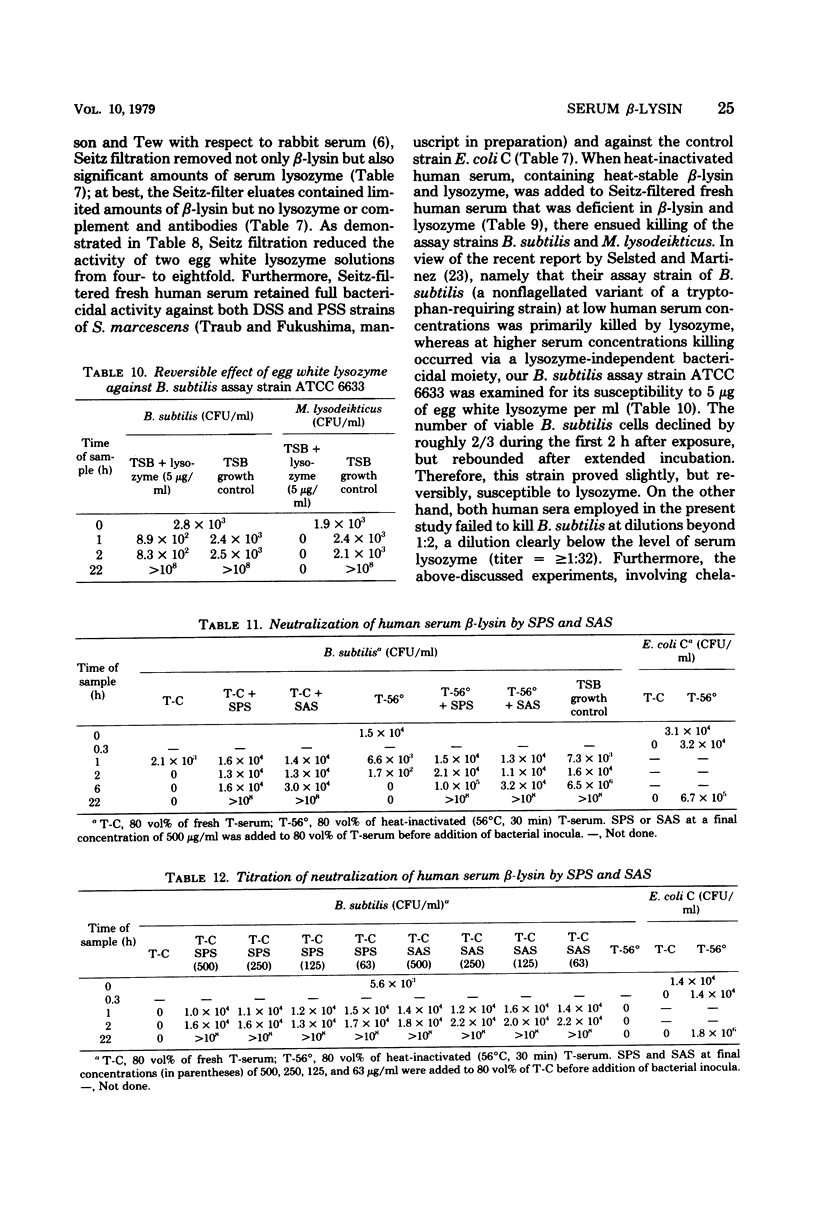
Normal fresh and heat-inactivated (56°C, 30 min) human sera (80 vol%, i.e., 80% [vol/vol] of a 2-ml assay volume) killed Bacillus subtilis ATCC 6633 cell inocula of 1.5 × 104 colony-forming units per ml within 1 to 2 h after exposure. The B. subtilis assay strain proved slightly and reversibly susceptible to 5 μg of egg white lysozyme per ml. Seitz filtration of fresh human serum completely removed β-lysin activity; significant amounts of serum lysozyme were removed as well, as determined with the bioassay strain Micrococcus lysodeikticus ATCC 4698. However, bactericidal activity of human serum via classical or alternative complement pathway activation remained intact. Addition of 0.01 M dithiothreitol to fresh human serum abolished β-lysin activity, but not that of serum lysozyme. Chelation of fresh and heat-inactivated human serum with 0.01 M MgCl2 + 0.01 M ethylene glycol tetraacetic acid, but not with 0.01 M ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid, markedly retarded β-lysin activity; however, lysozyme activity remained unaffected. Chelation of serum with 0.01 M MgCl2 + 0.01 M ethylene glycol tetraacetic acid + 0.01 M CaCl2 completely abrogated β-lysin activity, but not that of lysozyme. Absorption of human serum with 10 mg of bentonite per ml (10 min, 37°C) completely removed β-lysin and lysozyme activity, but failed to affect serum bactericidal activity against Escherichia coli control strain C. Reconstitution of 50 vol% of bentonite-absorbed serum with 40 vol% of heat-inactivated human serum restored both β-lysin and lysozyme activity. Addition of either 63 to 500 μg of sodium polyanetholsulfonate per ml or 63 to 500 μg of sodium amylosulfate per ml to 80 vol% of fresh human serum completely neutralized β-lysin activity for the entire observation period of 22 h.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Belding M. E., Klebanoff S. J. Effect of sodium polyanetholesulfonate on antimicrobial systems in blood. Appl Microbiol. 1972 Nov;24(5):691–698. doi: 10.1128/am.24.5.691-698.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DONALDSON D. M., ELLSWORTH B., MATHESON A. SEPARATION AND PURIFICATION OF BETA-LYSIN FROM NORMAL SERUM. J Immunol. 1964 Jun;92:896–901. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Des Prez R. M., Bryan C. S., Hawiger J., Colley D. G. Function of the classical and alternate pathways of human complement in serum treated with ethylene glycol tetraacetic acid and MgCl2-ethylene glycol tetraacetic acid. Infect Immun. 1975 Jun;11(6):1235–1243. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.6.1235-1243.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donaldson D. M., Roberts R. R., Larsen H. S., Tew J. G. Interrelationship between serum beta-lysin, lysozyme, and the antibody-complement system in killing Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1974 Sep;10(3):657–666. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.3.657-666.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donaldson D. M., Tew J. G. beta-Lysin of platelet origin. Bacteriol Rev. 1977 Jun;41(2):501–513. doi: 10.1128/br.41.2.501-513.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eng J., Holten E. Gelatin neutralization of the inhibitory effect of sodium polyanethol sulfonate on Neisseria meningitidis in blood culture media. J Clin Microbiol. 1977 Jul;6(1):1–3. doi: 10.1128/jcm.6.1.1-3.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eng J., Iveland H. Inhibitory effect in vitro of sodium polyanethol sulfonate on the growth of Neisseria meningitidis. J Clin Microbiol. 1975 May;1(5):444–447. doi: 10.1128/jcm.1.5.444-447.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feingold D. S., Goldman J. N., Kuritz H. M. Locus of the action of serum and the role of lysozyme in the serum bactericidal reaction. J Bacteriol. 1968 Dec;96(6):2118–2126. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.6.2118-2126.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodkofsky I., Lepow I. H. Functional relationship of factor B in the properdin system to C3 proactivator of human serum. J Immunol. 1971 Oct;107(4):1200–1204. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graves M. H., Morello J. A., Kocka F. E. Sodium polyanethol sulfonate sensitivity of anaerobic cocci. Appl Microbiol. 1974 Jun;27(6):1131–1133. doi: 10.1128/am.27.6.1131-1133.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall M. M., Warren E., Ilstrup D. M., Washington J. A., 2nd Comparison of sodium amylosulfate and sodium polyanetholsulfonate in blood culture media. J Clin Microbiol. 1976 Feb;3(2):212–213. doi: 10.1128/jcm.3.2.212-213.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kocka F. E., Arthur E. J., Searcy R. L. Comparative effects of two sulfated polyanions used in blood culture on anaerobic cocci. Am J Clin Pathol. 1974 Jan;61(1):25–27. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/61.1.25. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kocka F. E., Arthur E. J., Searcy R. L., Smith M., Grodner B. Clinical evaluation of sodium amylosulfate in human blood cultures. Appl Microbiol. 1973 Sep;26(3):421–422. doi: 10.1128/am.26.3.421-422.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kocka F. E., Magoc T., Searcy R. L. New anticoagulant for combating antibacterial activity of human blood. 1. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1972 Sep;140(4):1231–1234. doi: 10.3181/00379727-140-36648. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowrance B. L., Traub W. H. Inactivation of the bactericidal activity of human serum by liquoid (sodium polyanetholsulfonate). Appl Microbiol. 1969 Jun;17(6):839–842. doi: 10.1128/am.17.6.839-842.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olson P. R., Weiblen B. J., O'Leary J. J., Moscowitz A. J., McCullough J. A simple technique for the inactivation of IgM antibodies using dithiothreitol. Vox Sang. 1976;30(2):149–159. doi: 10.1111/j.1423-0410.1976.tb02806.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selsted M. E., Martinez R. J. Lysozyme: primary bactericidin in human plasma serum active against Bacillus subtilis. Infect Immun. 1978 Jun;20(3):782–791. doi: 10.1128/iai.20.3.782-791.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stuart R. D. The Value of Liquoid for Blood Culture. J Clin Pathol. 1948 Nov;1(5):311–314. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traub W. H. Assay of the antibiotic activity of serum. Appl Microbiol. 1969 Jul;18(1):51–56. doi: 10.1128/am.18.1.51-56.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traub W. H., Fukushima P. I. Neutralization of human serum lysozyme by sodium polyanethol sulfonate but not by sodium amylosulfate. J Clin Microbiol. 1978 Sep;8(3):306–312. doi: 10.1128/jcm.8.3.306-312.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traub W. H., Kleber I. Inactivation of classical and alternative pathway-activated bactericidal activity of human serum by sodium polyanetholsulfonate. J Clin Microbiol. 1977 Mar;5(3):278–284. doi: 10.1128/jcm.5.3.278-284.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traub W. H., Kleber I. Selective activation of classical and alternative pathways of human complement by "promptly serum-sensitive" and "delayed serum-sensitive" strains of Serratia marcescens. Infect Immun. 1976 May;13(5):1343–1346. doi: 10.1128/iai.13.5.1343-1346.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traub W. H., Lowrance B. L. Anticomplementary, anticoagulatory, and serum-protein precipitating activity of sodium polyanetholsulfonate. Appl Microbiol. 1970 Sep;20(3):465–468. doi: 10.1128/am.20.3.465-468.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traub W. H. Studies on neutralization of human serum bactericidal activity by sodium amylosulfate. J Clin Microbiol. 1977 Aug;6(2):128–131. doi: 10.1128/jcm.6.2.128-131.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkins T. D., West S. E. Medium-dependent inhibition of Peptostreptococcus anaerobius by sodium polyanetholsulfonate in blood culture media. J Clin Microbiol. 1976 Apr;3(4):393–396. doi: 10.1128/jcm.3.4.393-396.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



