Abstract
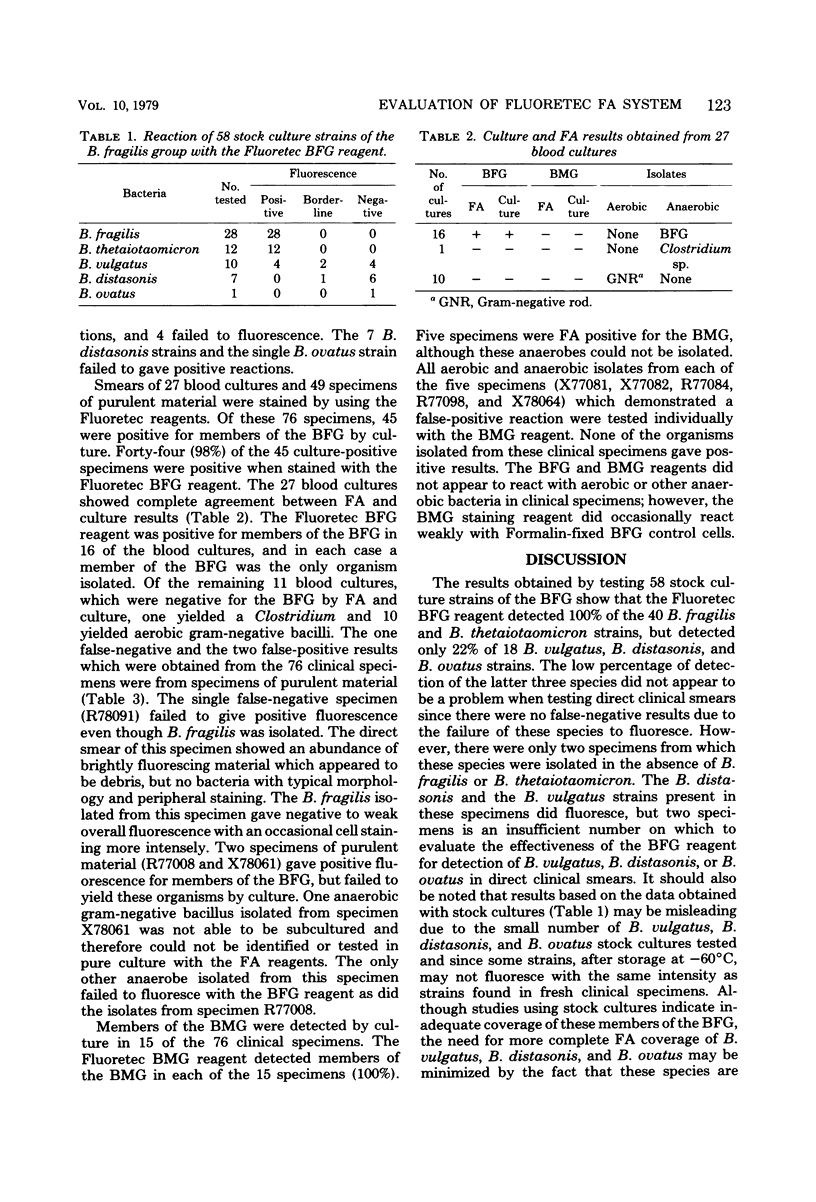
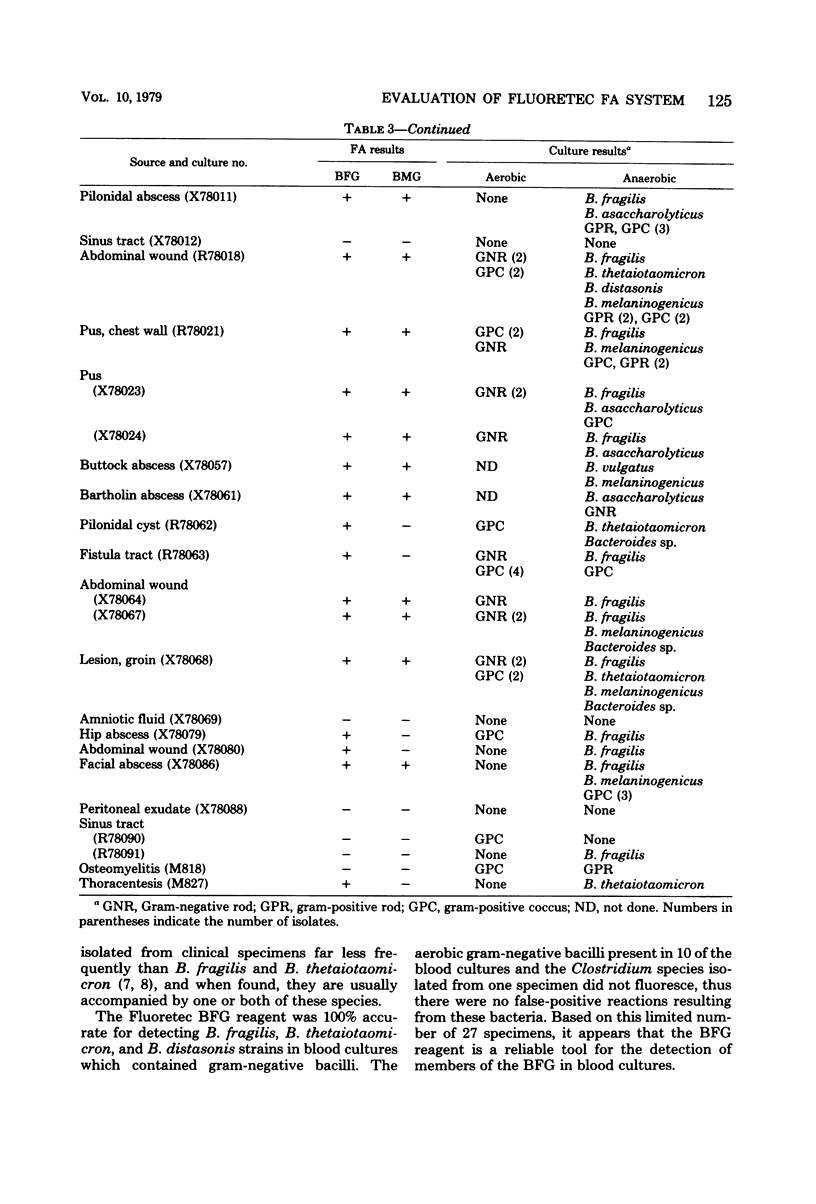
The Fluoretec fluorescent antibody test kit (Pfizer Inc., New York, N.Y.), developed for the rapid detection of members of the Bacteroides fragilis and B. melaninogenicus groups, was evaluated by testing 58 stock cultures and 76 clinical specimens. The test reagents detected 100% of 40 B. fragilis and B. thetaiotaomicron stock culture strains, although only 22% of 18 B. vulgatus, B. distasonis, and B. ovatus strains showed positive fluorescence. The 76 clinical specimens were evaluated by examining fluorescent antibody-stained smears of 49 specimens of purulent material and smears of 27 blood cultures which were positive for gram-negative bacilli by Gram stain or subculture. The fluoretec reagent detected members of the B. fragilis group in 28 (97%) of the 29 specimens of purulent material and all (100%) of the 16 blood cultures in which these anaerobes were demonstrated by culture. Overall, the Fluoretec reagent detected members of B. fragilis group in 44 (98%) of the 45 clinical specimens which were shown by culture to contain these anaerobes. Two of the 76 clinical specimens gave positive fluorescence for members of the B. fragilis group but failed to yield these organisms by culture. Members of the B. melaninogenicus group were detected by culture in 15 specimens and in each case their presence was demonstrated by the Fluoretec reagent. No members of the B. melaninogenicus group were isolated from five clinical specimens that gave positive fluorescence with the B. melaninogenicus reagent.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Fales W. H., Teresa G. W. Fluorescent antibody technique for identifying isolates of Sphaerophorus necrophorus of bovine hepatic abscess origin. Am J Vet Res. 1972 Nov;33(11):2323–2329. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felner J. M., Dowell V. R., Jr "Bacteroides" bacteremia. Am J Med. 1971 Jun;50(6):787–796. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(71)90187-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia M. M., Neil D. H., McKay K. A. Application of immunofluorescence to studies on the ecology of Sphaerophorus necrophorus. Appl Microbiol. 1971 May;21(5):809–814. doi: 10.1128/am.21.5.809-814.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffin M. H. Fluorescent antibody techniques in the identification of the gram-negative nonsporeforming anaerobes. Health Lab Sci. 1970 Apr;7(2):78–83. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holland J. W., Gagnet S. M., Lewis S. A., Stauffer L. R. Clinical evaluation of a simple, rapid procedure for the presumptive identification of anaerobic bacteria. J Clin Microbiol. 1977 Apr;5(4):416–426. doi: 10.1128/jcm.5.4.416-426.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holland J. W., Hill E. O., Altemeier W. A. Numbers and types of anaerobic bacteria isolated from clinical specimens since 1960. J Clin Microbiol. 1977 Jan;5(1):20–25. doi: 10.1128/jcm.5.1.20-25.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambe D. W., Jr Determination of Bacteroides melaninogenicus serogroups by fluorescent antibody staining. Appl Microbiol. 1974 Oct;28(4):561–567. doi: 10.1128/am.28.4.561-567.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin W. J. Isolation and indentification of anaerobic bacteria in the clinical laboratory. A 2-year experience. Mayo Clin Proc. 1974 May;49(5):300–308. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stauffer L. R., Hill E. O., Holland J. W., Altemeier W. A. Indirect fluorescent antibody procedure for the rapid detection and identification of Bacteroides and Fusobacterium in clinical specimens. J Clin Microbiol. 1975 Oct;2(4):337–344. doi: 10.1128/jcm.2.4.337-344.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



