Abstract
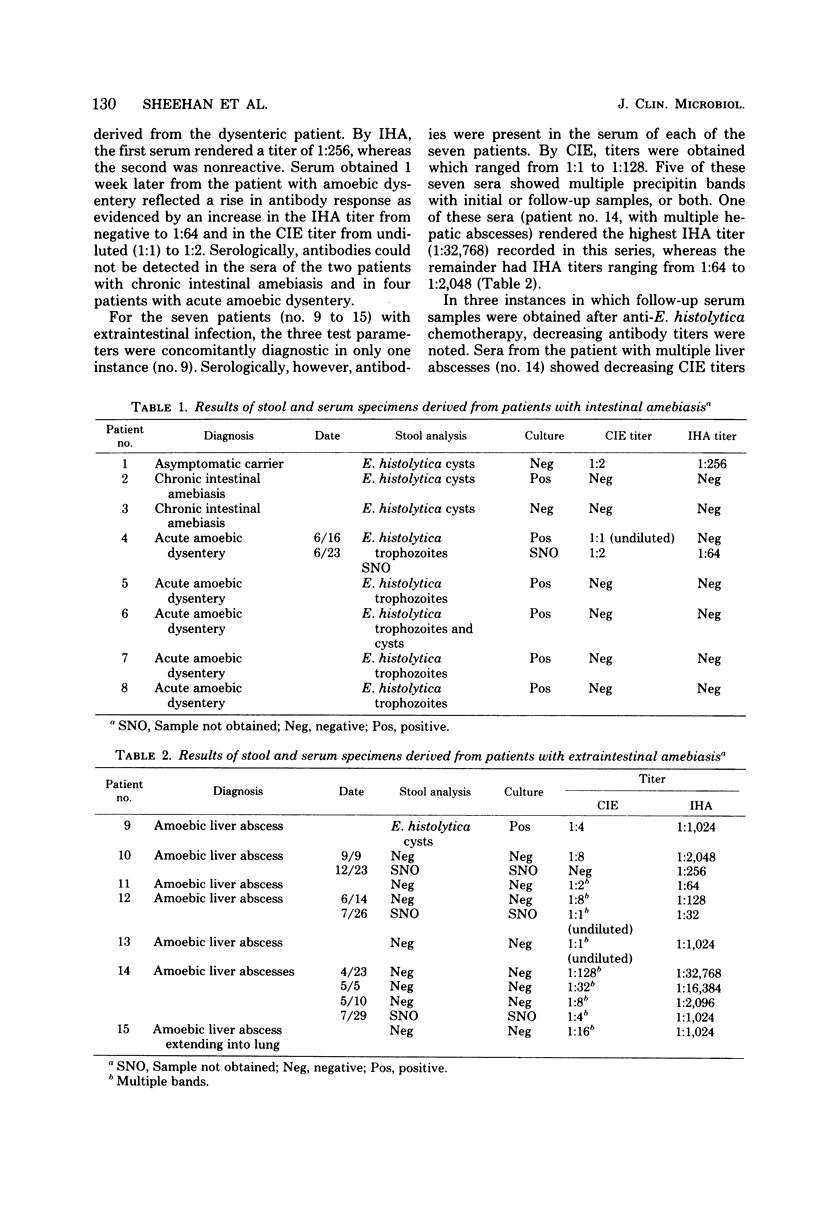
Of 110 subjects with clinical evidence of amebiasis, 15 (14%) were shown to be infected with Entamoeba histolytica. Microscopic examination of stool specimens rendered a diagnosis in all eight cases of localized intestinal infection, but in only one of seven patients with invasive amebiasis. Culture was concomitantly diagnostic in six patients intestinal amebiasis and in one patient with extraintestinal infection. Assay for antibody to E. histolytica by counterimmunoelectrophoresis and indirect hemagglutination were each 100% effective in all cases of invasive amebiasis and in diagnosing two of eight patients with intestinal infection. Stool specimens of 15 patients revealing intestinal parasites other than E. histolytica failed to demonstrate cultural or serological evidence of amebiasis. Low levels of antibody were observed in the indirect hemagglutination assay in four patients with disease other than amebiasis and in three control sera positive for rheumatoid factor. By counterimmunoelectrophoresis, reactive sera were only encountered among those derived from patients with amebiasis. Six of seven patients with hepatic amebiasis may have gone undiagnosed if not for serology.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Edelman M. H., Spingarn C. L. Cultivation of Entamoeba histolytica as a diagnostic procedure: a brief review. Mt Sinai J Med. 1977 Jan-Feb;44(1):27–32. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krogstad D. J., Spencer H. C., Jr, Healy G. R. Current concepts in parasitology. Amebiasis. N Engl J Med. 1978 Feb 2;298(5):262–265. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197802022980507. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krupp I. M. Comparison of counterimmunoelectrophoresis with other serologic tests in the diagnosis of amebiasis. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1974 Jan;23(1):27–30. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1974.23.27. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krupp I. M., Powell S. J. Antibody response to invasive amebiasis in Durban, South Africa. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1971 May;20(3):414–420. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1971.20.414. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krupp I. M., Powell S. J. Comparative study of the antibody response in amebiasis. Persistence after successful treatment. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1971 May;20(3):421–424. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1971.20.421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahajan R. C., Ganguly N. K., Chitkara N. L., Dutta D. V., Chhuttani P. N. Precipitating antibodies against Entamoeba histolytica in liver pus--a preliminary communication. Indian J Med Res. 1975 Feb;63(2):229–231. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


