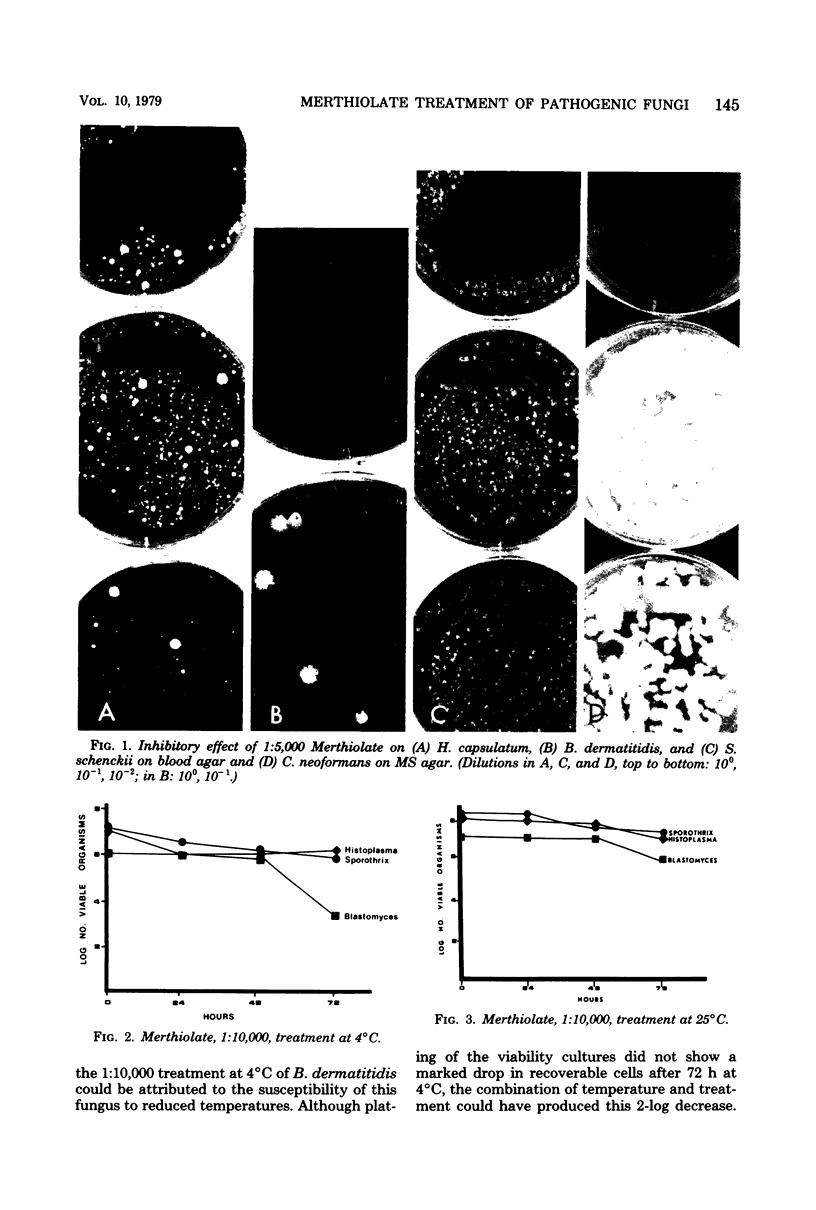
Abstract
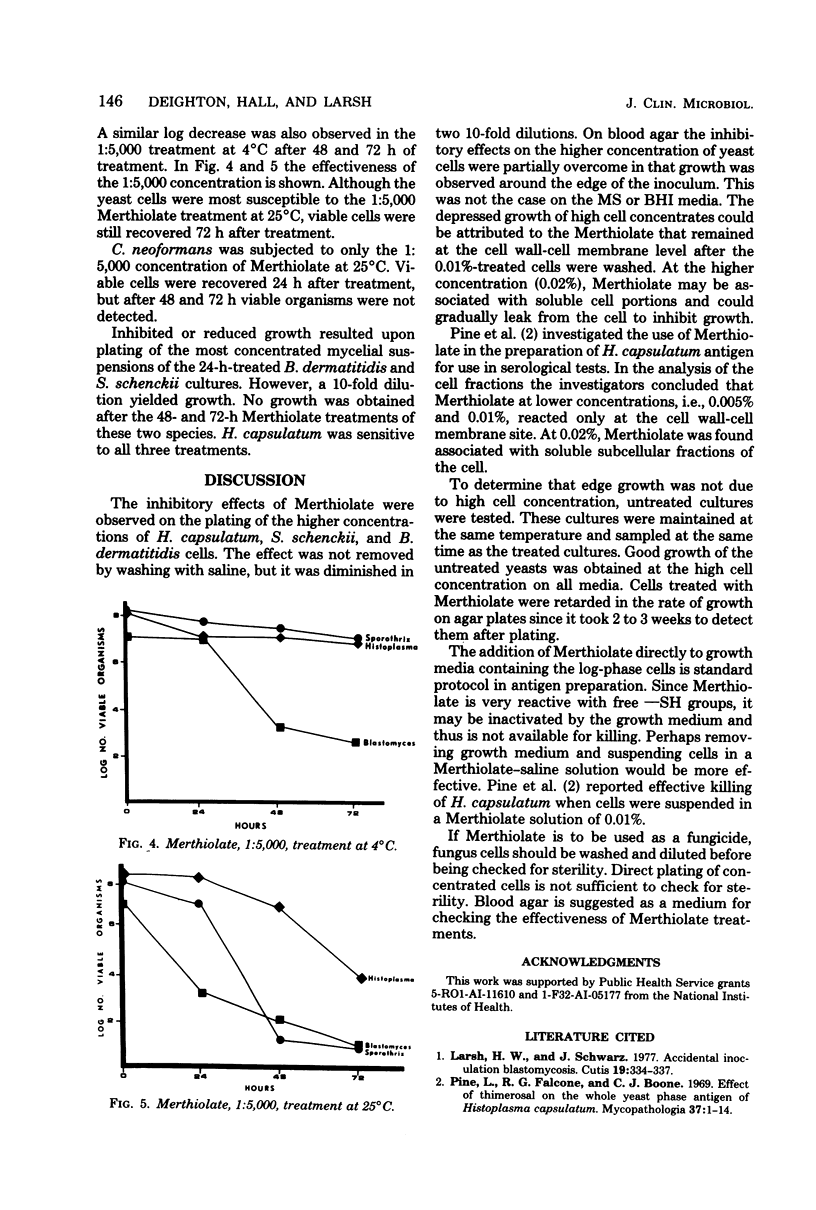
The action of Merthiolate on the pathogenic yeasts Blastomyces, dermatitidis, Histoplasma capsulatum, and Sporothrix schenckii was compared to the effect of treatment with formaldehyde. Concentrations of 1:10,000 and 1:5,000 Merthiolate for three exposure times (24, 48, and 72 h) at 4 and 25 degrees C were tested on three media (brain heart infusion with and without blood, and modified Sabouraud agar). The effect of Merthiolate on these three yeasts was primarily fungistatic, with maximum effect using 1:5,000 Merthiolate at 25 degrees C for at least 48 h. Mycelial suspensions of B. dermatitidis, H. capsulatum, S. shenckii, and the yeast phase of Cryptococcus neoformans were susceptible to the 1:5,000 Merthiolate concentration after 24 h of treatment. The antifungal effect of Methiolate varies with species and growth phase of the fungus. Concentration, time of exposure, and temperature of incubation are important variables.
Full text
PDF
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Larsh H. W., Schwarz J. Accidental inoculation blastomycosis. Cutis. 1977 Mar;19(3):334-5, 337. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pine L., Falcone R. G., Boone C. J. Effect of thimerosal on the whole yeast phase antigen of Histoplasma capsulatum. Mycopathol Mycol Appl. 1969 Jan 29;37(1):1–14. doi: 10.1007/BF02051325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]