Abstract
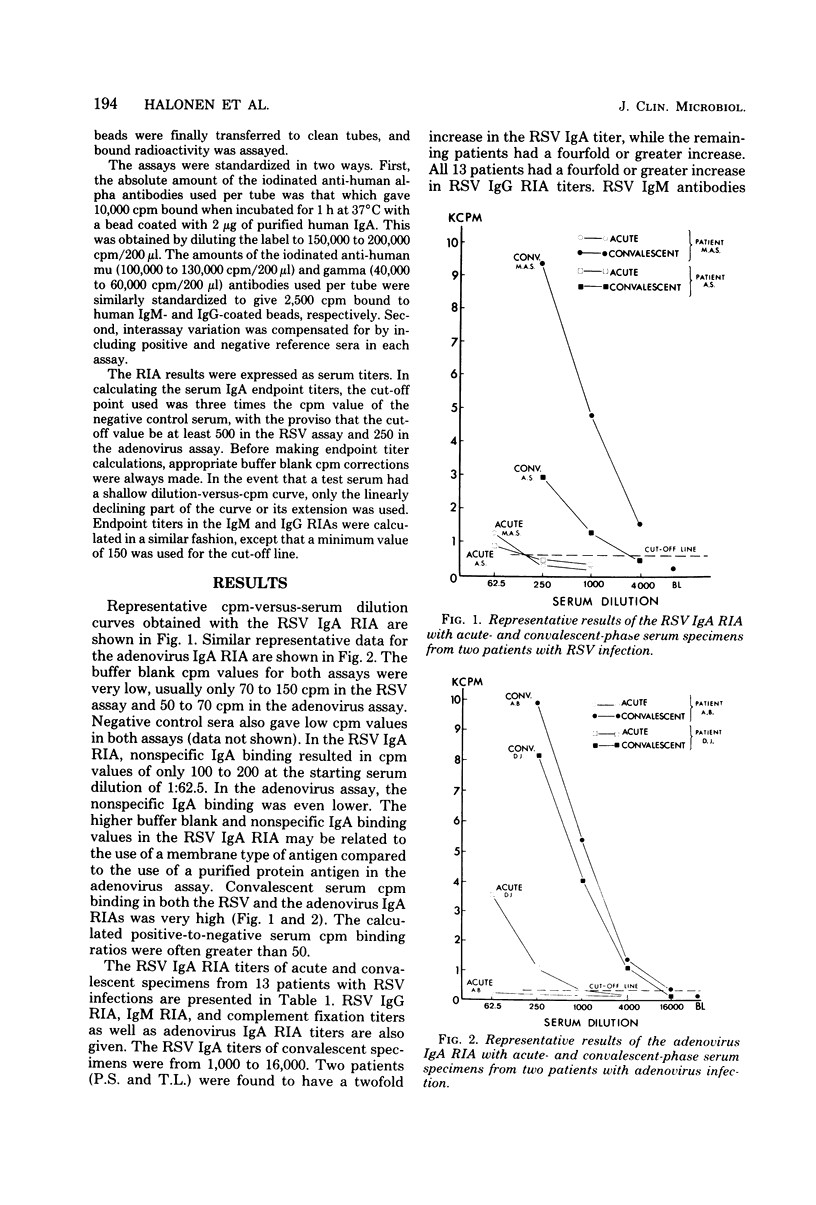
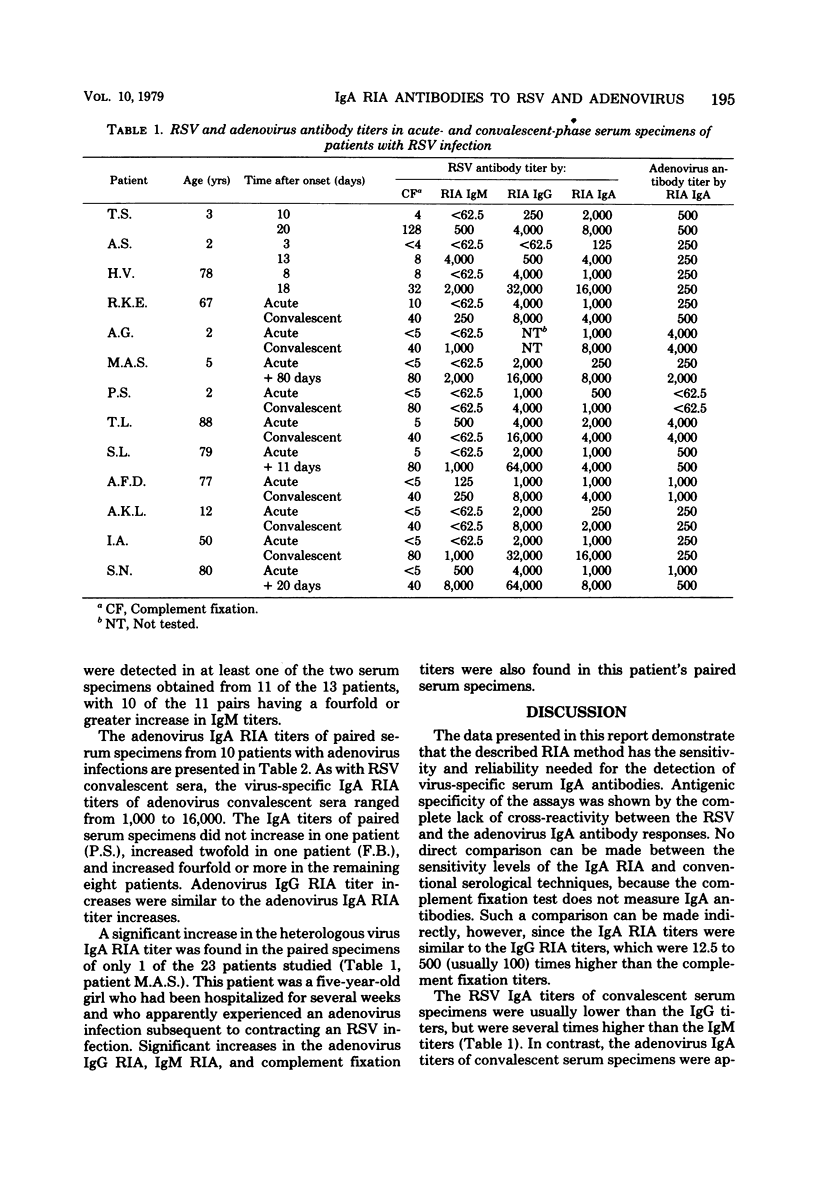
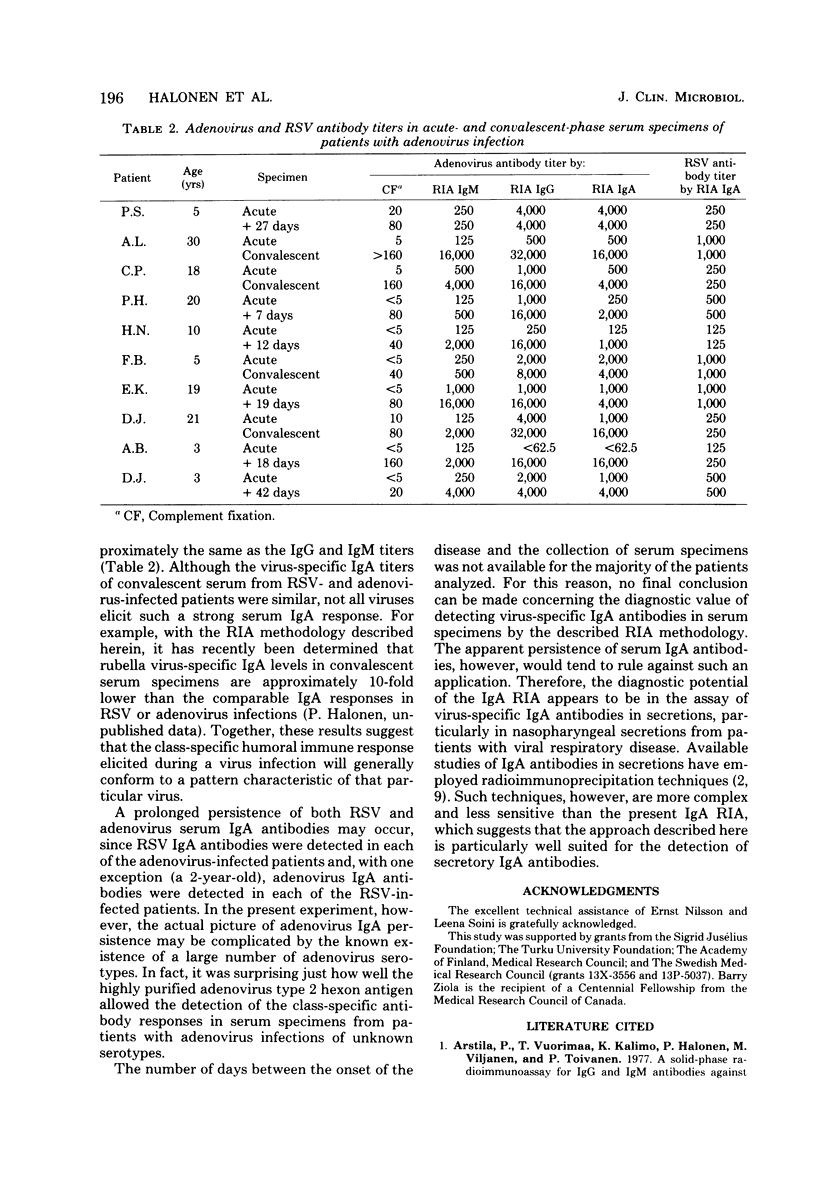
A solid-phase radioimmunoassay for detecting respiratory syncytial virus and adenovirus serum immunoglobulin A (IgA) antibodies was developed. An antigen consisting of purified adenovirus type 2 hexons or a crude lysate of respiratory syncytial virus-infected cells was first adsorbed onto polystyrene beads. The coated beads were then incubated with dilutions of serum, and IgA antibodies which attached to the solid-phase virus antigen were subsequently detected with 125I-labeled anti-human alpha antibodies. The anti-human alpha antibodies used were isolated by immunosorbent chromatography from rabbit antiserum produced by immunization with IgA purified from serum of an IgA myeloma patient. A total of 46 serum specimens from 13 patients with respiratory syncytial virus infections and 10 patients with adenovirus infections were tested. Complement fixation, homologous IgG and IgM radioimmunoassay, and heterologous IgA radioimmunoassay testing were also done. Specific values higher than 10,000 cpm were often reached with convalescent serum specimens, and positive-to-negative serum binding ratios of 50 or more were frequently obtained with lower serum dilutions. IgA titers of convalescent sera were from 1,000 to 16,000, and with few exceptions a fourfold or greater rise in the IgA titer was detected in the homologous IgA radioimmunoassay.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arstila P., Vuorimaa T., Kalimo K., Halonen P., Viljanen M., Granfors K., Toivanen P. A solid-phase radioimmunoassay for IgG and IgM antibodies against measles virus. J Gen Virol. 1977 Jan;34(1):167–176. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-34-1-167. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cambiaso C. L., Goffinet A., Vaerman J. P., Heremans J. F. Glutaraldehyde-activated aminohexyl- derivative of Sepharose 4B as a new verstile immunoabsorbent. Immunochemistry. 1975 Apr;12(4):273–278. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(75)90175-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frisch-Niggemeyer W., Halonen P., Heinz F., Kunz C., Ziola B. Festphasen-Radioimmunoassay zur Messung klassenspezifischer Immunglobuline gegen das Virus der Frühsommer-Meningoenzephalitis. Immun Infekt. 1978 Jun;6(3):110–117. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUNTER W. M., GREENWOOD F. C. Preparation of iodine-131 labelled human growth hormone of high specific activity. Nature. 1962 May 5;194:495–496. doi: 10.1038/194495a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jornvall H., Pettersson U., Philipson L. Structural studies of adenovirus type-2 hexon protein. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Oct 1;48(1):179–192. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03755.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalimo K. O., Meurman O. H., Halonen P. E., Ziola B. R., Viljanen M. K., Granfors K., Toivanen P. Solid-phase radioimmunoassay of rubella virus immunoglobulin G and immunoglobulin M antibodies. J Clin Microbiol. 1976 Aug;4(2):117–123. doi: 10.1128/jcm.4.2.117-123.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalimo K. O., Ziola B. R., Viljanen M. K., Granfors K., Toivanen P. Solid-phase radioimmunoassay of herpes simplex virus IgG and IgM antibodies. J Immunol Methods. 1977;14(2):183–195. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(77)90008-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasel J. A., Six H. R., Oborn C. J., Dreesman G. R. Immunoglobulin-specific radioimmunoprecipitation assays for quantitation of nasal secretory antibodies to hemagglutinin of type A influenza viruses. J Clin Microbiol. 1978 Aug;8(2):171–176. doi: 10.1128/jcm.8.2.171-176.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lonberg-Holm K., Philipson L. Early events of virus-cell interaction in an adenovirus system. J Virol. 1969 Oct;4(4):323–338. doi: 10.1128/jvi.4.4.323-338.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meurman O. H., Viljanen M. K., Granfors K. Solid-phase radioimmunoassay of rubella virus immunoglobulin M antibodies: comparison with sucrose density gradient centrifugation test. J Clin Microbiol. 1977 Mar;5(3):257–262. doi: 10.1128/jcm.5.3.257-262.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pettersson U., Höglund S. Sructural proteins of adenoviruses. 3. Purification and characterization of the adenovirus type 2 penton antigen. Virology. 1969 Sep;39(1):90–106. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(69)90351-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pettersson U., Philipson L., Höglund S. Structural proteins of adenoviruses. I. Purification and characterization of the adenovirus type 2 hexon antigen. Virology. 1967 Dec;33(4):575–590. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(67)90057-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porath J., Axen R., Ernback S. Chemical coupling of proteins to agarose. Nature. 1967 Sep 30;215(5109):1491–1492. doi: 10.1038/2151491a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziola B., Meurman O., Matikainen M. T., Salmi A., Kalliomäki J. L. Determination of human immunoglobulin M rheumatoid factor by a solid-phase radioimmunoassay which uses human immunoglobulin G in antigen-antibody complexes. J Clin Microbiol. 1978 Aug;8(2):134–141. doi: 10.1128/jcm.8.2.134-141.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


