Abstract
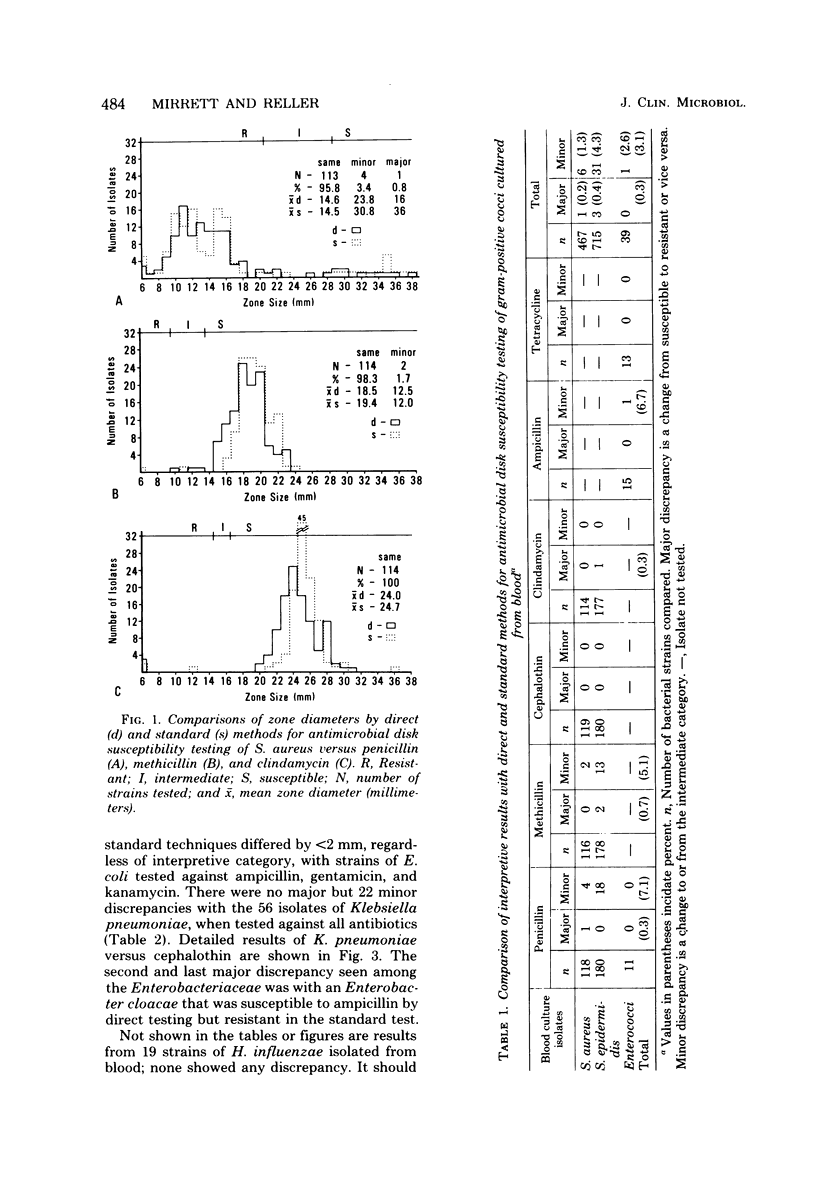
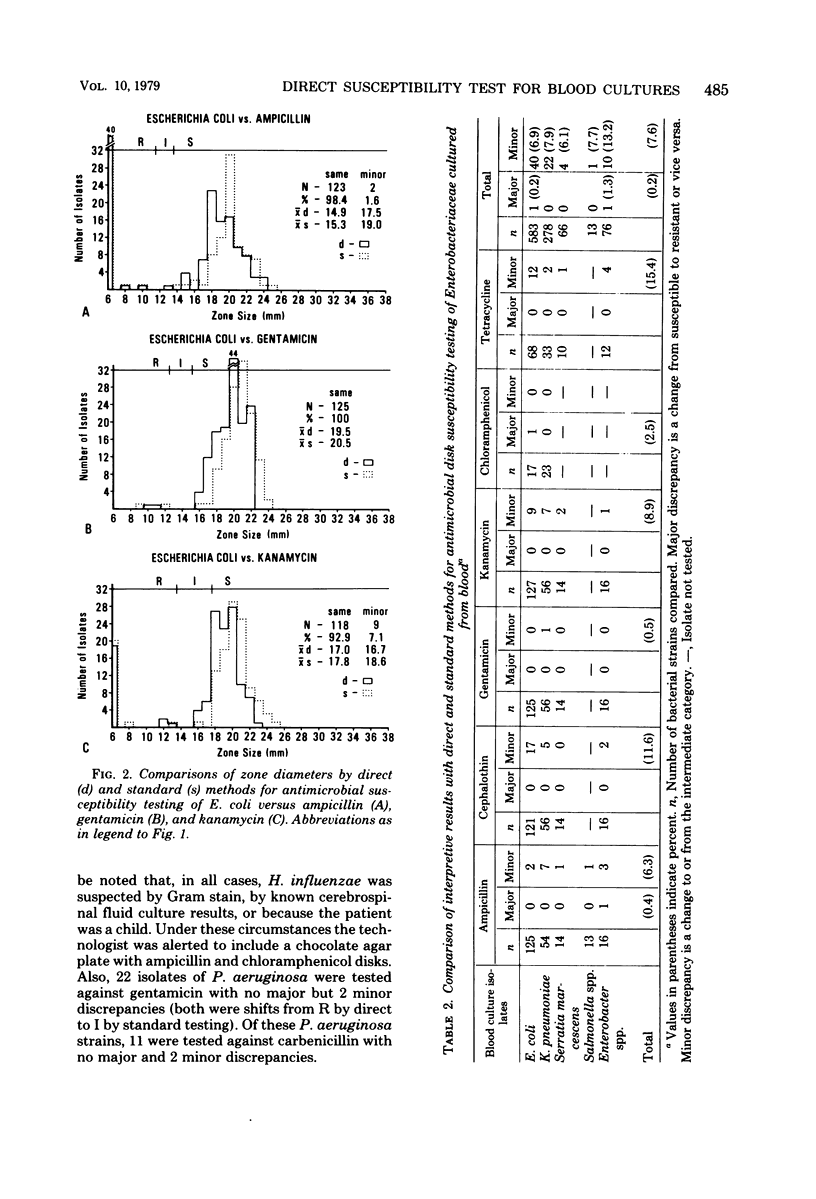
To determine the reliability of early antimicrobial susceptibility testing, we compared the results of direct and standard single-disk diffusion methods for 581 positive blood cultures processed routinely by the clinical microbiology laboratory. The direct procedure differed from the standard one only in that the 0.5 McFarland inoculum was prepared from 1 ml of turbid broth rather than five isolated colonies from a subculture plate. A major discrepancy in results was defined as a change from susceptible to resistant or vice versa according to interpretive standards for zone diameters, whereas a minor discrepancy was defined as a shift to or from the intermediate category when paired direct and standard tests were compared. The overall agreement between the two methods was 94.6% of 2,308 comparisons. There were 119 minor (5.2%) and 6 major (0.3%) discrepancies. The major discrepancies were seen with three strains of Staphylococcus epidermidis and one strain each of S. aureus, Escherichia coli, and Enterobacter sp. Direct susceptibility testing of positive blood cultures that were pure by gram-stained smear provided reliable results 24 to 36 h earlier than conventional procedures; therefore, we recommended this procedure to guide early antimicrobial therapy in patients with bacterial sepsis.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Agger W. A., Maki D. G. Efficacy of direct Gram stain in differentiating staphylococci from streptococci in blood cultures positive for gram-positive cocci. J Clin Microbiol. 1978 Feb;7(2):111–113. doi: 10.1128/jcm.7.2.111-113.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barry A. L., Joyce L. J., Adams A. P., Benner E. J. Rapid determination of antimicrobial susceptibility for urgent clinical situations. Am J Clin Pathol. 1973 May;59(5):693–699. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/59.5.693. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartlett R. C., Mazens M. Analytical variability in the single disk antimicrobial susceptibility test. Am J Clin Pathol. 1973 Mar;59(3):376–383. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/59.3.376. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bauer A. W., Kirby W. M., Sherris J. C., Turck M. Antibiotic susceptibility testing by a standardized single disk method. Am J Clin Pathol. 1966 Apr;45(4):493–496. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blazevic D. J., Stemper J. E., Matsen J. M. Comparison of macroscopic examination, routine gram stains, and routine subcultures in the initial detection of positive blood cultures. Appl Microbiol. 1974 Mar;27(3):537–539. doi: 10.1128/am.27.3.537-539.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellner P. D., Johnson E. Unreliability of direct antibiotic susceptibility testing on wound exudates. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976 Feb;9(2):355–356. doi: 10.1128/aac.9.2.355. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fay D., Oldfather J. E. Standardization of direct susceptibility test for blood cultures. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Mar;9(3):347–350. doi: 10.1128/jcm.9.3.347-350.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hermans P. E., Washington J. A., 2nd Polymicrobial bacteremia. Ann Intern Med. 1970 Sep;73(3):387–392. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-73-3-387. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollick G. E., Washington J. A., 2nd Comparison of direct and standardized disk diffusion susceptibility testing of urine cultures. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976 May;9(5):804–809. doi: 10.1128/aac.9.5.804. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson J. E., Washington J. A., 2nd Comparison of direct and standardized antimicrobial susceptibility testing of positive blood cultures. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976 Aug;10(2):211–214. doi: 10.1128/aac.10.2.211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kluge R. M. Accuracy of Kirby-Bauer susceptibility tests read at 4, 8, and 12 hours of incubation: comparison with readings at 18 to 20 hours. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1975 Aug;8(2):139–145. doi: 10.1128/aac.8.2.139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunin C. M. Antibiotic sensitivity tests: how to get the most out of them. Wis Med J. 1971 Sep;70(9):206–208. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liberman D. F., Robertson R. G. Evaluation of a rapid Bauer-Kirby antibiotic susceptibility determination. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1975 Mar;7(3):250–255. doi: 10.1128/aac.7.3.250. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minshew B. H., Pollock H. M., Schoenknecht F. D., Sherris J. C. Emergence in a burn center of populations of bacteria resistant to gentamicin, tobramycin, and amikacin: evidence for the need for changes in zone diameter interpretative standards. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1977 Dec;12(6):688–696. doi: 10.1128/aac.12.6.688. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shahidi A., Ellner P. D. Effect of mixed cultures on antibiotic susceptibility testing. Appl Microbiol. 1969 Nov;18(5):766–770. doi: 10.1128/am.18.5.766-770.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stemper J. E., Matsen J. M. Device for turbidity standardizing of cultures for antibiotic sensitivity testing. Appl Microbiol. 1970 Jun;19(6):1015–1016. doi: 10.1128/am.19.6.1015-1016.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thornsberry C., Gavan T. L., Sherris J. C., Balows A., Matsen J. M., Sabath L. D., Schoenknecht F., Thrupp L. D., Washington J. A., 2nd Laboratory evaluation of a rapid, automatic susceptibility testing system: report of a collaborative study. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1975 Apr;7(4):466–480. doi: 10.1128/aac.7.4.466. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thornsberry C., Kirven L. A. Antimicrobial susceptibility of Haemophilus influenzae. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1974 Nov;6(5):620–624. doi: 10.1128/aac.6.5.620. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wegner D. L., Mathis C. R., Neblett T. R. Direct method to determine the antibiotic susceptibility of rapidly growing blood pathogens. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976 May;9(5):861–862. doi: 10.1128/aac.9.5.861. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wegner D. L., Neblett T. R. Procedure for expediting determinations of antibiotic susceptibility of gram-negative, urinary tract pathogens. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976 Dec;10(6):921–922. doi: 10.1128/aac.10.6.921. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



