Abstract
Background
Depressive symptoms and anxiety are common in heart failure patients as well as their spousal caregivers. However, it is not known whether their emotional distress contributes to their partner's quality of life (QoL). This study examined the effect of patients' and partners' depressive symptoms and anxiety on quality of life in patient-spouse dyads using an innovative dyadic analysis technique, the Actor-Partner Interdependence Model (APIM).
Method
A total of 58 dyads (patient: 43% in males, mean age 62 years, mean ejection fraction 34% ± 11, 43% in NYHA III-IV) participated in the study. Depressive symptoms and anxiety were assessed using the Brief Symptom Inventory. QoL was assessed using the Minnesota Living with Heart Failure Questionnaire. Dyadic data were analyzed using the APIM with distinguishable dyad regression model. In APIM, actor effect is the impact of a person's emotional distress on his/her own QoL. Partner effect is the impact of a person's emotional distress on his/her partner's QoL.
Result
Depressive symptoms exhibited actor effect of both patients (p <.001) and spouses (p < .001) and only partner effect of patients (p < .05) on QoL. Patients and spouses with higher depressive symptoms had poorer quality of life. Patients whose spouses had higher depressive symptoms were more likely to indicate their own quality of life was poorer. Anxiety has similar actor and partner effects on QoL as depressive symptoms.
Conclusion
Interventions to reduce depression and anxiety and to improve patients' quality of life should include both patients and spouses.
Keywords: heart failure, depressive symptoms, anxiety, quality of life, actor-partner interdependence model
INTRODUCTION
Depressive symptoms and anxiety are common psychological problems for both family caregivers and patients with chronic heart failure (HF). Depressive symptoms in patients with HF are more prevalent than among healthy individuals [1] or among those with other chronic diseases, including other forms of heart disease [2-4]. A meta analysis of 27 HF studies found that the prevalence of depressive symptoms in patients with HF ranged from 9% to 60% and the overall mean prevalence was 20.3% [5]. Severe depressive symptoms are commonly observed among hospitalized individuals with HF [6] . Although less is known about anxiety in patients with HF, 18% to 45% of patients with HF reported anxiety [7-9], and 18% of patients suffer at least one anxiety disorder such as panic disorder and generalized anxiety disorder [8]. According to De Jong et al. [10], anxiety is more common in patients with HF than patients with acute myocardial infarction; 62.5% of patients with HF reported higher anxiety than the mean anxiety score on the Brief Symptom Inventory (BSI) for a healthy reference group compared to 38.8% of patients with acute myocardial infarction.
Family caregivers of patients with HF also experience similar emotional distress. As many as 45% of family caregivers of patients with end-stage HF experience depressive symptoms and 50% are anxious [11]. According to Karmilovich, family caregivers of HF patients experienced moderate levels of stress and their general stress levels were 50% higher than the average level of healthy individuals [12]. The prevalence of depressive symptoms in spousal caregivers of HF patients is approximately 23% to 47% [13, 14].
There has been substantial research on the association between emotional distress in patients with HF and poor clinical outcomes such as increased risk of hospitalization and mortality. HF patients with severe depressive symptoms have twice the risk of functional decline as those without depressive symptoms [15]. Similarly, those with depressive symptoms have a three times greater risk of readmission and two times greater risk of death than those without depressive symptoms [16]. It has been reported that community dwelling spousal caregivers have 63% higher risk of mortality than non-caregivers [17] and caregivers who had a high level of caregiving responsibility for an ill spouse have 82% increased risk of coronary heart disease [18]. Little is known about effects of emotional distress on outcomes in family caregivers with HF patients.
Researchers have only recently begun to include family caregivers in patients' outcome research. To date, two studies have investigated the effect of depressive symptoms in patient-spouse dyads on quality of life outcome. According to Martensson and his colleagues [13], depressive symptoms of patients with HF and spousal caregivers were correlated with only their own mental component of quality of life assessed using the SF-12, but were not correlated with their partner's quality of life in 48 patient-spouse dyads. Phil and his colleagues [14] reported that depressive symptoms of 47 patients and spousal caregivers were correlated with their own physical and mental component of the quality of life assessed using the SF-36. In addition, they found that spousal caregivers' depressive symptoms were correlated with patients' mental component of the quality of life. Both studies found that depressive symptoms predicted only a person's own mental component of quality of life, not their partner's quality of life, but a limitation of both studies was that the analysis did not include data from both patient and caregiver in the same model. Although data were collected from couples concurrently, it is notable that the effects of depressive symptoms were studied from each member of the dyads separately using an analysis method that is based on the assumption of independence of observations, rather than treating both members of the dyads as the unit of analysis. Because patients and family caregivers are affected by patients' health status, interactions in patient and caregiver dyads are unavoidable and inevitable in the HF self-care process. The relationship between patient and caregiver is non-independent. Thus, it is logical that the study of the impact of emotional distress on health outcomes should involve the dyad as the unit of analysis. The Actor-Partner Independence Model (APIM), a paired regression technique [19, 20], allows investigation of the relationship within couples using a regression framework that does not require independence of observations. Although there is accumulating evidence that family caregivers' emotional distress is associated with poor patient outcomes, research on this area is quite limited and includes only the study of depression. There are no studies of whether patients' and family caregivers' anxiety contribute to partners' quality of life. The purposes of this study were to: (1) investigate whether there were differences in the levels of depressive symptoms, anxiety, and quality of life between patients with HF and spousal caregivers; and (2) examine whether patients' and spousal caregivers' depressive symptoms and anxiety predicted their own quality of life as well as their spouse's quality of life.
METHODS
Design and sample
This was a cross-sectional, descriptive study in which depressive symptoms, anxiety, and quality of life were assessed concurrently in both patients with HF and spousal caregivers. We invited patients who had a chronic HF diagnosis and their spousal caregiver to participate. We included patients with HF who were on stable doses of HF medications for at least one month. We excluded patients who had acute myocardial infarction within the previous three months or who had a co-morbid terminal illness such as cancer, end-stage liver or renal disease. We included only a spousal caregiver who was identified as a primary caregiver in the self-care management by patients with HF. A spouse caregiver was eligible if they were: (1) a spouse or significant other living in a committed relationship with a HF patient; (2) without cognitive impairment; (3) without one of the following major co-morbidities--HF, cancer, renal failure, or liver failure. When both patients and spousal caregivers met sample inclusion criteria, we recruited the dyads in cardiac outpatient clinics at a major academic center in central Kentucky or by phone contact.
Measures
Brief Symptom Inventory
Depressive symptoms and anxiety were assessed using a depressive symptom and anxiety subscales of the Brief Symptom Inventory (BSI) [21]. Each subscale consists of 6-items that are rated on a 5-point scale from 0 (not at all) to 4 (extremely). For each subscale, the item scores were summed and the mean obtained. Higher scores indicate higher levels of depressive symptoms and anxiety. The mean scores in healthy populations for depressive symptoms is 0.28 ± 0.41 and for anxiety is 0.35 ± 0.45 [21]. Previous research supports convergent and construct validity [21, 22]. Reliability has been reported with internal consistency assessed by Cronbach's alpha of.90 to .92 for depressive symptoms and from .85 to .90 for anxiety in individuals with heart disease [23-25]. In this study, Cronbach's alpha for depressive symptoms was 0.92 for patients and .083 for spouses. Cronbach's alpha for anxiety was 0.86 for patients and 0.87 for spouses.
Minnesota Living with Heart Failure Questionnaire
Quality of life was assessed using the Minnesota Living with Heart Failure Questionnaire (MLHFQ) [26, 27]. The MLHFQ is a 21-item instrument rated on a 6-point of scale from 0 (no effect) to 5 (very much). Item ratings are summed for a total score. Total scores can range from 0 to 105. Higher scores reflect worse quality of life. The reliability of the MLHFQ has been reported with Cronbach's alpha ranging from 0.73 to 0.93 and construct validity of the MLHFQ has been supported [26-29].
The MLHFQ is a disease specific instrument to assess quality of life from the perceptiveness of patient with HF. We chose to use a disease specific instrument rather than a generic instrument. Generic instruments such as the SF-12 or SF-36 have limited ability to detect the impact of specific illnesses on quality of life. HF affects unique domains of quality of life in unique ways that can even differ from the impact of other chronic illnesses and generics instruments often are not capable of registering the specific effects of HF.
In this study, we also were interested in caregivers' quality of life that was specifically related to their caregiving experiences in taking care of ill spouses with HF. In order to directly compare quality of life using APIM regression, it is optimal to use the same instrument. Thus, we chose the MLHFQ rather than a generic instrument although there is no healthy adult version for MLHFQ. We modified the introduction of the original MLHFQ to fit the context relevant to caregivers of HF patients by explaining that `these questions concern how your family member's heart failure (heart condition) has prevented you from living as you wanted during the last month'. We also modified two items to fit in caregiver's view. Item 16 `giving you side effects from medications?' was replaced with `giving you less time to take care of your own physical health?' and item 17 `making you feel you are a burden to your family or friends?' was replaced to `feeling burdened by your family member?' These modifications were developed by three researchers who were nurses with expertise in the care of patients with HF; had a doctoral degree; and who had used the original instrument in more than one research study. In this study, Cronbach's alpha was 0.93 for patients and 0.95 for spouses.
We also collected demographic data (i.e., gender, age, education, and length of marriage) and medical history in separate brief interviews with patients and caregivers using a structured questionnaire. The New York Heart Association (NYHA) class of patients was assessed by trained cardiac nurse researchers by interview. Clinical characteristics of patients (i.e., medication history, etiology, left ventricular ejection fraction, co-mobility) were collected by medical chart review.
Procedures
After approval from the University of Kentucky Internal Review Board, patients were recruited from those referred to the project by their primary physicians or nurse practitioners. Patients were referred from outpatient cardiology practices associated with a major academic medical center in Central Kentucky. All cardiology practitioners in the center seeing heart failure patients referred appropriate patients to the project. Questionnaire packets were either given to participants at a clinic visit or were mailed to their homes. Patients and spouses were asked to complete their questionnaires without discussing their answers with each other. Completed questionnaires were returned to the investigators by mail. Participants received reminder calls if necessary when the packet was not returned on time.
Data analysis
Descriptive statistics such as frequency distributions or means and standard deviations were obtained to summarize demographic and clinical characteristics, emotional distress, and quality of life. Comparisons of demographic characteristics between patients and spousal caregivers were made using paired sample t-tests and chi-square. Paired sample t-tests were used to determine differences in depressive symptoms, anxiety, and quality of life between patients and spousal caregivers and Pearson product-moment correlation coefficients were used to determine correlations among these continuous variables. To determine the impact of patients' and spousal caregivers' depressive symptoms and anxiety on their own quality of life as well as their partner's quality of life, the APIM with distinguishable dyads regression model was used [19]. The APIM regression is used to determine how outcomes are influenced by both members of the dyad, in this case patients and spouse caregivers. For this study, the actor effect was the impact of a person's emotional distress on his or her own quality of life outcome. The partner effect was the impact of each person's emotional distress on his or her partner's quality of life. Using APIM regression, the patient and spouse predictor variables are regressed on the patient and spouse outcome variables in a single regression model. All analyses were done using SPSS for windows, version 15; an alpha level of .05 was used throughout. A power analysis was conducted prior to data collection and was based on the initial goal of 40 dyads. While a power analysis algorithm has not been developed specifically for the APIM, the basis for this technique is regression. With a sample size of 40 dyads, assuming an alpha level of .05, the power of the regression F-test to detect a significant prediction model for quality of life is approximately 82% in the presence of a medium effect size and greater than 95% if the effect size is large [30]. Power estimates were obtained using NQuery Advisor [31]. Given the actual sample is larger than that planned, the power for the analyses described here is even greater.
Results
Characteristics of patient-spouse dyads
A total of 58 patient-spouse dyads participated in this study (Table 1). The mean age of patients was 61.7 years (SD = 12.5) and 43 patients (74%) were male. Most were white (93%) with only four African Americans patients (7%). Half of the patients (50%) had a high school diploma or less. The average length of marriage was 29 years (SD = 16). On average, the patients were 4.2 years older than spousal caregivers, but patients and spouses had similar education levels (Table 2). In this study, 60% of patients were prescribed an ACEI, while 76 % were prescribed a beta-blocker. There was no difference in the percentage of patients and spouses taking antidepressants (15% vs. 10%, p> .05).
Table 1.
Descriptive summary of patients
| Characteristics | Mean (± SD) or N (%) |
|---|---|
| Gender, Male | 43 (74.1%) |
| Age, years | 61 (±12.5) |
| Ethnicity, White | 53 (93.1%) |
| Education, ≤ high school diploma | 29 (50.0%) |
| Length of marriage, years | 29 (±16.2) |
| Left ventricular ejection fraction, % | 34.2 (±13.3) |
| NYHA class: III/IV | 24 (42.9%) |
| Etiology - Ischemic | 25 (43.3%) |
| Idiopathic | 7 (12.1%) |
| Hypertension | 7 (12.1%) |
| Other | 19 (32.7%) |
| History of Hypertension | 40 (69.0%) |
| History of Diabetes Mellitus | 24 (41.3%) |
| Medication-Angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitor | 34 (60.0%) |
| Beta-blockers | 43 (76.8%) |
| Diuretics | 37 (66.1%) |
| Antidepressants | 9 (15.8%) |
Table 2.
Comparisons between patients and spouses on demographic and study variables
| Characteristics | Patients | Spouses | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean (SD) | Mean (SD) | Paired t | p-value | |
| Age, years | 61.7 (12.5) | 57.5 (11.9) | 4.4 | <.001 |
| Education, years | 13.4 (3.8) | 13.5 (3.7) | 1.0 | >.05 |
| Depressive symptom, BSI | 0.74 (0.96) | 0.77 (1.18) | -0.2 | >.05 |
| Anxiety, BSI | 0.64 (0.76) | 0.55 (0.66) | 0.6 | >.05 |
| Quality of life, MLHFQ | 38.3 (23.4) | 21.8 (22.6) | 5.1 | <.001 |
Note: SD= standard deviation, BSI = Brief Symptom Inventory, MLHFQ= Minnesota Living with Heart Failure
Emotional distress and quality of life in patient-spousal caregiver dyads
Levels of depressive symptoms and anxiety were similar between patients with HF and spousal caregivers but patients' quality of life was worse than spouses' quality of life (Table 2). Both patients and spousal caregivers had substantially greater depressive symptoms and anxiety than the mean reported in healthy populations. In this study, 33 patients (56.9%) and 33 spousal caregivers (56.9%) had a depressive symptoms score that exceeded the mean of .28 that was reported in a community sample of healthy adults[21, 22] In addition, 25 patients (43.1%) and 27 spousal caregivers (46.6%) had anxiety levels that exceeded the mean of .35 reported in the healthy population.
There were no gender differences in depressive symptoms levels in patients (female M = 1.0 vs. male M = 0.64; t = -1.53, p >.05) or spouses (female M = 0.81 vs. male M = 0.64; t = -0.5, p > .05). There was no gender difference in anxiety level in spouse caregivers (female M = 0.90 vs. male M = 0.54; t = -1.6, p > .05) but female spouses reported a slightly higher anxiety level than male spouses (female M = 0.63 vs. male M = 0.32; t = -2.2, p < .05).
Patients' depressive symptoms and anxiety were correlated with both their own quality of life and their partner's quality of life (Table 3). Spousal caregivers' depressive symptoms and anxiety were correlated with their own quality of life but not with their partner's quality of life.
Table 3.
Correlations among predictors and outcomes in patient-spouse dyads
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Patient depressive symptoms | - | ||||
| 2. | Spouse depressive symptoms | .094 | ||||
| 3. | Patient anxiety | .720** | .101 | |||
| 4. | Spouse anxiety | -.037 | .571** | -.011 | ||
| 5. | Patient quality of life | .639** | .254 | .538** | .025 | |
| 6. | Spouse quality of life | .289** | .564** | .350** | .551** | .431** |
p <. 001
Impact of emotional distress on quality of life
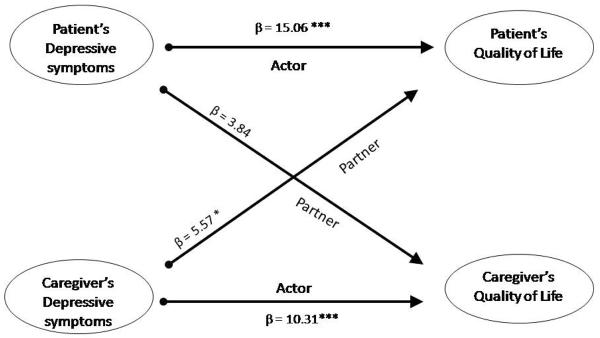
Two separate APIM regression models were tested. In one model, patient and spouse depressive symptoms were regressed on patient and spouse quality of life. In the second model, patient and spouse anxiety scores were regressed on patient and spouse quality of life. Depressive symptoms exhibited both patient and caregiver actor effects on quality of life (Table 4 and Figure 1). Patients and spousal caregivers with higher depressive symptoms had poorer quality of life. With regard to partner effects, however, only the spousal caregiver depressive symptoms have a partner effect on patients' quality of life. The partner effect of patients' depressive symptoms on caregivers' quality of life was not significant (p = .058). Patients whose spouses had higher depressive symptoms were more likely to indicate their own quality of life was poorer. However, patients' depressive symptoms did not impact caregivers' quality of life.
Table 4.
The Actor-Partner Independence Model demonstrating the actor and partner relationship of depressive symptoms and anxiety to quality of life
| Effect | Patients | Spouses | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| β | t | p-value | β | t | p-value | |
| Depressive symptoms | ||||||
| Actor | 15.06 | 6.2 | <.001 | 10.31 | 5.1 | <.001 |
| Partner | 3.84 | 1.9 | .058 | 5.57 | 2.2 | .031 |
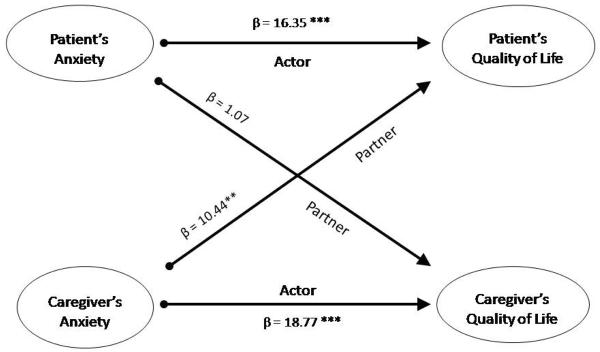
| Anxiety | ||||||
| Actor | 16.35 | 4.7 | <.001 | 18.77 | 5.4 | <.001 |
| Partner | 1.07 | 0.3 | .789 | 10.44 | 3.5 | .001 |
Figure 1.
Depressive symptoms: The actor and partner effects as predictors of quality of life
Actor-Partner Interdependence Model with distinguishable dyads regression model * p <.05; *** p <.001
Anxiety exerted a significant actor effect for both patients and caregivers (Table 4). The partner effect for caregivers' anxiety on the quality of life was significant but the partner effect of patients' anxiety on the caregivers' quality of life was not significant (Figure 2). Thus, patients and spousal caregivers with higher anxiety had poorer quality of life. Patients whose spouses who had higher anxiety were more likely to indicate their own quality of life was poorer. However, patients' anxiety did not predict spousal caregivers' quality of life.
Figure 2.
Anxiety: The actor and partner effects as predictors of quality of life
Actor-Partner Interdependence Model with distinguishable dyads regression model ** p <.01; *** p <.001
Discussion
In this dyadic analysis, we found that both patient' and spousal caregivers' depressive symptoms and anxiety influenced their own quality of life. This finding was consistent with previous studies findings on depressive symptoms effects on quality of life [13, 14]. The most important finding of this study was the link between spousal caregivers' emotional distress (i.e., both depressive symptoms and anxiety) and patients' poor quality of life. Many studies have reported that patients' depressive symptoms are associated with an increase their own mortality and rehospitalization. However, little is known about the effects of spousal emotional distress on patients' outcome. In this study, we found that spousal caregivers' depressive symptoms and anxiety negatively impacted patients' quality of life, with high depressive symptoms or anxiety in the caregiver spouse predicting poorer quality of life in the patient. In contrast, we found neither patients' depressive symptoms nor anxiety predict their spouses' quality of life although the impact of patients' depressive symptoms on their caregivers' quality of life was marginal, with p = .06. The results of this study demonstrate the substantial impact of caregivers' emotional distress on patients' quality of life and suggest that patients with HF may be particularly vulnerable to the emotional distress of their spouse caregivers. This finding was consistent with prior research findings that caregivers' depressive symptoms correlate to HF patients' poor quality of life, but extend this research by demonstrating the effect in a more appropriate analysis that recognizes the non-independence of patient and spouse data [13, 14, 32, 33].
We also found that both patients with HF and spousal caregivers experienced substantial emotional distress. The high prevalence of emotional distress is consistent with findings reported in recent studies examining the prevalence of depressive symptoms or anxiety using symptoms questionnaires [5]. Furthermore, we found that patients and spousal caregivers experienced similar levels of depressive symptoms and anxiety. This suggests that the emotional aspects of dealing with HF may affect spousal caregivers as much as their partners who have the illness. The results of this study were inconsistent with a prior report that HF patients had higher depressive symptoms levels than those of spousal caregivers [13], but it agrees with a study suggesting both patients and caregivers had similar depressive symptoms [14]. Although there is no identified mechanism to explain this similarity in emotional distress, one possible explanation may be founded in the theory of emotional contagion. This theory posits that emotions are easily transferred to another person when two individuals are in an intimate interpersonal relationships [34, 35].
There are several implications resulting from the findings in this study. First, to improve patients' quality of life, depressive symptoms and anxiety should be routinely assessed in both patients and spouses. A short instrument such as the BSI may be useful for detecting emotional distress in both patients and spouses in clinical settings. Second, intervention formats should be expanded to include spouse caregivers. Many current interventions focus on improving depressive symptoms/ anxiety and quality of life only for patients [36, 37]. These interventions have included using individual or group sessions but have neglected depressed family caregivers who have a substantial influence on patients' quality of life. Dyadic interventions, however, has not been attempted in the cardiovascular health area. Future research should focus on interventions to decrease depressive symptoms and anxiety and that include both patients and spouses. Third, although we found that spousal caregivers' emotional distress influenced patients' quality of life, the long-term effect of spousal caregivers' emotional distress on patients' outcome such as mortality and morbidity is not known, so this should be addressed in future research.
This study has limitations that affect generalizability. First, marital quality and perceived support were not measured. Marital quality is a known predictor of quality of life or well-being in married couples. According to Rohrbaugh and colleagues [38], emotional distress of HF patient-spouse dyads was negatively associated with marital quality. It is possible that patient-caregiver married couples who have conflict in their marriage exhibit different relationships between emotional distress and quality of life compared to couples without conflict. Further investigation is necessary to determine the affect of marital quality on the relationship between emotional distress and quality of life. Secondly, we limited this study to patient-spouse dyads, though non-spousal family caregivers may experience similar emotional distress when caring for a family member with HF. It is not known whether non-spousal family caregivers have the same effects on patient outcomes as the results found in this study with spouse caregivers. Further investigation is needed to determine the effects of emotional distress on patients' outcomes for other caregiver-patient relationship types. A third limitation of this study was the observational, cross-sectional nature of the design, which does not allow any inferences of causality between psychological distress and quality of life. Thus, it is unknown whether spousal caregivers' distress impacts patients' quality of life in the long-term.
Including family caregivers in patients' outcome research in cardiovascular health including HF is receiving greater attention. One possible reason for increased attention may be emphasis to include family members as collaborators or partners in the patients' self-management and monitoring of their symptoms. Another reason may be a greater awareness of the vital link between family caregivers' support and patients' health outcomes due to the accumulating evidence showing the positive influence of family support on reduction of readmission in patient with HF [33, 39]. Consequently, there is a need to enhance our understanding of the dynamic interactions that occur in patient-caregiver dyads. New statistical analysis techniques such as the APIM used in this study are now available for family or dyadic research [19, 20]. These techniques will enhance our understanding of the complex interactions between caregivers and patients which will lead to novel dyadic-based interventions.
Acknowledgement
This study was funded from the NIH/NINR K23 Mentored Patient-Oriented Career Development Grant to Dr. Chung (1K23NR010011-01: 2006-2009), the University of Kentucky Faculty Research Support Grant (2005-2006) to Dr. Chung, and NIH/NINR Center for Biobehavioral Research in Self-management (1P20NR010679) to Dr. Moser (center director), the University of Kentucky.
Footnotes
Publisher's Disclaimer: This is a PDF file of an unedited manuscript that has been accepted for publication. As a service to our customers we are providing this early version of the manuscript. The manuscript will undergo copyediting, typesetting, and review of the resulting proof before it is published in its final citable form. Please note that during the production process errors may be discovered which could affect the content, and all legal disclaimers that apply to the journal pertain.
References
- [1].Heo S, Moser DK, Lennie TA, Zambroski CH, Chung ML. A comparison of health-related quality of life between older adults with heart failure and healthy older adults. Heart Lung. 2007 Jan-Feb;36(1):16–24. doi: 10.1016/j.hrtlng.2006.06.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [2].Havranek EP, Ware MG, Lowes BD. Prevalence of depression in congestive heart failure. Am J Cardiol. 1999 Aug 1;84(3):348–50. A9. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9149(99)00293-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [3].Penninx BW, Beekman AT, Honig A, Deeg DJ, Schoevers RA, van Eijk JT, et al. Depression and cardiac mortality: results from a community-based longitudinal study. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2001 Mar;58(3):221–7. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.58.3.221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [4].Koenig HG. Depression in hospitalized older patients with congestive heart failure. General hospital psychiatry. 1998 Jan;20(1):29–43. doi: 10.1016/s0163-8343(98)80001-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [5].Rutledge T, Reis VA, Linke SE, Greenberg BH, Mills PJ. Depression in heart failure a meta-analytic review of prevalence, intervention effects, and associations with clinical outcomes. Journal of the American College of Cardiology. 2006 Oct 17;48(8):1527–37. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2006.06.055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [6].Freedland KE, Rich MW, Skala JA, Carney RM, Davila-Roman VG, Jaffe AS. Prevalence of depression in hospitalized patients with congestive heart failure. Psychosomatic medicine. 2003 Jan-Feb;65(1):119–28. doi: 10.1097/01.psy.0000038938.67401.85. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [7].Friedmann E, Thomas SA, Liu F, Morton PG, Chapa D, Gottlieb SS. Relationship of depression, anxiety, and social isolation to chronic heart failure outpatient mortality. American heart journal. 2006 Nov;152(5):940e1–8. doi: 10.1016/j.ahj.2006.05.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [8].Haworth JE, Moniz-Cook E, Clark AL, Wang M, Cleland JG. An evaluation of two self-report screening measures for mood in an out-patient chronic heart failure population. International journal of geriatric psychiatry. 2007 Nov;22(11):1147–53. doi: 10.1002/gps.1807. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [9].Szekely A, Balog P, Benko E, Breuer T, Szekely J, Kertai MD, et al. Anxiety predicts mortality and morbidity after coronary artery and valve surgery--a 4-year follow-up study. Psychosomatic medicine. 2007 Sep-Oct;69(7):625–31. doi: 10.1097/PSY.0b013e31814b8c0f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [10].De Jong MJ, Moser DK, An K, Chung ML. Anxiety is not manifested by elevated heart rate and blood pressure in acutely ill cardiac patients. Eur J Cardiovasc Nurs. 2004 Sep;3(3):247–53. doi: 10.1016/j.ejcnurse.2004.06.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [11].Scott LD. Caregiving and care receiving among a technologically dependent heart failure population. Ans. 2000 Dec;23(2):82–97. doi: 10.1097/00012272-200012000-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [12].Karmilovich SE. Burden and stress associated with spousal caregiving for individuals with heart failure. Progress in cardiovascular nursing. 1994;9(1):33–8. Winter. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [13].Martensson J, Dracup K, Canary C, Fridlund B. Living with heart failure: depression and quality of life in patients and spouses. J Heart Lung Transplant. 2003 Apr;22(4):460–7. doi: 10.1016/s1053-2498(02)00818-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [14].Pihl E, Jacobsson A, Fridlund B, Stromberg A, Martensson J. Depression and health-related quality of life in elderly patients suffering from heart failure and their spouses: a comparative study. Eur J Heart Fail. 2005 Jun;7(4):583–9. doi: 10.1016/j.ejheart.2004.07.016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [15].Vaccarino V, Kasl SV, Abramson J, Krumholz HM. Depressive symptoms and risk of functional decline and death in patients with heart failure. Journal of the American College of Cardiology. 2001 Jul;38(1):199–205. doi: 10.1016/s0735-1097(01)01334-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [16].Jiang W, Alexander J, Christopher E, Kuchibhatla M, Gaulden LH, Cuffe MS, et al. Relationship of depression to increased risk of mortality and rehospitalization in patients with congestive heart failure. Archives of internal medicine. 2001 Aug 13-27;161(15):1849–56. doi: 10.1001/archinte.161.15.1849. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [17].Schulz R, Beach SR. Caregiving as a risk factor for mortality: the Caregiver Health Effects Study. Jama. 1999 Dec 15;282(23):2215–9. doi: 10.1001/jama.282.23.2215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [18].Lee S, Colditz GA, Berkman LF, Kawachi I. Caregiving and risk of coronary heart disease in U.S. women: a prospective study. American journal of preventive medicine. 2003 Feb;24(2):113–9. doi: 10.1016/s0749-3797(02)00582-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [19].Kenny DA, Kashy DA, Cook WL. Dyadic data analysis. The Guilford Press; New York, NY: 2006. [Google Scholar]
- [20].Rayens MK, Svavarsdottir EK. A new methodological approach in nursing research: an actor, partner, and interaction effect model for family outcomes. Research in nursing & health. 2003 Oct;26(5):409–19. doi: 10.1002/nur.10100. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [21].Derogatis LR, Melisaratos N. The Brief Symptom Inventory: an introductory report. Psychological medicine. 1983 Aug;13(3):595–605. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [22].Derogatis LR. Brief Symptom Inventory: Administrations, Scoring, and Procedures Manual. Minneapolis: National Computer Systems. 1993 [Google Scholar]
- [23].Kim KA, Moser DK, Garvin BJ, Riegel BJ, Doering LV, Jadack RA, et al. Differences between men and women in anxiety early after acute myocardial infarction. Am J Crit Care. 2000 Jul;9(4):245–53. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [24].Moser DK, Dracup K. Is anxiety early after myocardial infarction associated with subsequent ischemic and arrhythmic events? Psychosomatic medicine. 1996 Sep-Oct;58(5):395–401. doi: 10.1097/00006842-199609000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [25].Moser DK, Dracup K, McKinley S, Yamasaki K, Kim CJ, Riegel B, et al. An international perspective on gender differences in anxiety early after acute myocardial infarction. Psychosomatic medicine. 2003 Jul-Aug;65(4):511–6. doi: 10.1097/01.psy.0000041543.74028.10. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [26].Rector TS, Cohn JN. Assessment of patient outcome with the Minnesota Living with Heart Failure questionnaire: reliability and validity during a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of pimobendan. Pimobendan Multicenter Research Group. American heart journal. 1992 Oct;124(4):1017–25. doi: 10.1016/0002-8703(92)90986-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [27].Rector TS, Kubo SH, Cohn JN. Validity of the Minnesota Living with Heart Failure questionnaire as a measure of therapeutic response to enalapril or placebo. The American journal of cardiology. 1993 May 1;71(12):1106–7. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(93)90582-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [28].Middel B, Bouma J, de Jongste M, van Sonderen E, Niemeijer MG, Crijns H, et al. Psychometric properties of the Minnesota Living with Heart Failure Questionnaire (MLHF-Q) Clinical rehabilitation. 2001 Oct;15(5):489–500. doi: 10.1191/026921501680425216. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [29].Riegel B, Moser DK, Glaser D, Carlson B, Deaton C, Armola R, et al. The Minnesota Living With Heart Failure Questionnaire: sensitivity to differences and responsiveness to intervention intensity in a clinical population. Nursing research. 2002 Jul-Aug;51(4):209–18. doi: 10.1097/00006199-200207000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [30].Cohen JD. Statistical power analysis for the behavioral sciences. Lawrence Erlbaum Associates; Hillsdale, NJ: 1988. [Google Scholar]
- [31].nQuery Advisor. Version 6.0. ed. Statistical Solutions; Sangus, MA: 19952005. [Google Scholar]
- [32].Evangelista LS, Dracup K, Doering L, Westlake C, Fonarow GC, Hamilton M. Emotional well-being of heart failure patients and their caregivers. Journal of cardiac failure. 2002 Oct;8(5):300–5. doi: 10.1054/jcaf.2002.128005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [33].Schwarz KA, Elman CS. Identification of factors predictive of hospital readmissions for patients with heart failure. Heart Lung. 2003 Mar-Apr;32(2):88–99. doi: 10.1067/mhl.2003.15. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [34].Gump BB, Kulik JA. Stress, affiliation, and emotional contagion. J Pers Soc Psychol. 1997 Feb;72(2):305–19. doi: 10.1037//0022-3514.72.2.305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [35].Neumann R, Strack F. “Mood contagion”: the automatic transfer of mood between persons. J Pers Soc Psychol. 2000 Aug;79(2):211–23. doi: 10.1037//0022-3514.79.2.211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [36].Sears SF, Sowell LD, Kuhl EA, Kovacs AH, Serber ER, Handberg E, et al. The ICD shock and stress management program: a randomized trial of psychosocial treatment to optimize quality of life in ICD patients. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol. 2007 Jul;30(7):858–64. doi: 10.1111/j.1540-8159.2007.00773.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [37].Lewin RJ, Coulton S, Frizelle DJ, Kaye G, Cox H. A brief cognitive behavioural pre-implantation and rehabilitation programme for patients receiving an Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillator improves physical health and reduces psychological morbidity and unplanned re-admissions. Heart. 2007 Dec 10; doi: 10.1136/hrt.2007.129890. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [38].Rohrbaugh MJ, Cranford JA, Shoham V, Nicklas JM, Sonnega JS, Coyne JC. Couples coping with congestive heart failure: role and gender differences in psychological distress. J Fam Psychol. 2002 Mar;16(1):3–13. doi: 10.1037//0893-3200.16.1.3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [39].Chin MH, Goldman L. Correlates of early hospital readmission or death in patients with congestive heart failure. The American journal of cardiology. 1997 Jun 15;79(12):1640–4. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9149(97)00214-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]