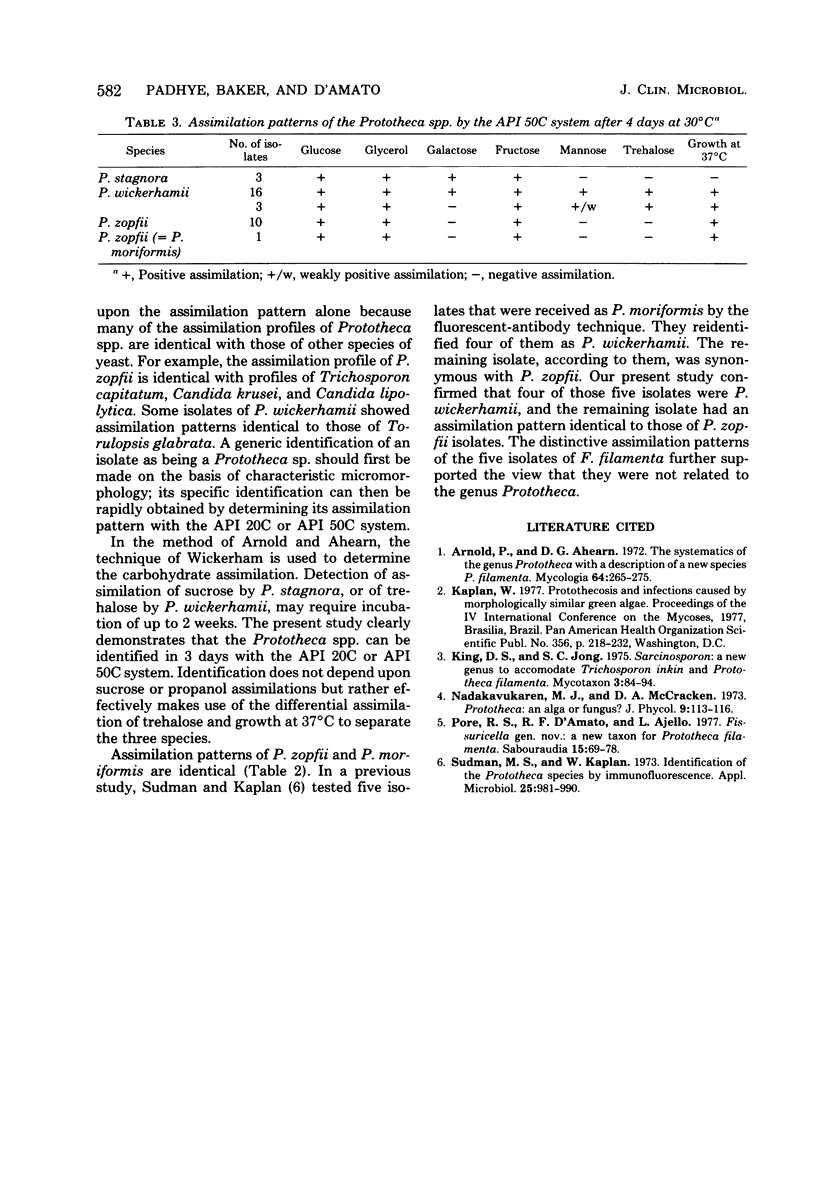
Abstract
The conventional auxanographic method of testing for the assimilation of carbohydrates and alcohols by the various species of Prototheca requires at least 2 weeks of incubation at 25 to 30 degrees C before definitive results are obtained. Even though Prototheca spp., in culture as well as in fixed tissues, can be identified more rapidly by fluorescent-antibody techniques in which species-specific reagents are used, such diagnostic facilities and reagents are not available in most diagnostic laboratories. The API 20C clinical yeast identification system, a commercially available ready-to-use micromethod, was found to permit the definitive identification of P. stagnora, P. wickerhamii, and P. zopfii within 4 days.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Pore R. S., D'Amato R. F., Ajello L. Fissuricella gen. nov.: a new taxon for Prototheca filamenta. Sabouraudia. 1977 Mar;15(1):69–78. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sudman M. S., Kaplan W. Identification of the Prototheca species by immunofluorescence. Appl Microbiol. 1973 Jun;25(6):981–990. doi: 10.1128/am.25.6.981-990.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



