Abstract
Pneumocystis carinii has been successfully cultured with WI-38 human embryonic lung fibroblasts. Inoculum was obtained from infected lungs of cortisone-treated Sprague-Dawley rats. Trophozoites reached peak numbers between days 4 and 8 and grew in two subcultures, but then proliferation ceased. If primary cultures were harvested and new medium were added, a second and sometimes a third harvest could be obtained. Cell monolayers were not destroyed. After growth of the initial inoculum had ceased, monolayers supported growth of a new inoculum. Harvested organisms had few contaminating tissue culture cells. Additional studies of growth requirements are needed. Although cultures cannot be used to diagnose P. carinii infection, cultured organisms should be useful for studies of biology and pathogenesis and for the development of immunodiagnostic techniques.
Full text
PDF
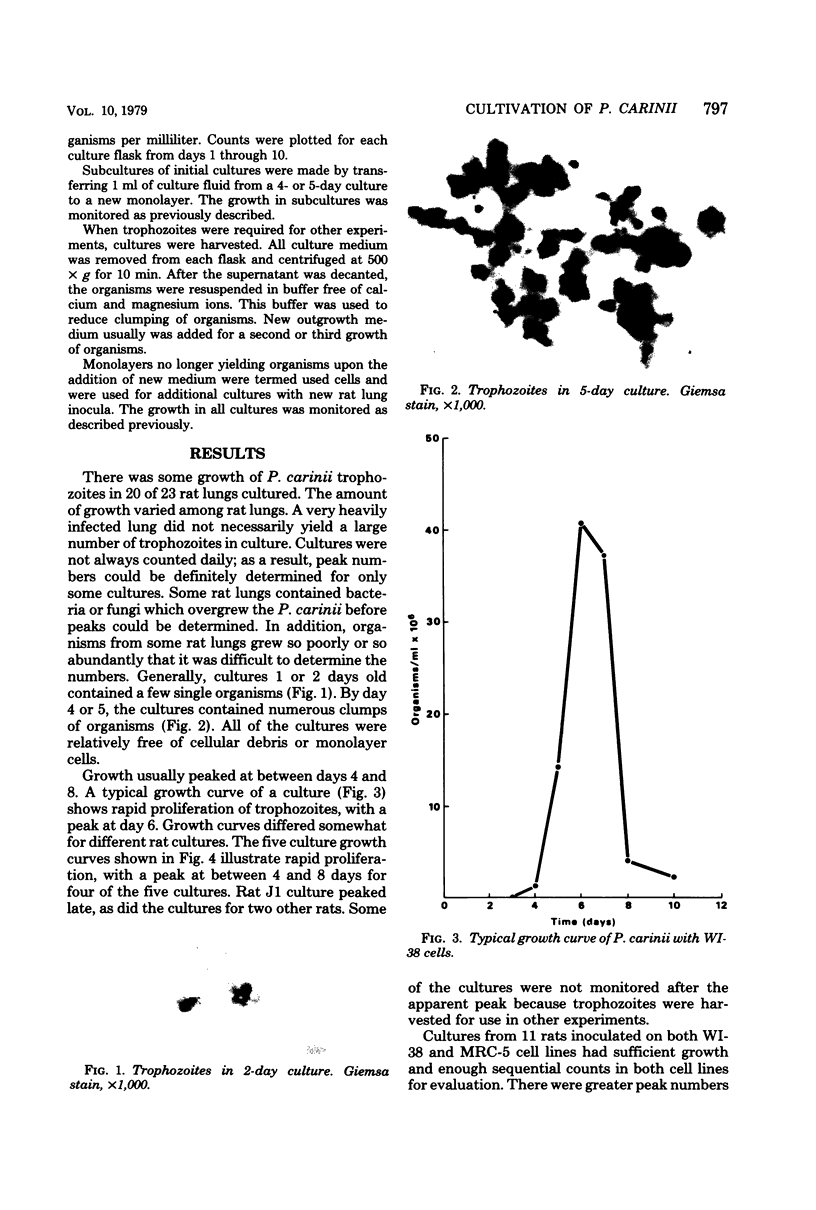
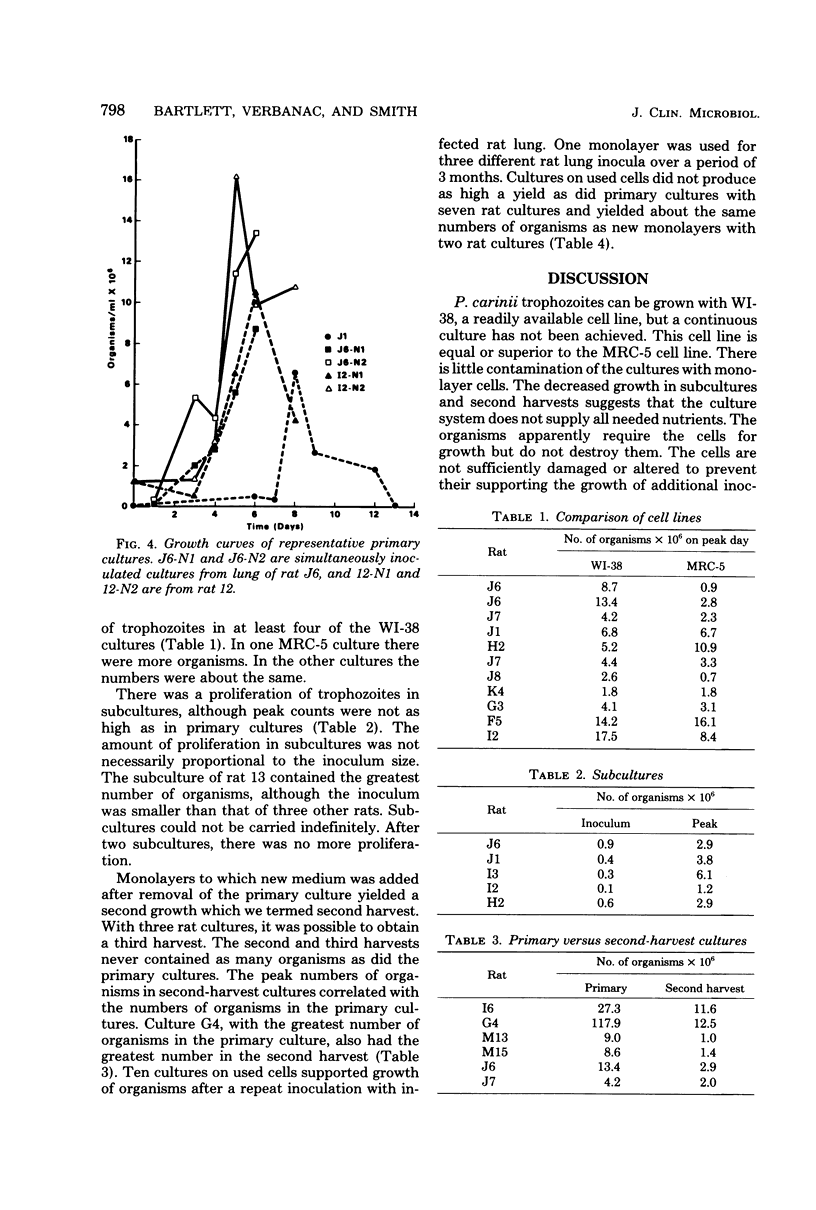

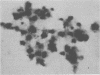
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Frenkel J. K., Good J. T., Shultz J. A. Latent Pneumocystis infection of rats, relapse, and chemotherapy. Lab Invest. 1966 Oct;15(10):1559–1577. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Latorre C. R., Sulzer A. J., Norman L. G. Serial propagation of Pneumocystis carinii in cell line cultures. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1977 May;33(5):1204–1206. doi: 10.1128/aem.33.5.1204-1206.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy M. J., Pifer L. L., Hughes W. T. Pneumocystis carinii in vitro: A study by scanning electron microscopy. Am J Pathol. 1977 Feb;86(2):387–401. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pifer L. L., Hughes W. T., Murphy M. J., Jr Propagation of Pneumocystis carinii in vitro. Pediatr Res. 1977 Apr;11(4):305–316. doi: 10.1203/00006450-197704000-00010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]