Abstract
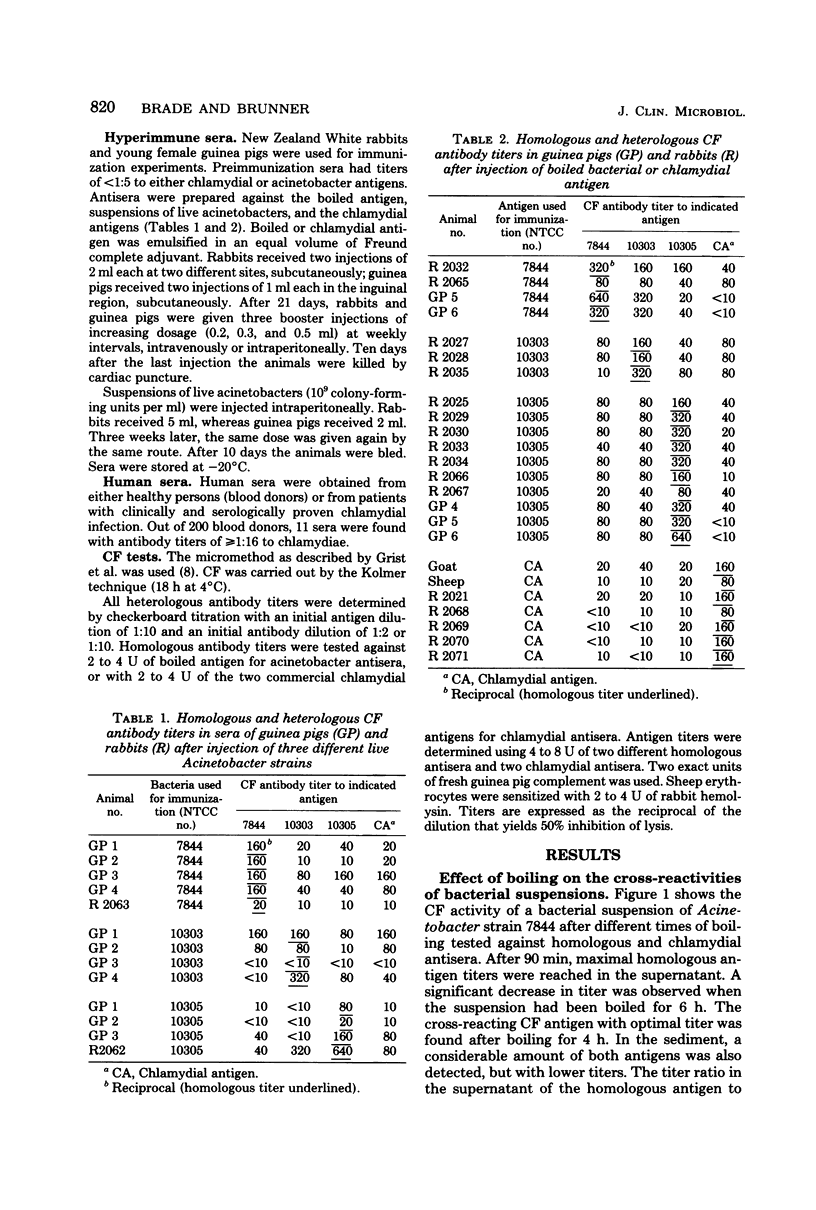
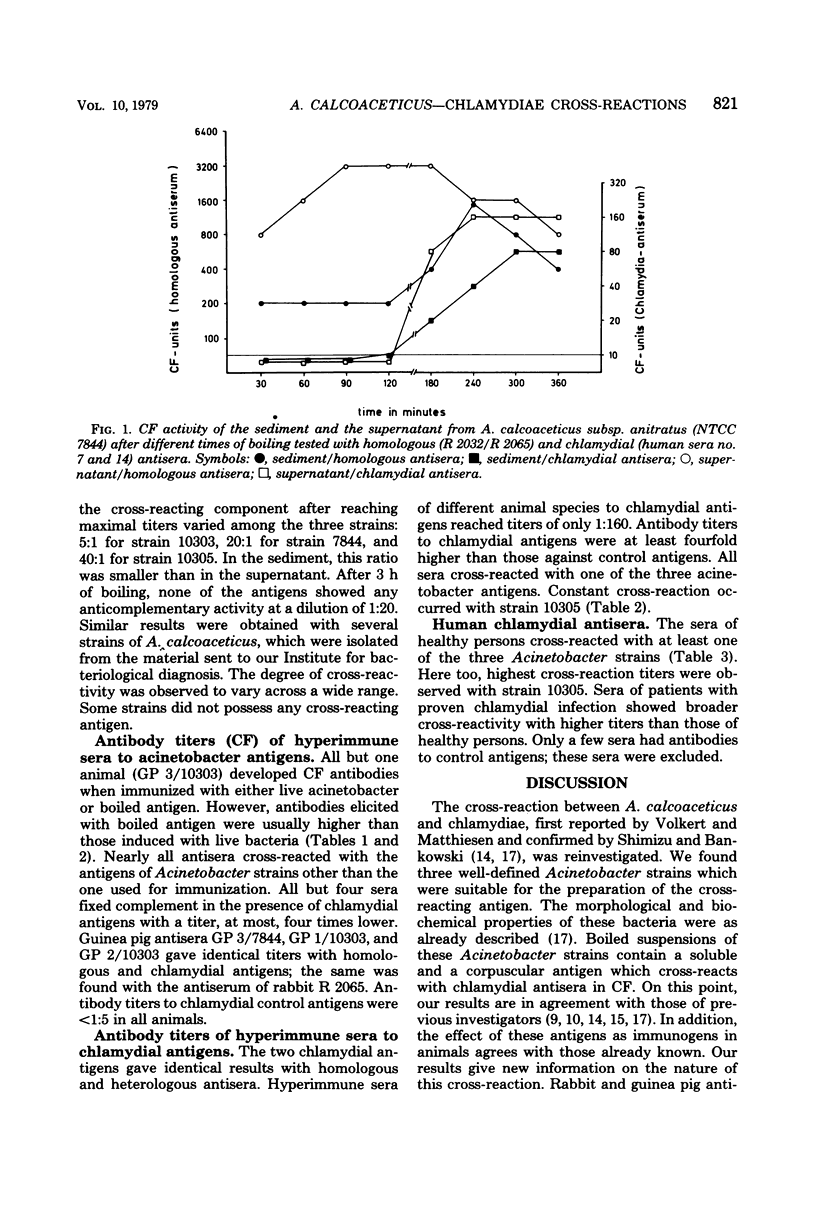
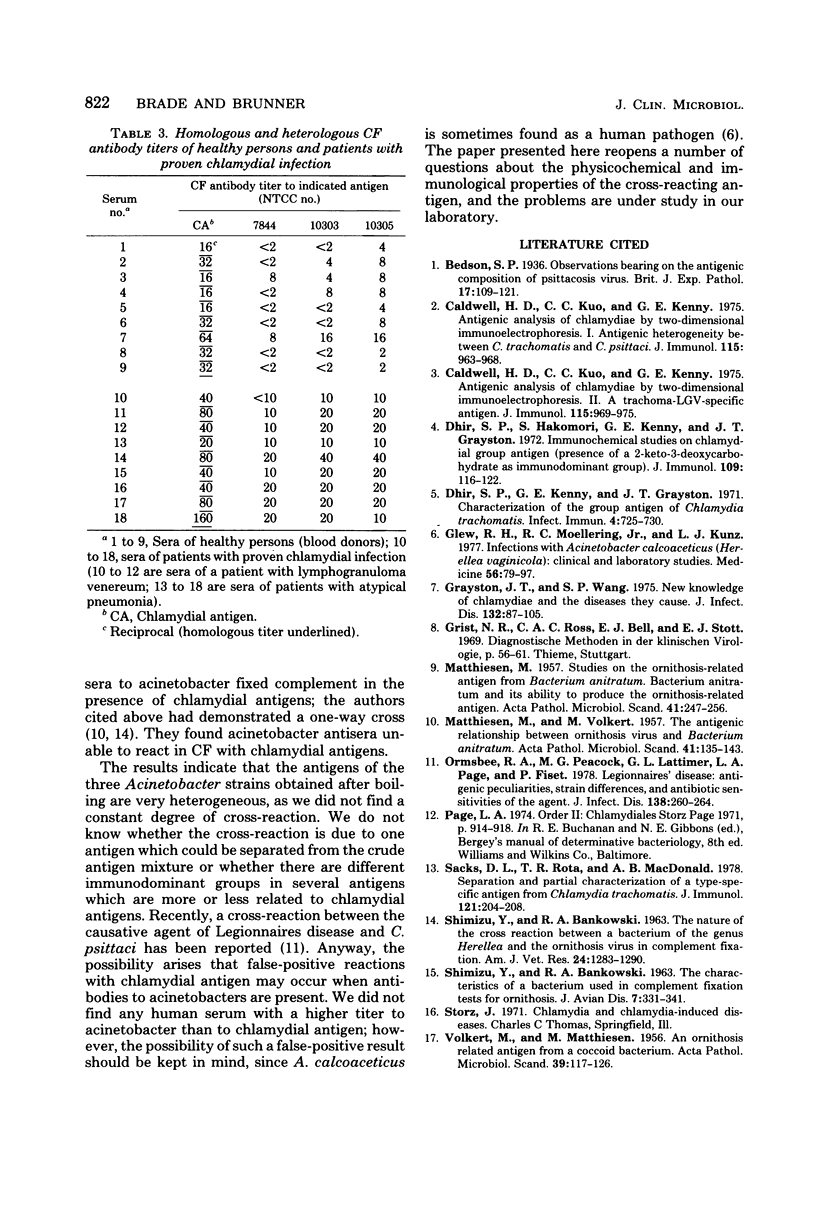
A cross-reaction between Acinetobacter calcoaceticus and chlamydiae is described. A water-soluble, heat stable, non-dialyzable antigen was extracted from Acinetobacter species by boiling. This antigen fixed complement in the presence of homologous hyperimmune sera from rabbits or guinea pigs and in the presence of heterologous human or hyperimmunized animal sera containing chlamydial antibodies. Hyperimmune antisera to the extracted antigen, or to suspensions of live acinetobacters, also reacted in complement fixation with a group-specific antigen.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Caldwell H. D., Kuo C. C., Kenny G. E. Antigenic analysis of Chlamydiae by two-dimensional immunoelectrophoresis. I. Antigenic heterogeneity between C. trachomatis and C. psittaci. J Immunol. 1975 Oct;115(4):963–968. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caldwell H. D., Kuo C. C., Kenny G. E. Antigenic analysis of Chlamydiae by two-dimensional immunoelectrophoresis. II. A trachoma-LGV-specific antigen. J Immunol. 1975 Oct;115(4):969–975. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dhir S. P., Hakomori S., Kenny G. E., Grayston J. T. Immunochemical studies on chlamydial group antigen (presence of a 2-keto-3-deoxycarbohydrate as immunodominant group). J Immunol. 1972 Jul;109(1):116–122. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dhir S. P., Kenny G. E., Grayston J. T. Characterization of the group antigen of Chlamydia trachomatis. Infect Immun. 1971 Dec;4(6):725–730. doi: 10.1128/iai.4.6.725-730.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glew R. H., Moellering R. C., Jr, Kunz L. J. Infections with Acinetobacter calcoaceticus (Herellea vaginicola): clinical and laboratory studies. Medicine (Baltimore) 1977 Mar;56(2):79–97. doi: 10.1097/00005792-197703000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grayston J. T., Wang S. New knowledge of chlamydiae and the diseases they cause. J Infect Dis. 1975 Jul;132(1):87–105. doi: 10.1093/infdis/132.1.87. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MATTHIESEN M. Studies on the ornithosis-related antigen from Bacterium anitratum; Bacterium anitratum and its ability to produce the ornithosis-related antigen. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1957;41(3):247–256. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1957.tb01022.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MATTHIESEN M., VOLKERT M. An ornithosis related antigen from a coccoid bacterium. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1956;39(2):117–126. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1956.tb03383.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MATTHIESEN M., VOLKERT M. The antigenic relationship between Ornithosis virus and Bacterium anitratum. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1957;41(2):135–143. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1957.tb01009.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ormsbee R. A., Peacock M. G., Lattimer G. L., Page L. A., Fiset P. Legionnaires' disease: antigenic peculiarities, strain differences, and antibiotic sensitivities of the agent. J Infect Dis. 1978 Aug;138(2):260–264. doi: 10.1093/infdis/138.2.260. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHIMIZU Y., BANKOWSKI R. A. THE NATURE OF THE CROSS REACTIONS BETWEEN A BACTERIUM OF THE GENUS HERELLEA AND THE ORNITHOSIS VIRUS IN COMPLEMENT FIXATION. Am J Vet Res. 1963 Nov;24:1283–1290. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sacks D. L., Rota T. R., MacDonald A. B. Separation and partial characterization of a type-specific antigen from Chlamydia trachomatis. J Immunol. 1978 Jul;121(1):204–208. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimizu Y., Bankowski R. A. The characteristics of a bacterium used in complement fixation tests for ornithosis. Avian Dis. 1963 Aug;7(3):331–341. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



