Abstract
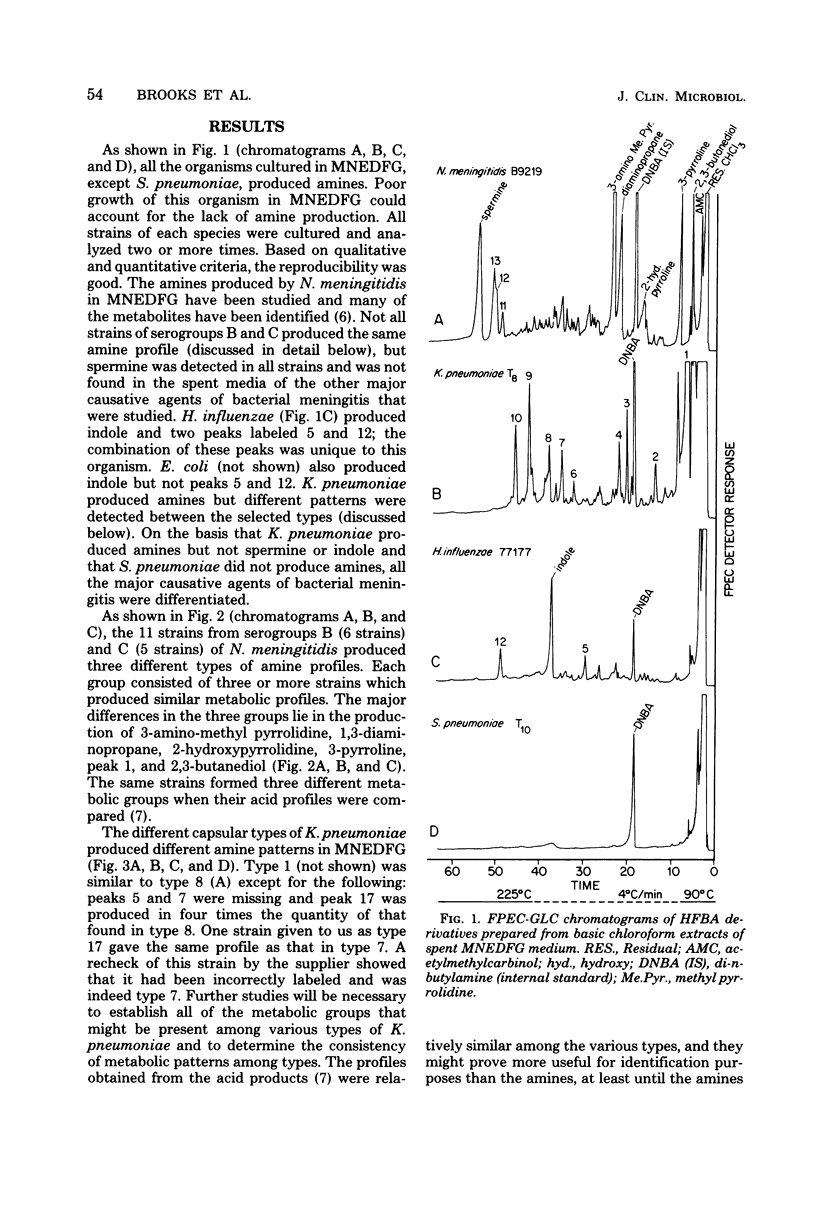
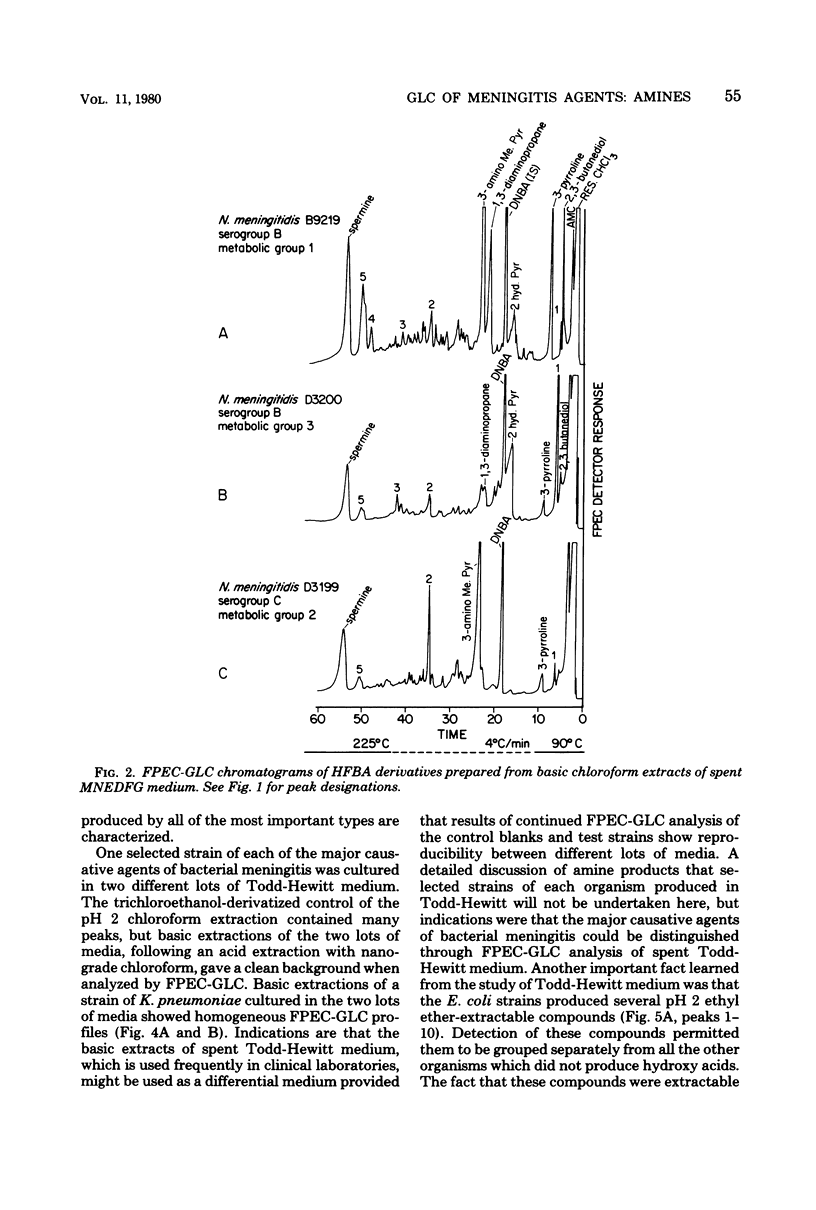
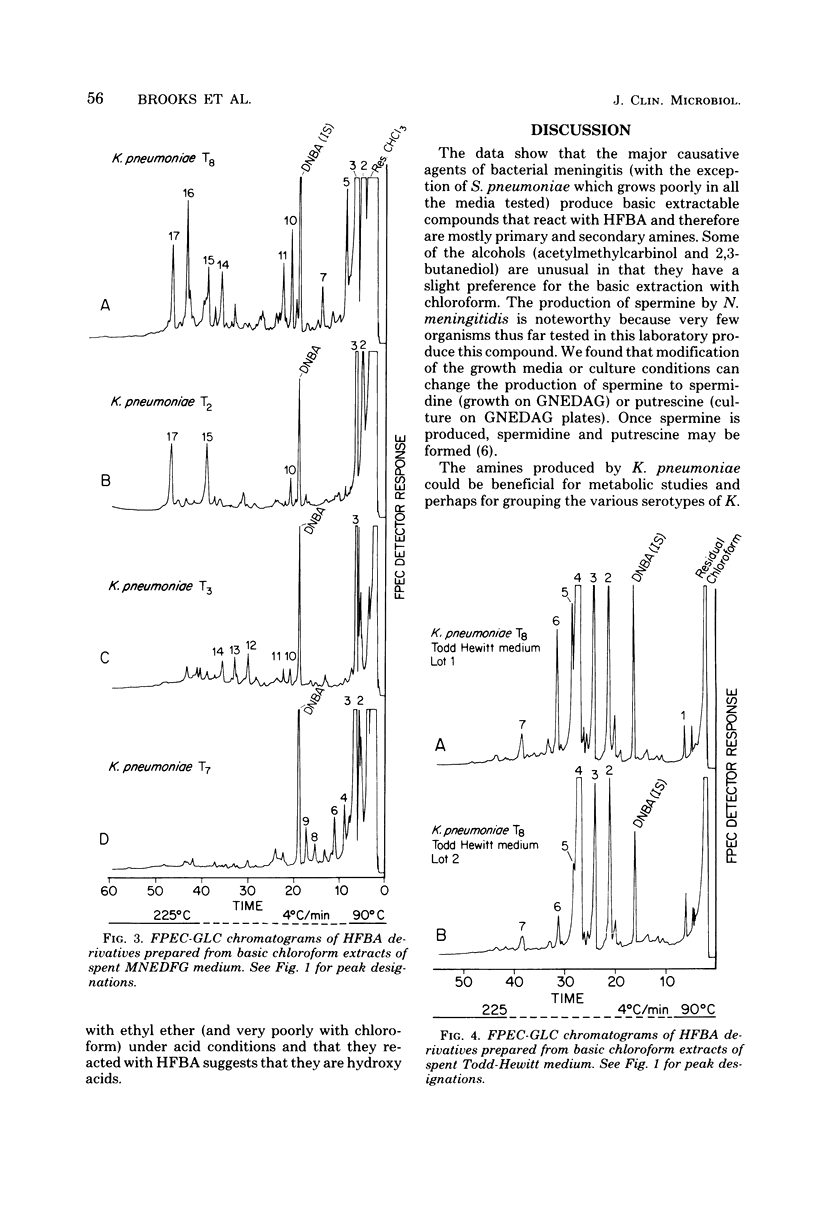
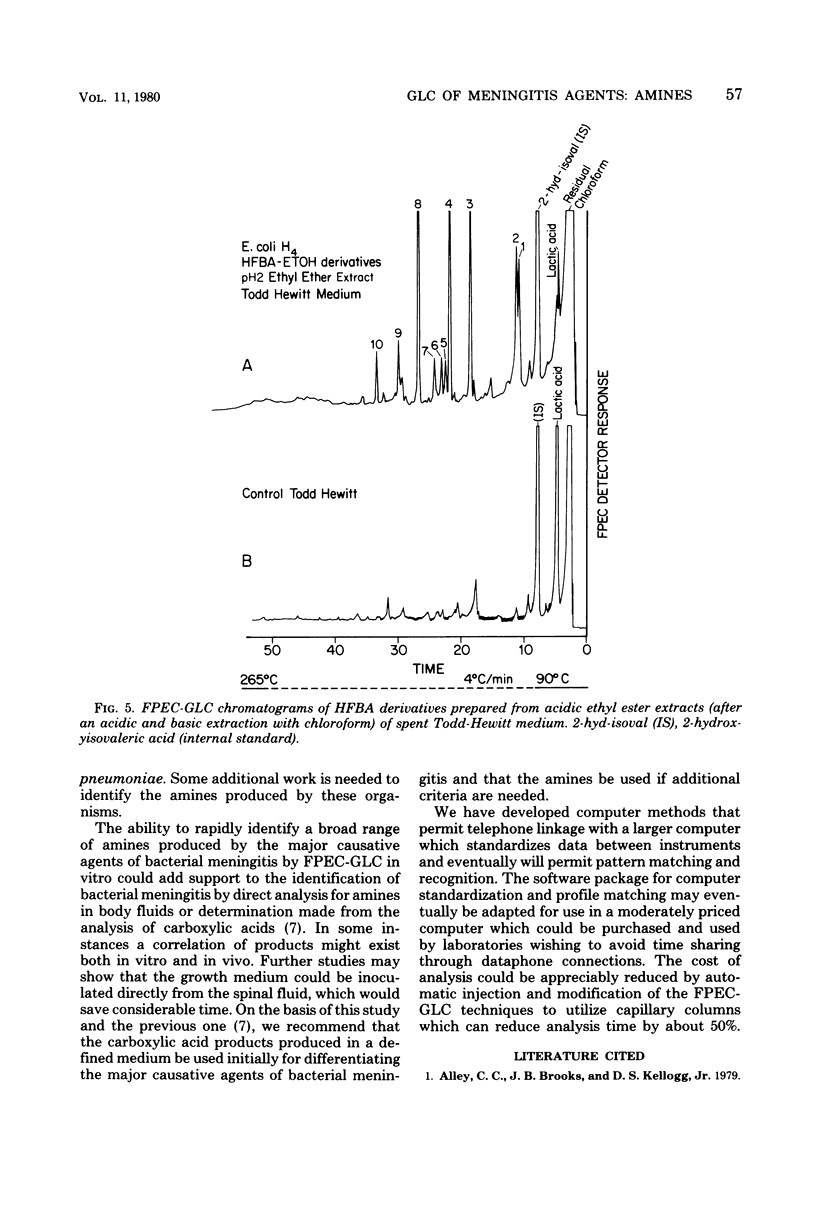
The major causative agents of bacterial meningitis (Haemophilus influenzae serogroup B, Neisseria meningitidis serogroups B and C, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Steptococcus pneumoniae, and two types of Escherichia coli) were cultured in a chemically defined medium, and selected strains were further studied in Todd-Hewitt medium. After acidic extraction of the spent media with chloroform, a basic extraction was made with chloroform to obtain amines. A third extraction was performed on re-acidified Todd-Hewitt medium with ethyl ether to obtain hydroxyacids. The extracts were derivatized with heptafluorobutyric anhydride-ethanol to form electron-capturing derivatives, and the derivatives were analyzed on a frequency-pulsed electron capture gas-liquid chromatograph (FPEC-GLC) equipped with a PEP-2 computer. The data obtained from the study showed that amines were produced by these organisms that formed characteristic patterns. Different serotypes of K. pneumoniae and the two serogroups of N. meningitidis produced different types of FPEC-GLC profiles within serotypes. E. coli produced several hydroxy acids on Todd-Hewitt medium that made it unique among the organisms studied. The methods used are practical and the techniques have potential for use in clinical laboratories and hospitals as a valuable aid for the rapid identification of the major causative agents of bacterial meningitis.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brooks J. B., Craven R. B., Schlossberg D., Alley C. C., Pitts F. M. Possible use of frequency-pulse-modulated electron capture gas-liquid chromatography to identify septic and aseptic causes of pleural effusions. J Clin Microbiol. 1978 Aug;8(2):203–208. doi: 10.1128/jcm.8.2.203-208.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brooks J. B. Detection of bacterial metabolites in spent culture media and body fluids by electron capture gas-liquid chromatography. Adv Chromatogr. 1977;15:1–31. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brooks J. B., Kellogg D. S., Alley C. C., Short H. B., Handsfield H. H., Huff B. Gas chromatography as a potential means of diagnosing arthritis. I. Differentiation between staphylococcal, streptococcal, gonococcal, and traumatic arthritis. J Infect Dis. 1974 Jun;129(6):660–668. doi: 10.1093/infdis/129.6.660. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brooks J. B., Kellogg D. S., Jr, Choudhary G., Alley C. C., Liddle J. A. Identification of some basic extractable compounds produced by Neisseria gonorrhoeae and Neisseria meningitidis in a defined medium. J Clin Microbiol. 1978 May;7(5):415–418. doi: 10.1128/jcm.7.5.415-418.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brooks J. B., Kellogg D. S., Jr, Shepherd M. E., Alley C. C. Rapid differentiation of the major causative agents of bacterial meningitis by use of frequency-pulsed electron capture gas-liquid chromatograph: analysis of acids. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Jan;11(1):45–51. doi: 10.1128/jcm.11.1.45-51.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brooks J. B., Melton A. R. Electron capture gas-liquid chromatographic study of metabolites produced by some arthritic transudate-associated organisms in vitro and in vivo in rabbit models. J Clin Microbiol. 1978 Oct;8(4):402–409. doi: 10.1128/jcm.8.4.402-409.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catlin B. W. Nutritional profiles of Neisseria gonorrhoeae, Neisseria meningitidis, and Neisseria lactamica in chemically defined media and the use of growth requirements for gonococcal typing. J Infect Dis. 1973 Aug;128(2):178–194. doi: 10.1093/infdis/128.2.178. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craven R. B., Brooks J. B., Edman D. C., Converse J. D., Greenlee J., Schlossberg D., Furlow T., Gwaltney J. M., Jr, Miner W. F. Rapid diagnosis of lymphocytic meningitis by frequency-pulsed electron capture gas-liquid chromatography: differentiation of tuberculous, cryptococcal, and viral meningitis. J Clin Microbiol. 1977 Jul;6(1):27–32. doi: 10.1128/jcm.6.1.27-32.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jorgensen J. H., Lee J. C. Rapid diagnosis of gram-negative bacterial meningitis by the Limulus endotoxin assay. J Clin Microbiol. 1978 Jan;7(1):12–17. doi: 10.1128/jcm.7.1.12-17.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morse C. D., Brooks J. B., Kellogg D. S., Jr Identification of Neisseria by electron capture gas-liquid chromatography of metabolites in a chemically defined growth medium. J Clin Microbiol. 1977 Nov;6(5):474–481. doi: 10.1128/jcm.6.5.474-481.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


