Abstract
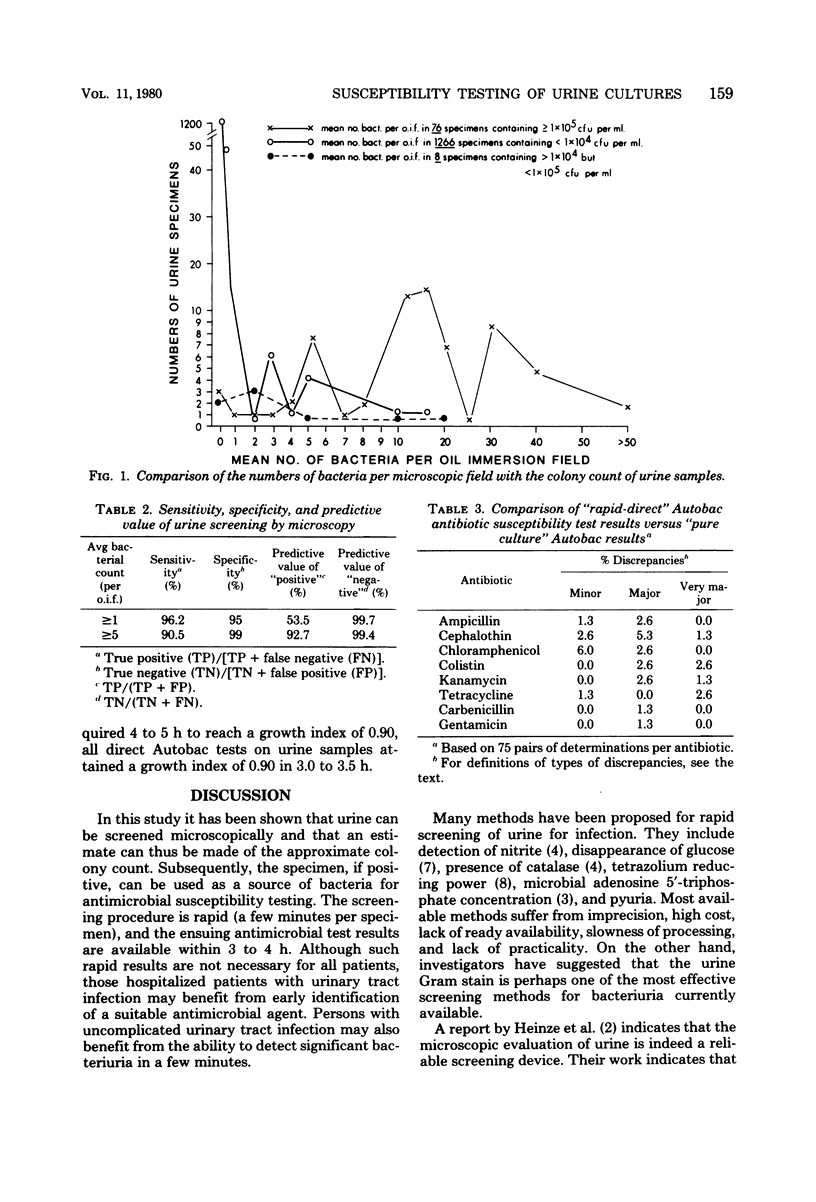
Two screening methods for urine microbiology are proposed: one in which the Gram-stained smear is used to detect significant bacteriuria, and another in which Autobac antibiotic susceptibility tests are performed directly on positive urine samples. Results on 1,350 specimens indicated that an average of 18 bacteria per oil immersion field were observed in the urine of patients with significant bacteriuria, and an average of less than 1 bacterium per oil immersion field was found in the urine of patients without significant bacteriuria. Direct susceptibility testing by Autobac proved to be rapid (3 h versus 24 h) and reliable (0.5 to 1.2% discrepancies).
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Heinze P. A., Thrupp L. D., Anselmo C. R. A rapid (4--6-hour) urine-culture system for direct identification and direct antimicrobial susceptibility testing. Am J Clin Pathol. 1979 Feb;71(2):177–183. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/71.2.177. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKusick V. A., Weilbaecher R. G., Gragg G. W. Recessive inheritance of a congenital malformation syndrome: unilateral absence deformity of leg and congenital cataracts. JAMA. 1968 Apr 8;204(2):113–118. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SIMMONS N. A., WILLIAMS J. D. A simple test for significant bacteriuria. Lancet. 1962 Jun 30;1(7244):1377–1378. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(62)92488-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thornsberry C., Gavan T. L., Sherris J. C., Balows A., Matsen J. M., Sabath L. D., Schoenknecht F., Thrupp L. D., Washington J. A., 2nd Laboratory evaluation of a rapid, automatic susceptibility testing system: report of a collaborative study. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1975 Apr;7(4):466–480. doi: 10.1128/aac.7.4.466. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



