Abstract
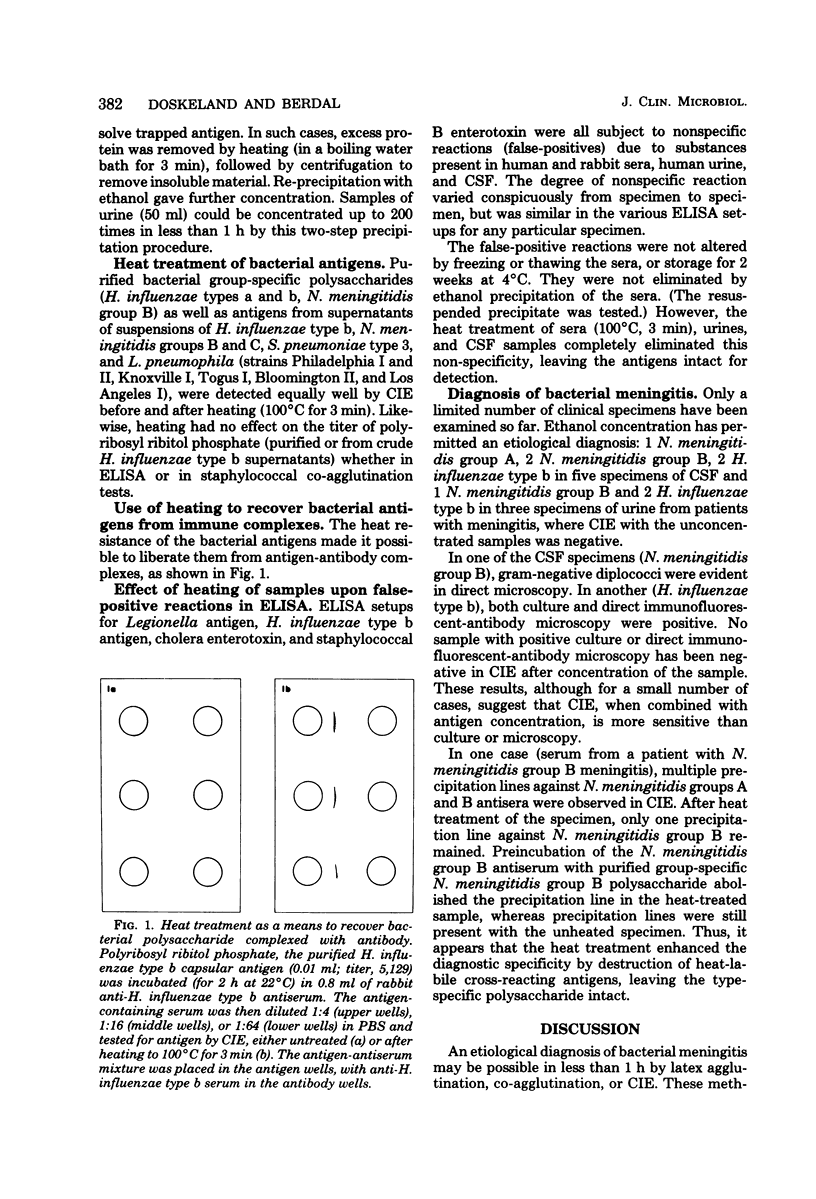
We sought procedures which would allow a rapid concentration in high yield of bacterial antigens from tissue fluids of patients and which could be applied also to protein-rich fluids like serum. Ethanol precipitation at a subzero temperature with albumin added as an antigen coprecipitant made it possible to achieve a more than 20-fold concentration of antigen in 15 min and a 200-fold concentration in 45 min. Heat-stable antigens could be concentrated from protein-rich fluids (like serum) after the sample had been deproteinized by boiling. Such heating (100 degrees C, 3 min) also liberated bacterial polysaccharides from antibody complexes and elminated the nonspecific interference of serum in enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berdal B. P., Farshy C. E., Feeley J. C. Detection of Legionella pneumonophila antigen in urine by enzyme-linked immunospecific assay. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 May;9(5):575–578. doi: 10.1128/jcm.9.5.575-578.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beuvery E. C., van Rossum F., Lauwers S., Coignau H. Comparison of counterimmunoelectrophoresis and ELISA for diagnosis of bacterial meningitis. Lancet. 1979 Jan 27;1(8109):208–208. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(79)90599-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CULLIFORD B. J. PRECIPITIN REACTIONS IN FORENSIC PROBLEMS. A NEW METHOD FOR PRECIPITIN REACTIONS ON FORENSIC BLOOD, SEMEN AND SALIVA STAINS. Nature. 1964 Mar 14;201:1092–1093. doi: 10.1038/2011092a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coonrod J. D., Leach R. P. Immunoelectrophoresis for detection of polysaccharides in immune complexes. J Clin Microbiol. 1978 Aug;8(2):257–259. doi: 10.1128/jcm.8.2.257-259.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coonrod J. D., Rytel M. W. Detection of type-specific pneumococcal antigens by counterimmunoelectrophoresis. I. Methodology and immunologic properties of pneumococcal antigens. J Lab Clin Med. 1973 May;81(5):770–777. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coonrod J. D., Rytel M. W. Determination of aetiology of bacterial meningitis by counter-immunoelectrophoresis. Lancet. 1972 May 27;1(7761):1154–1157. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(72)91376-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feigin R. D., Wong M., Shackelford P. G., Stechenberg B. W., Dunkle L. M., Kaplan S. Countercurrent immunoelectrophoresis of urine as well as of CSF and blood for diagnosis of bacterial meningitis. J Pediatr. 1976 Nov;89(5):773–775. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(76)80802-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Førre O., Gaustad P. An evaluation of two immunological methods in the diagnosis of bacterial meningitis: the effect of ultrasonic treatment of the cerebrospinal fluid. Scand J Infect Dis. 1977;9(4):285–288. doi: 10.3109/inf.1977.9.issue-4.05. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaldor J., Asznowicz R., Buist D. G. Latex agglutination in diagnosis of bacterial infections, with special reference to patients with meningitis and septicemia. Am J Clin Pathol. 1977 Aug;68(2):284–289. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/68.2.284. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kronvall G. A rapid slide-agglutination method for typing pneumococci by means of specific antibody adsorbed to protein A-containing staphylococci. J Med Microbiol. 1973 May;6(2):187–190. doi: 10.1099/00222615-6-2-187. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myhre E. B. Rapid diagnosis of bacterial meningitis. Demonstration of bacterial antigen by counterimmunoelectrophoresis. Scand J Infect Dis. 1974;6(3):237–239. doi: 10.3109/inf.1974.6.issue-3.05. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newman R. B., Stevens R. W., Gaafar H. A. Latex agglutination test for the diagnosis of Haemophilus influenzae meningitis. J Lab Clin Med. 1970 Jul;76(1):107–113. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Reilly R. J., Anderson P., Ingram D. L., Peter G., Smith D. H. Circulating polyribophosphate in Hemophilus influenzae, type b meningitis. Correlation with clinical course and antibody response. J Clin Invest. 1975 Oct;56(4):1012–1022. doi: 10.1172/JCI108148. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OMLAND T. SEROLOGICAL STUDIES ON HAEMOPHILUS INFLUENZAE AND RELATED SPECIES. 3. ADAPTATION OF THE GEL PRECIPITATION METHOD TO THE STUDY OF TYPE SPECIFIC ANTIGENS. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1963;59:341–356. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olcén P., Danielsson D., Kjellander J. The use of protein A-containing staphylococci sensitized with anti-meningococcal antibodies for grouping Neisseria meningitidis and demonstration of meningococcal antigen in cerebrospinal fluid. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B. 1975 Aug;83(4):387–396. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1975.tb00117.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oxenhandler R. W., Adelstein E. H., Rogers W. A. Rheumatoid factor: a cause of fals positive histoplasmin latex agglutination. J Clin Microbiol. 1977 Jan;5(1):31–33. doi: 10.1128/jcm.5.1.31-33.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pifer L., Elliott S., Woodard T., Woods D., Hughes W. T. An improved method for detection of Hemophilus influenzae b antigen in cerebrospinal fluid. J Pediatr. 1978 Feb;92(2):227–229. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(78)80009-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whittle H. C., Tugwell P., Egler L. J., Greenwood B. M. Rapid bacteriological diagnosis of pyogenic meningitis by latex agglutination. Lancet. 1974 Sep 14;2(7881):619–621. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(74)91943-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong K. H., Schalla W. O., Arko R. J., Bullard J. C., Feeley J. C. Immunochemical, serologic, and immunologic properties of major antigens isolated from the Legionnaires' disease bacterium. Observations bearing on the feasibility of a vaccine. Ann Intern Med. 1979 Apr;90(4):634–638. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-90-4-634. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


