Abstract
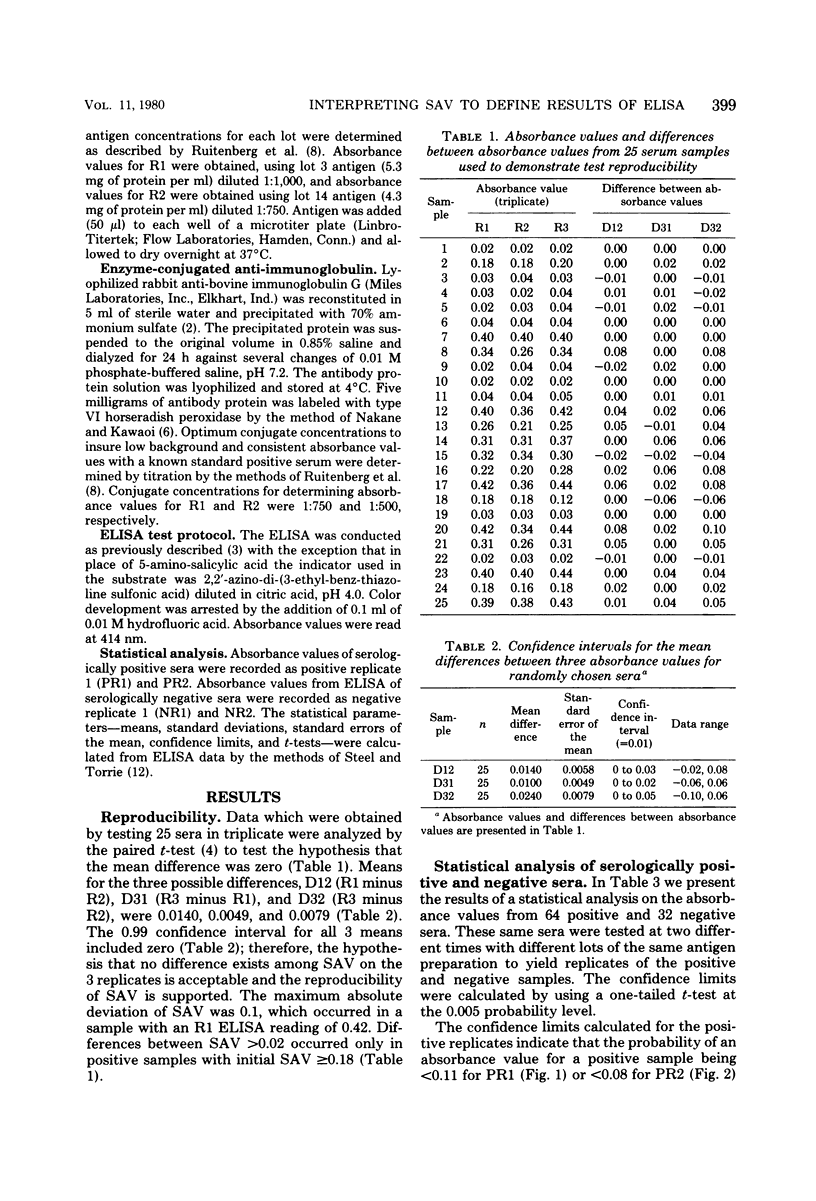
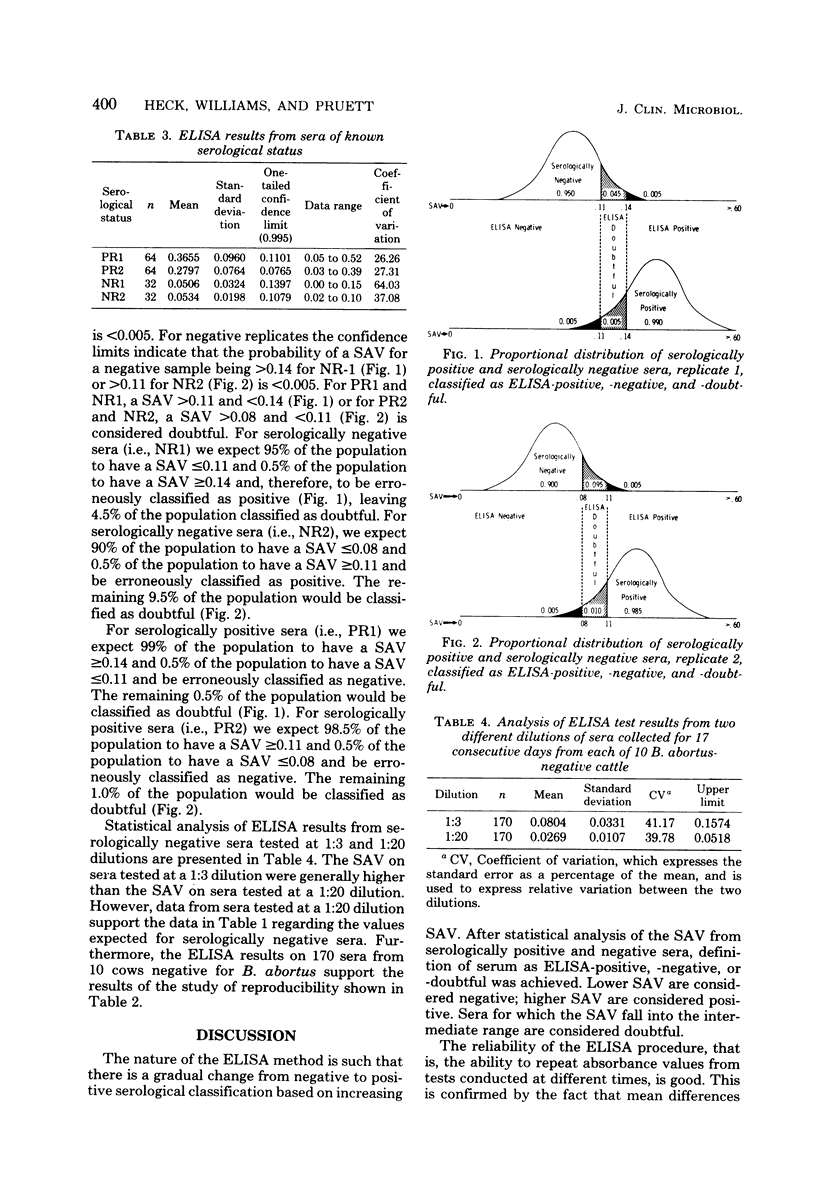
An enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay method was used to classify bovine serum as positive, negative, or doubtful for antibodies to Brucella abortus. Spectrophotometric data from assays of 64 serologically positive and 32 serologically negative bovine sera were analyzed statistically to define the range of spectrophotometric absorbance values which classify sera. Statistical analysis indicated that absorbance values less than 0.08 should be considered negative and values greater than 0.14 should be considered positive, with intermediate values declared doubtful, and that the probability of erroneously classifying a positive serum as negative or a negative serum as positive is less than 0.005.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beh K. J. Quantitative distribution of Brucella antibody amongst immunoglobulin classes in vaccinated and infected cattle. Res Vet Sci. 1974 Jul;17(1):1–4. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byrd J. W., Heck F. C., Hidalgo R. J. Evaluation of the enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for detecting Brucella abortus antibodies. Am J Vet Res. 1979 Jun;40(6):896–898. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Locarnini S. A., Coulepis A. G., Stratton A. M., Kaldor J., Gust I. D. Solid-phase enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for detection of hepatitis A-specific immunoglobulin M. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Apr;9(4):459–465. doi: 10.1128/jcm.9.4.459-465.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakane P. K., Kawaoi A. Peroxidase-labeled antibody. A new method of conjugation. J Histochem Cytochem. 1974 Dec;22(12):1084–1091. doi: 10.1177/22.12.1084. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruitenberg E. J., Brosi B. J., Steerenberg P. A. Direct measurement of microplates and its application to enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. J Clin Microbiol. 1976 May;3(5):541–542. doi: 10.1128/jcm.3.5.541-542.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saunders G. C., Clinard E. H. Rapid micromethod of screening for antibodies to disease agents using the indirect enzyme-labeled antibody test. J Clin Microbiol. 1976 Jun;3(6):604–608. doi: 10.1128/jcm.3.6.604-608.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saunders G. C. Development and evaluation of an enzyme-labeled antibody test for the rapid detection of hog cholera antibodies. Am J Vet Res. 1977 Jan;38(1):21–25. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saunders G. C., Wilder M. E. Disease screening with enzyme-labeled antibodies. J Infect Dis. 1974 Mar;129(3):362–364. doi: 10.1093/infdis/129.3.362. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thoen C. O., Armbrust A. L., Eacret W. G., Harrington R., Jr, Brown G. M. Use of an enzyme immunoassay test for characterizing the A and M antigens of Brucella. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Apr;9(4):485–487. doi: 10.1128/jcm.9.4.485-487.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voller A., Bidwell D. E. Enzyme-immunoassays for antibodies in measles, cytomegalovirus infections and after rubella vaccination. Br J Exp Pathol. 1976 Apr;57(2):243–247. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


