Abstract
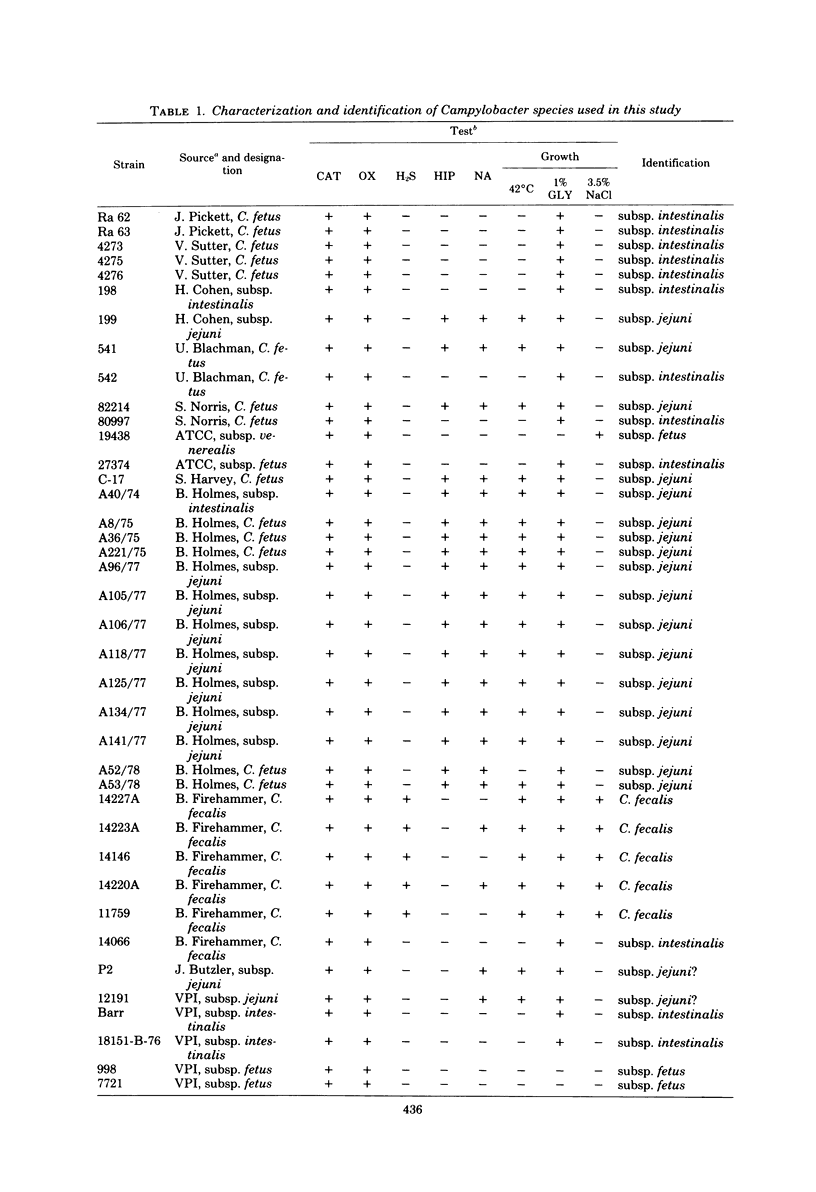
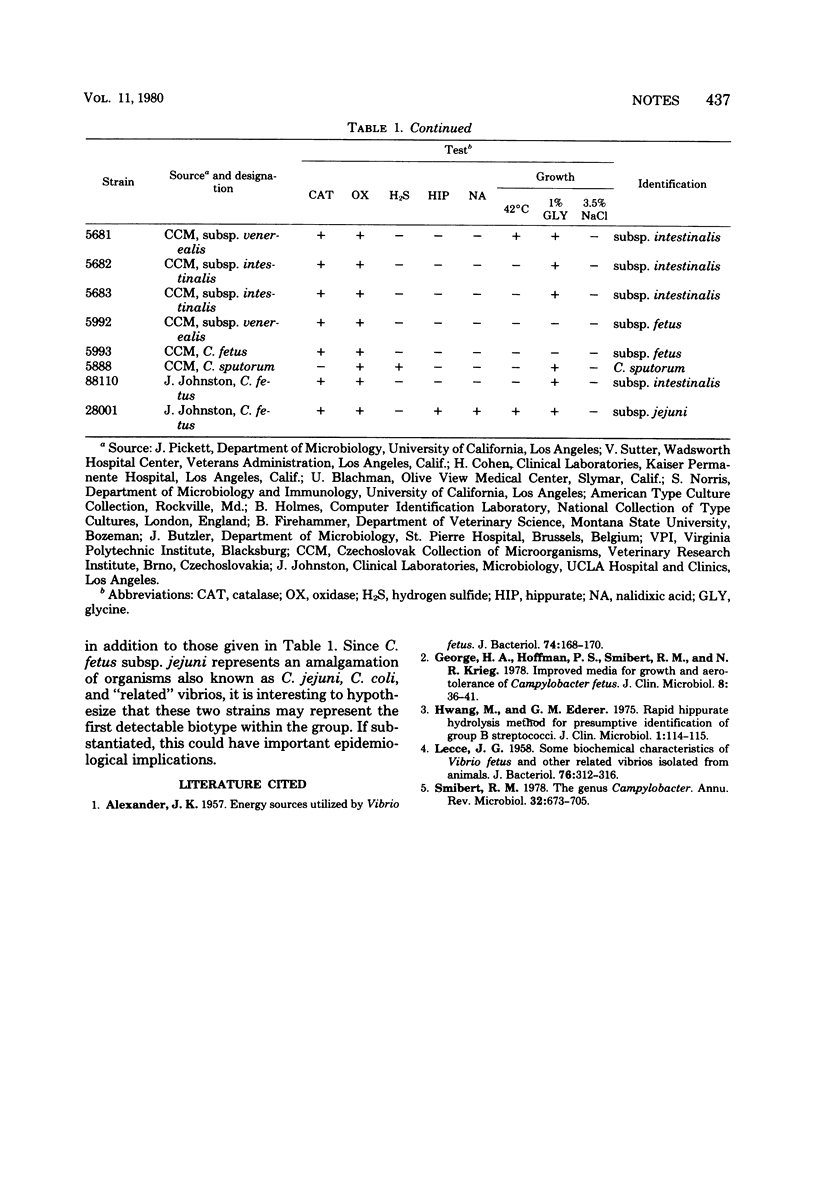
An additional method for differentiating between Campylobacter fetus subsp. jejuni and C. fetus subsp. intestinalis is reported. Strains of C. fetus subsp. jejuni (18/20) were shown to hydrolyze hippurate in the 2-h rapid test, whereas strains of C. fetus subsp. intestinalis did not.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ALEXANDER J. K. Energy sources utilized by Vibrio fetus. J Bacteriol. 1957 Aug;74(2):168–170. doi: 10.1128/jb.74.2.168-170.1957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- George H. A., Hoffman P. S., Smibert R. M., Krieg N. R. Improved media for growth and aerotolerance of Campylobacter fetus. J Clin Microbiol. 1978 Jul;8(1):36–41. doi: 10.1128/jcm.8.1.36-41.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hwang M. N., Ederer G. M. Rapid hippurate hydrolysis method for presumptive identification of group B streptococci. J Clin Microbiol. 1975 Jan;1(1):114–115. doi: 10.1128/jcm.1.1.114-115.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LECCE J. G. Some biochemical characteristics of Vibrio fetus and other related Vibrios isolated from animals. J Bacteriol. 1958 Sep;76(3):312–316. doi: 10.1128/jb.76.3.312-316.1958. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smibert R. M. The genus Campylobacter. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1978;32:673–709. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.32.100178.003325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


