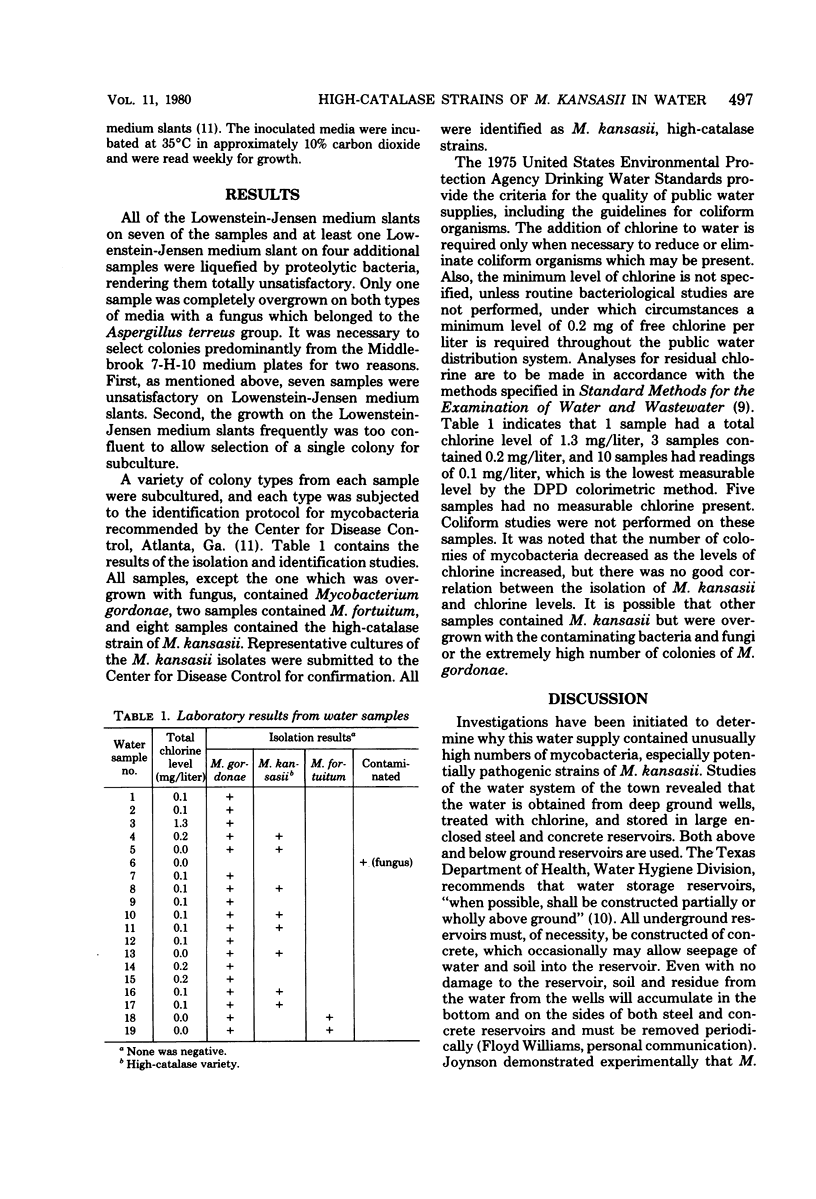
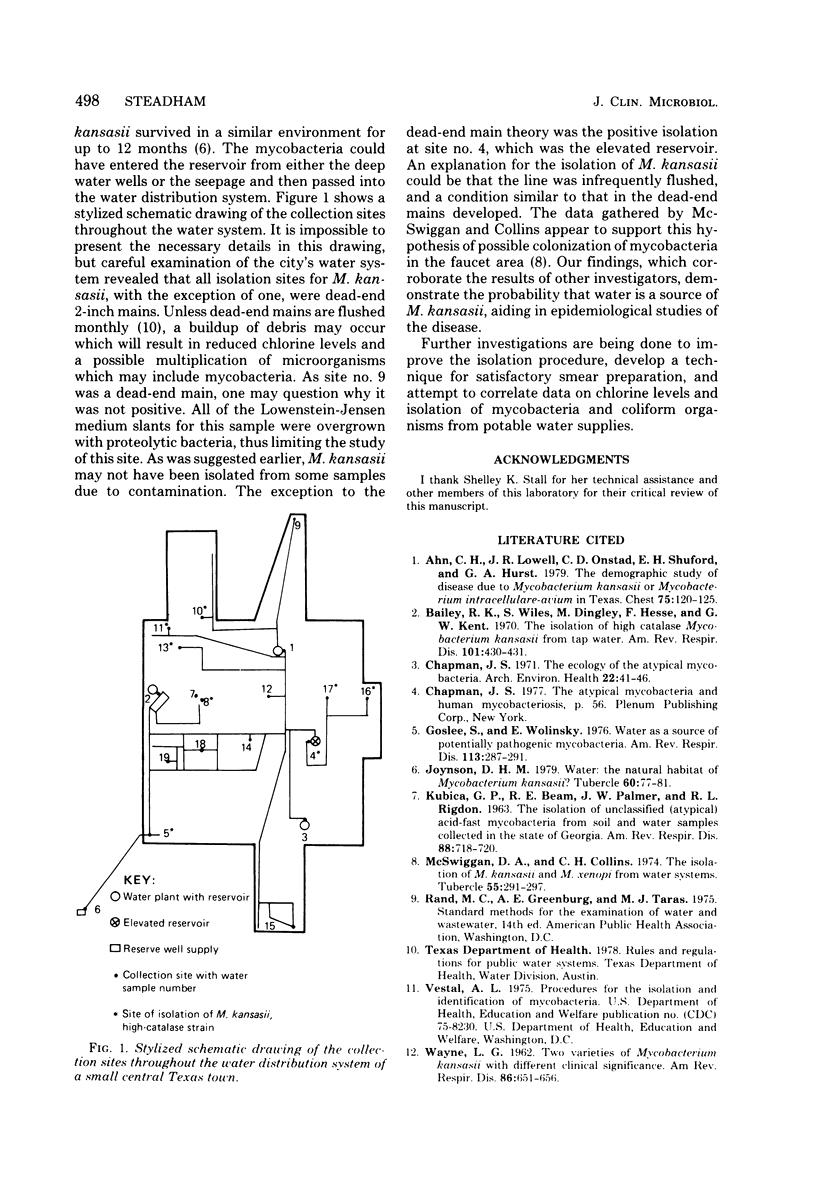
Abstract
Isolation techniques with membrane-filtered potable water samples resulted in the isolation of potentially pathogenic high-catalase strains of Mycobacterium kansasii from 8 of 19 representative outlets in a small central Texas town. Mycobacterium gordonae was isolated from all samples, and Mycobacterium fortuitum was isolated from two samples. Data on chlorine levels are presented along with a possible explanation for the unusually high numbers of mycobacteria in these potable water samples. Findings suggest that water is a source of M. kansasii and may be an important link in the epidemiological picture of the disease.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahn C. H., Lowell J. R., Onstad G. D., Shuford E. H., Hurst G. A. A demographic study of disease due to Mycobacterium kansasii or M intracellulare-avium in Texas. Chest. 1979 Feb;75(2):120–125. doi: 10.1378/chest.75.2.120. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bailey R. K., Wyles S., Dingley M., Hesse F., Kent G. W. The isolation of high catalase Mycobacterium kansasii from tap water. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1970 Mar;101(3):430–431. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1970.101.3.430. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chapman J. S. The ecology of the atypicalmycobacteria. Arch Environ Health. 1971 Jan;22(1):41–46. doi: 10.1080/00039896.1971.10665813. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goslee S., Wolinsky E. Water as a source of potentially pathogenic mycobacteria. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1976 Mar;113(3):287–292. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1976.113.3.287. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joynson D. H. Water: the natural habitat of Mycobacterium kansasii? Tubercle. 1979 Jun;60(2):77–81. doi: 10.1016/0041-3879(79)90039-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KUBICA G. P., BEAM R. E., PALMER J. W. A METHOD FOR THE ISOLATION OF UNCLASSIFIED ACID-FAST BACILLI FROM SOIL AND WATER. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1963 Nov;88:718–720. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1963.88.5.718. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McSwiggan D. A., Collins C. H. The isolation of M. kansasii and M. xenopi from water systems. Tubercle. 1974 Dec;55(4):291–297. doi: 10.1016/0041-3879(74)90038-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WAYNE L. G. Two varieties of Mycobacterium kansasii with different clinical significance. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1962 Nov;86:651–656. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1962.86.5.651. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


