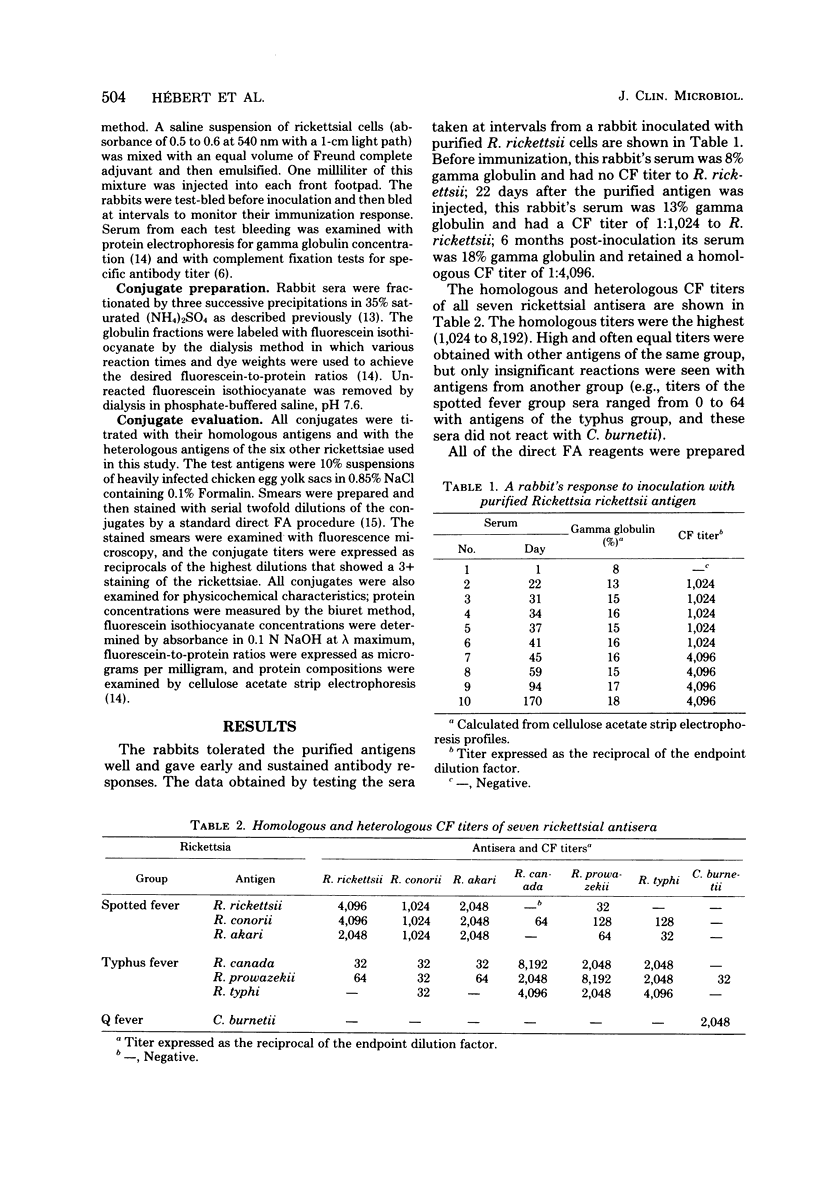
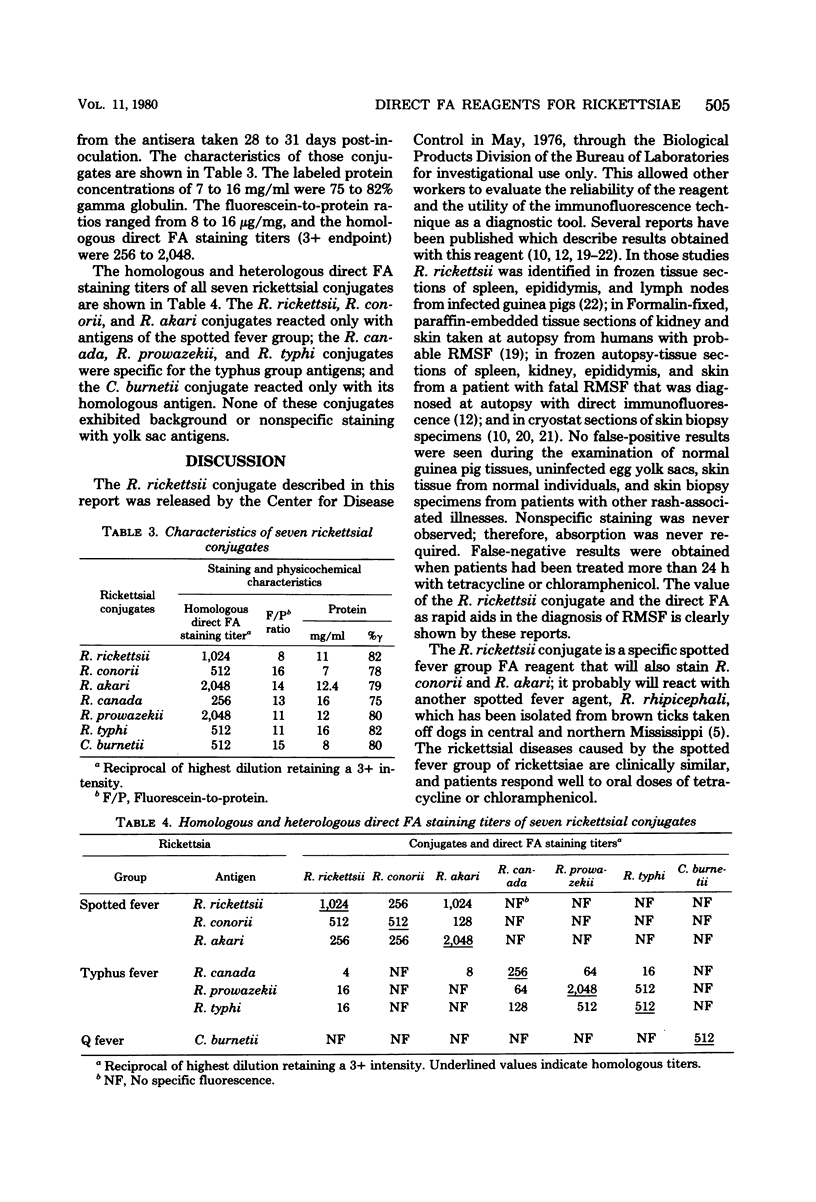
Abstract
Rabbits were inoculated with purified antigen preparations of Coxiella burnetii and representative species of the spotted fever and typhus groups of rickettsiae. Their antibody responses were monitored by complement fixation tests; high-titered antisera were fractionated with ammonium sulfate and then labeled with fluorescein isothiocyanate by the dialysis method. The conjugates had homologous 3+ staining titers of 1:256 to 1:2,048 and did not exhibit nonspecific staining. The Rickettsia rickettsii, R. conorii, and R. akari conjugates reacted only with rickettsiae of the spotted fever group; the R. canada, R. prowazekii, and R. typhi conjugates were specific for the typhus group rickettsiae; and the C. burnetii conjugate stained only homologous organisms. One of these conjugates (R. rickettsii) is currently being used to identify rickettsiae in clinical specimens and has already proven its value as a diagnostic tool.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BURGDORFER W., LACKMAN D. Identification of Rickettsia rickettsii in the wood tick, Dermacentor andersoni, by means of fluorescent antibody. J Infect Dis. 1960 Sep-Oct;107:241–244. doi: 10.1093/infdis/107.2.241. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bozeman F. M., Elisberg B. L., Humphries J. W., Runcik K., Palmer D. B., Jr Serologic evidence of Rickettsia canada infection of man. J Infect Dis. 1970 Apr;121(4):367–371. doi: 10.1093/infdis/121.4.367. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bozeman F. M., Masiello S. A., Williams M. S., Elisberg B. L. Epidemic typhus rickettsiae isolated from flying squirrels. Nature. 1975 Jun 12;255(5509):545–547. doi: 10.1038/255545a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgdorfer W. Hemolymph test. A technique for detection of rickettsiae in ticks. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1970 Nov;19(6):1010–1014. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgdorfer W., Sexton D. J., Gerloff R. K., Anacker R. L., Philip R. N., Thomas L. A. Rhipicephalus sanguineus: vector of a new spotted fever group rickettsia in the United States. Infect Immun. 1975 Jul;12(1):205–210. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.1.205-210.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COONS A. H., SNYDER J. C. Localization of antigen in tissue cells; antigens of rickettsiae and mumps virus. J Exp Med. 1950 Jan 1;91(1):31-8, pl. doi: 10.1084/jem.91.1.31. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fiset P., Wisseman C. L., Batawi Y. E. Immunologic evidence of human fetal infection with Coxiella burneti. Am J Epidemiol. 1975 Jan;101(1):65–69. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a112072. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleisher G., Lennette E. T., Honig P. Diagnosis of Rocky Mountain spotted fever by immunofluorescent identification of Rickettsia rickettsii in skin biopsy tissue. J Pediatr. 1979 Jul;95(1):63–65. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(79)80083-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GIMENEZ D. F. STAINING RICKETTSIAE IN YOLK-SAC CULTURES. Stain Technol. 1964 May;39:135–140. doi: 10.3109/10520296409061219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green W. R., Walker D. H., Cain B. G. Fatal viscerotropic Rocky Mountain spotted fever. Report of a case diagnosed by immunofluorescence. Am J Med. 1978 Mar;64(3):523–528. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(78)90247-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hebert G. A., Pelham P. L., Pittman B. Determination of the optimal ammonium sulfate concentration for the fractionation of rabbit, sheep, horse, and goat antisera. Appl Microbiol. 1973 Jan;25(1):26–36. doi: 10.1128/am.25.1.26-36.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Millis N. S., Kuhnley L. C. Evidence for the existence of Q fever in Northwest Texas. Am J Public Health. 1978 Jun;68(6):590–592. doi: 10.2105/ajph.68.6.590. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker D. H., Cain B. G. A method for specific diagnosis of Rocky Mountain spotted fever on fixed, paraffin-embedded tissue by immunofluorescence. J Infect Dis. 1978 Feb;137(2):206–209. doi: 10.1093/infdis/137.2.206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker D. H., Cain B. G., Olmstead P. M. Laboratory diagnosis of Rocky Mountain spotted fever by immunofluorescent demonstration of Rickettsia in Cutaneous lesions. Am J Clin Pathol. 1978 Jun;69(6):619–623. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/69.6.619. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker D. H., Harrison A., Henderson F., Murphy F. A. Identification of Rickettsia rickettsii in a guinea pig model by immunofluorescent and electron microscopic techniques. Am J Pathol. 1977 Feb;86(2):343–358. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson H. G., Neilson G. H., Galea E. G., Stafford G., O'Brien M. F. Q fever endocarditis in Queensland. Circulation. 1976 Apr;53(4):680–684. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.53.4.680. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodward T. E., Pedersen C. E., Jr, Oster C. N., Bagley L. R., Romberger J., Snyder M. J. Prompt confirmation of Rocky Mountain spotted fever: identification of rickettsiae in skin tissues. J Infect Dis. 1976 Sep;134(3):297–301. doi: 10.1093/infdis/134.3.297. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



