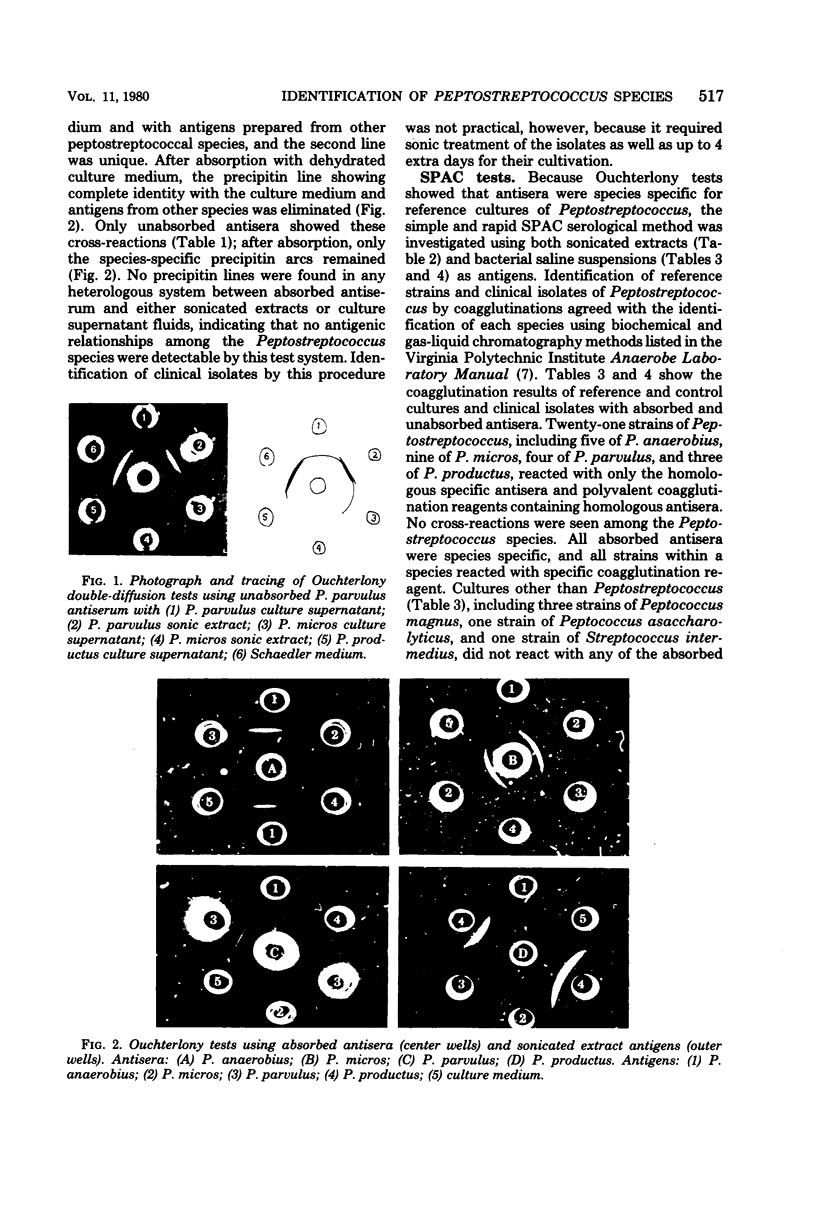
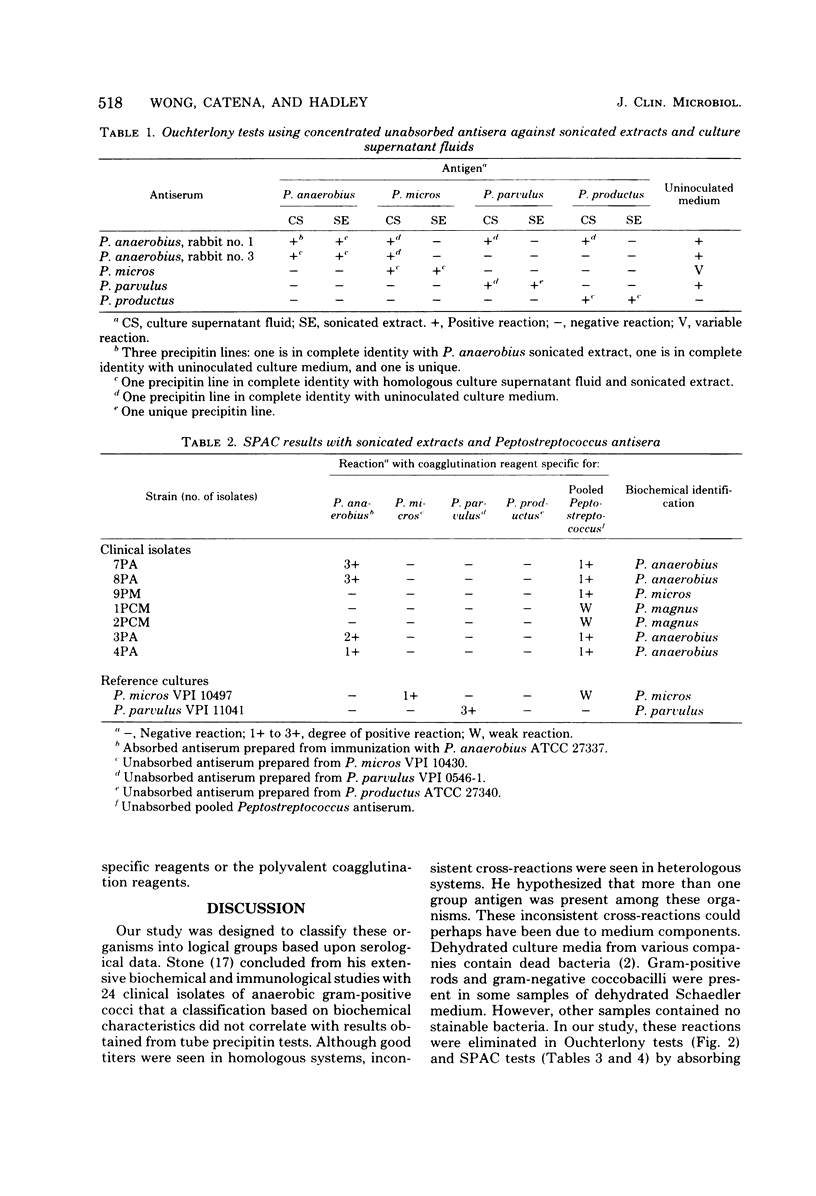
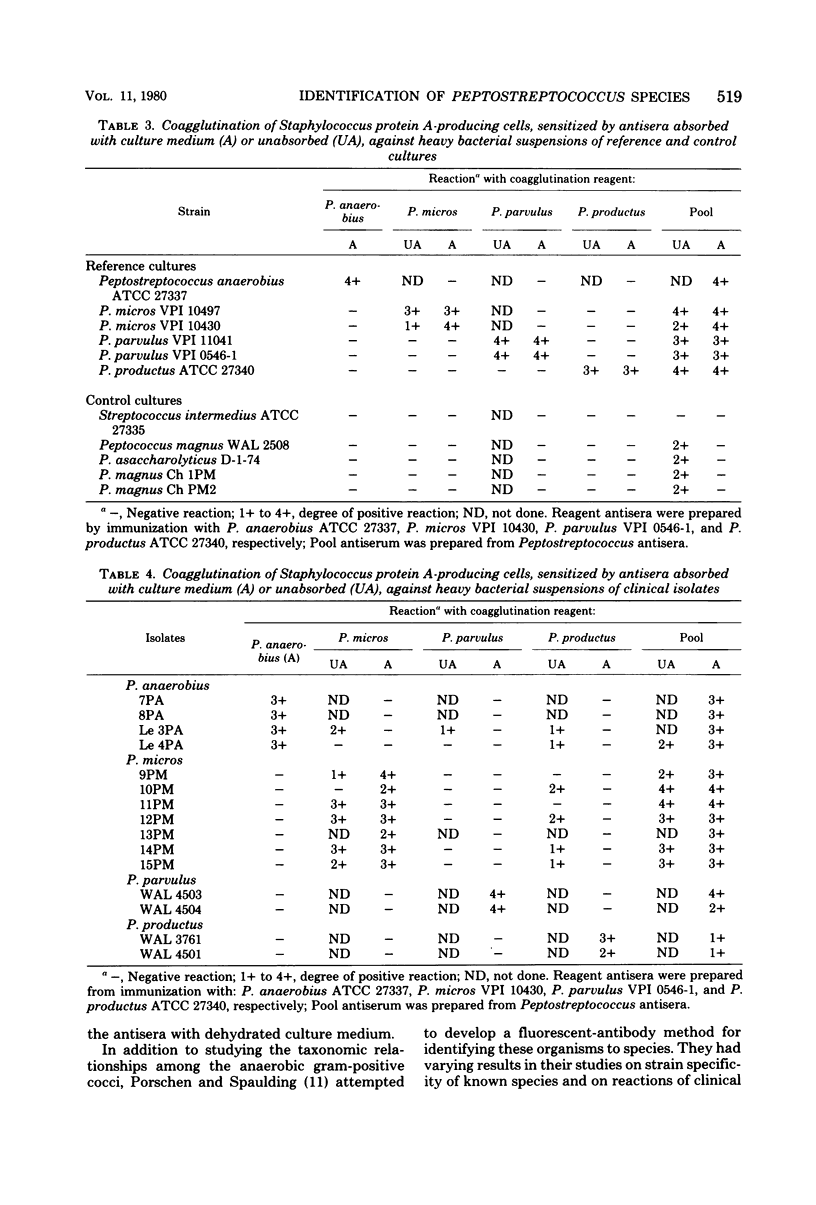
Abstract
Antisera against whole cells of each Peptostreptococcus species (P. anaerobius, P. micros, P. parvulus, and P. productus) were produced in rabbits. When these antisera were reacted against sonically disrupted cells and culture supernatant fluids in Ouchterlony tests, lines of identity were obtained among the antigens from all the species and uninoculated culture medium. When the antisera were subsequently absorbed with the dehydrated culture medium used to grow the peptostreptococci, all cross-reactions in heterologous antigen-antibody combinations were eliminated, leaving only species-specific precipitin arcs. These absorbed antisera, specific for each Peptostreptococcus species by Ouchterlony tests, were used for rapid identification studies. Staphylococcus aureus-bearing protein A was sensitized with each absorbed antiserum. These reagents produced specific coagglutination reactions with suspensions of each Peptostreptococcus reference strain and with 16 clinical isolates. No cross-reactions occurred with the Streptococcus intermedius, Peptococcus magnus, or Peptococcus asaccharolyticus strains tested.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bahn A. N., Kung P. C., Hayashi J. A. Chemical composition and serological analysis of the cell wall of Peptostreptococcus. J Bacteriol. 1966 May;91(5):1672–1676. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.5.1672-1676.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CUMMINS C. S., HARRIS H. The chemical composition of the cell wall in some gram-positive bacteria and its possible value as a taxonomic character. J Gen Microbiol. 1956 Jul;14(3):583–600. doi: 10.1099/00221287-14-3-583. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham M. B., Falkler W. A., Jr Extractable antigen shared by Peptostreptococcus anaerobius strains. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Apr;9(4):507–510. doi: 10.1128/jcm.9.4.507-510.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham M. B., Falkler W. A., Jr Serological reactions of the genus Peptostreptococcus. J Clin Microbiol. 1978 Apr;7(4):385–388. doi: 10.1128/jcm.7.4.385-388.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kronvall G. A rapid slide-agglutination method for typing pneumococci by means of specific antibody adsorbed to protein A-containing staphylococci. J Med Microbiol. 1973 May;6(2):187–190. doi: 10.1099/00222615-6-2-187. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambert M. A., Armfield A. Y. Differentiation of Peptococcus and Peptostreptococcus by gas-liquid chromatography of cellular fatty acids and metabolic products. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Oct;10(4):464–476. doi: 10.1128/jcm.10.4.464-476.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pien F. D., Thompson R. L., Martin W. J. Clinical and bacteriologic studies of anaerobic gram-positive cocci. Mayo Clin Proc. 1972 Apr;47(4):251–257. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porschen R. K., Spaulding E. H. Fluorescent antibody study of the gram-positive anaerobic cocci. Appl Microbiol. 1974 Nov;28(5):851–855. doi: 10.1128/am.28.5.851-855.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stargel D., Thompson F. S., Phillips S. E., Lombard G. L., Dowell V. R., Jr Modification of the Minitek Miniaturized Differentiation System for characterization of anaerobic bacteria. J Clin Microbiol. 1976 Mar;3(3):291–301. doi: 10.1128/jcm.3.3.291-301.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starr S. E., Thompson F. S., Dowell V. R., Jr, Balows A. Micromethod system for identification of anaerobic bacteria. Appl Microbiol. 1973 May;25(5):713–717. doi: 10.1128/am.25.5.713-717.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stone M. L. Studies on the Anaerobic Streptococcus : I. Certain Biochemical and Immunological Properties of Anaerobic Streptococci. J Bacteriol. 1940 May;39(5):559–582. doi: 10.1128/jb.39.5.559-582.1940. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wells C. L., Field C. R. Long-chain fatty acids of peptococci and peptostreptococci. J Clin Microbiol. 1976 Dec;4(6):515–521. doi: 10.1128/jcm.4.6.515-521.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]