Abstract
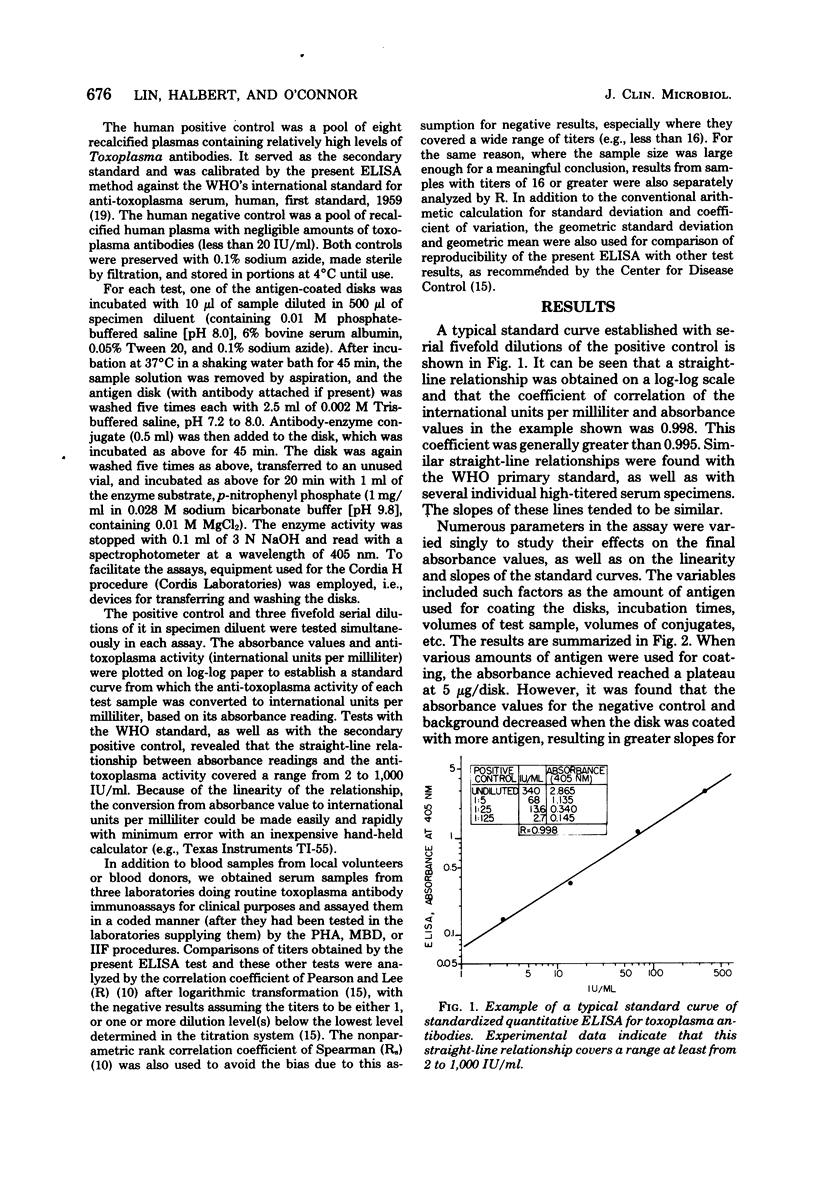
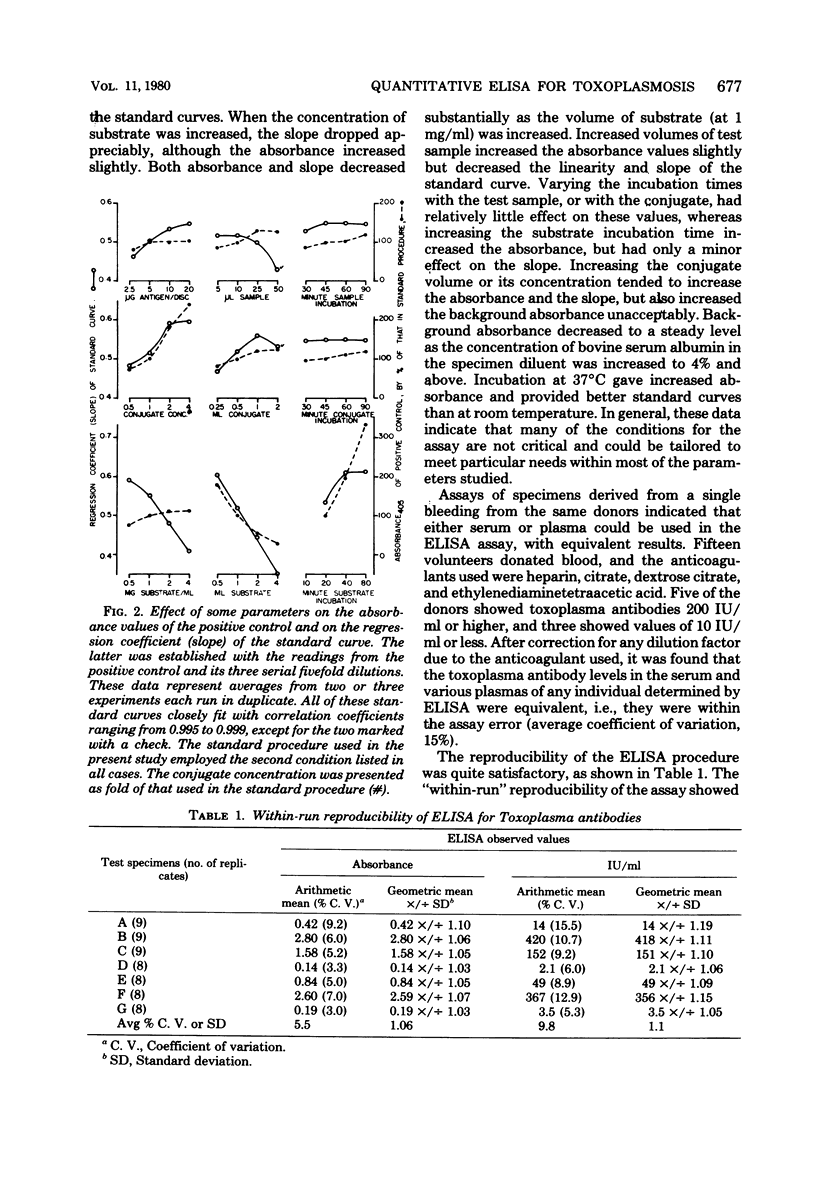
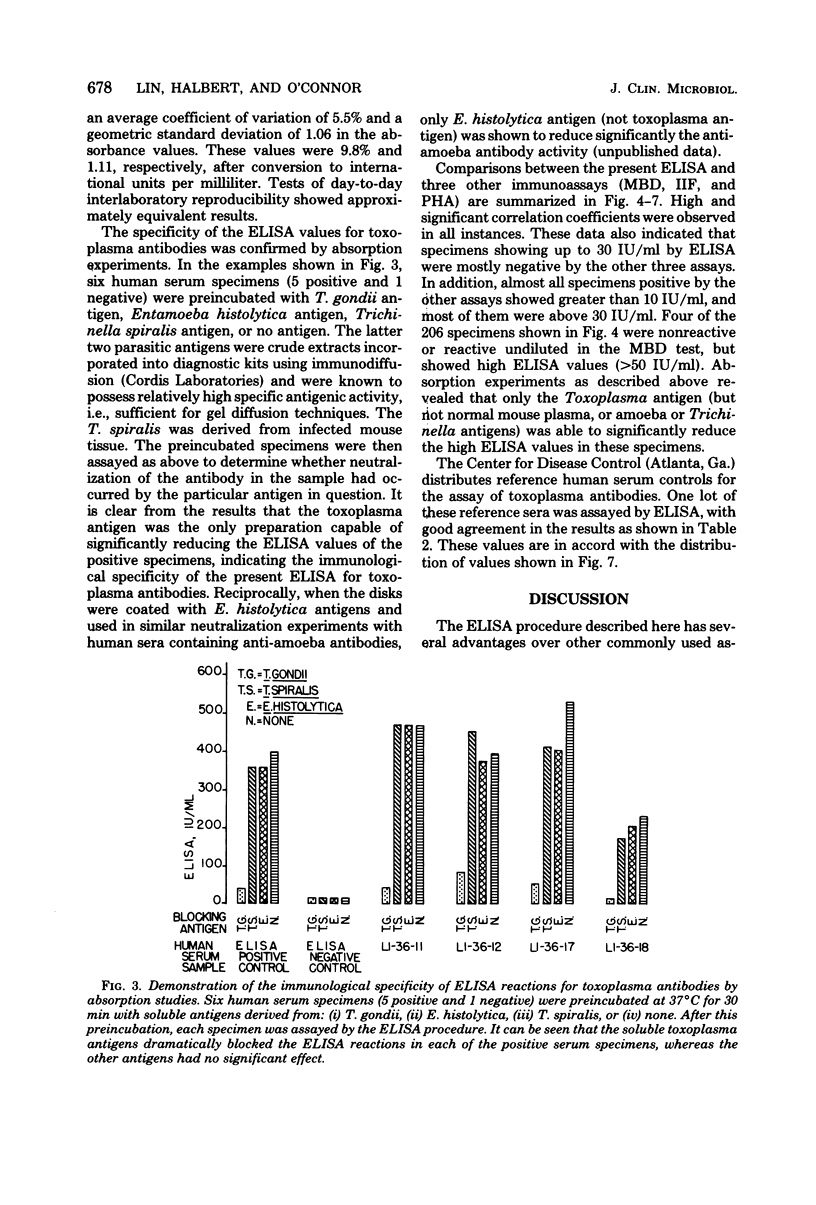
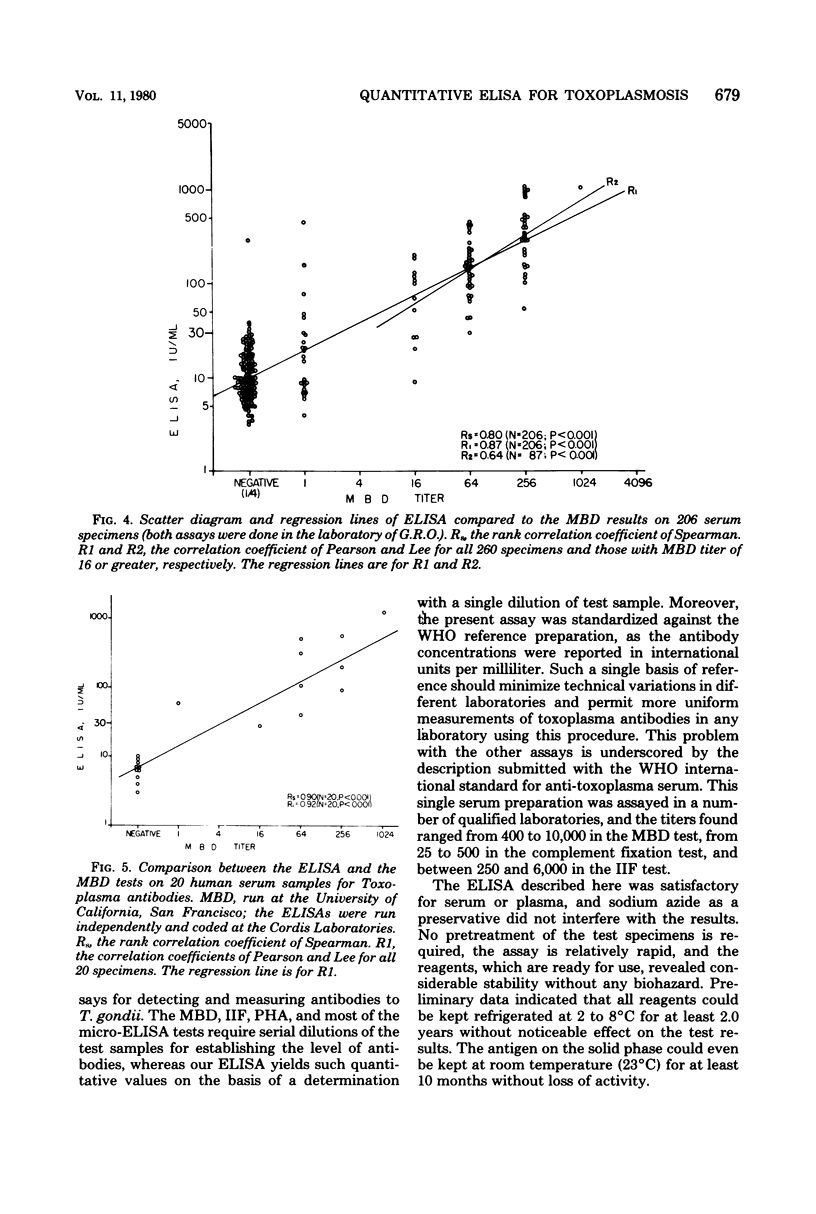
A quantitative and standardized enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay is described which uses lyophilized antigen-coated disks for the detection of human antibodies to Toxoplasma gondii. It does not require serial dilution of the test specimen, and the objective absorbance readings are converted into international units per milliliter traceable to the World Health Organization's reference standard preparation of toxoplasma antibodies. It was shown to be highly specific, reproducible, and sensitive. The reagents were stable, without biohazard, and ready for use. Studies of various parameters in the assay indicated that the test conditions were relatively flexible. The enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay results correlated satisfactorily with the methylene blue dye test, the indirect immunofluorescence test, and the passive hemagglutination test.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- CHORDI A., WALLS K. W., KAGAN I. G. ANALYSIS OF TOXOPLASMA GONDII ANTIGENS BY AGAR DIFFUSION METHODS. J Immunol. 1964 Dec;93:1034–1044. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camargo M. E., Ferreira A. W., Mineo J. R., Takiguti C. K., Nakahara O. S. Immunoglobulin G and immunoglobulin M enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays and defined toxoplasmosis serological patterns. Infect Immun. 1978 Jul;21(1):55–58. doi: 10.1128/iai.21.1.55-58.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capron A., Bout D., Dugimont J. C. Apport des méthodes immunoenzymologiques utilisant des antigèns purifiés au diagnostic spécifique et automatisé des infections parasitaires. Ann Soc Belg Med Trop. 1975;55(5):443–454. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chessum B. S., Denmark J. R. Inconstant ELISA. Lancet. 1978 Jan 21;1(8056):161–161. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(78)90468-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engvall E., Perlmann P. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Quantitative assay of immunoglobulin G. Immunochemistry. 1971 Sep;8(9):871–874. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(71)90454-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halbert S. P., Anken M. Detection of hepatitis B surface antigen (HBS Ag) with use of alkaline phosphatase-labeled antibody to HBS Ag. J Infect Dis. 1977 Oct;136 (Suppl):S318–S323. doi: 10.1093/infdis/136.supplement_2.s318. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'CONNOR G. R. Precipitating antibody to toxoplasma; a follow-up study on findings in the blood and aqueous humor. Am J Ophthalmol. 1957 Oct;44(4 Pt 2):75–85. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STRANNEGARD O. Studies of toxoplasma precipitinogens and their corresponding antibodies by means of diffusion-in-gel methods. Br J Exp Pathol. 1962 Dec;43:600–613. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sulzer A. J., Hall E. C. Indirect fluorescent antibody tests for parasitic diseases. IV. Statistical study of variation in the indirect fluorescent antibody (IFA) test for toxoplasmosis. Am J Epidemiol. 1967 Sep;86(2):401–407. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a120750. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor R. N., Fulford K. M., Huong A. Y. Comparison of kinetic and end-point diffusion methods for quantitating human serum immunoglobulins. J Clin Microbiol. 1978 Jul;8(1):23–27. doi: 10.1128/jcm.8.1.23-27.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voller A., Bidwell D. E., Bartlett A., Fleck D. G., Perkins M., Oladehin B. A microplate enzyme-immunoassay for toxoplasma antibody. J Clin Pathol. 1976 Feb;29(2):150–153. doi: 10.1136/jcp.29.2.150. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walls K. W., Bullock S. L., English D. K. Use of the enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) and its microadaptation for the serodiagnosis of toxoplasmosis. J Clin Microbiol. 1977 Mar;5(3):273–277. doi: 10.1128/jcm.5.3.273-277.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



