Abstract
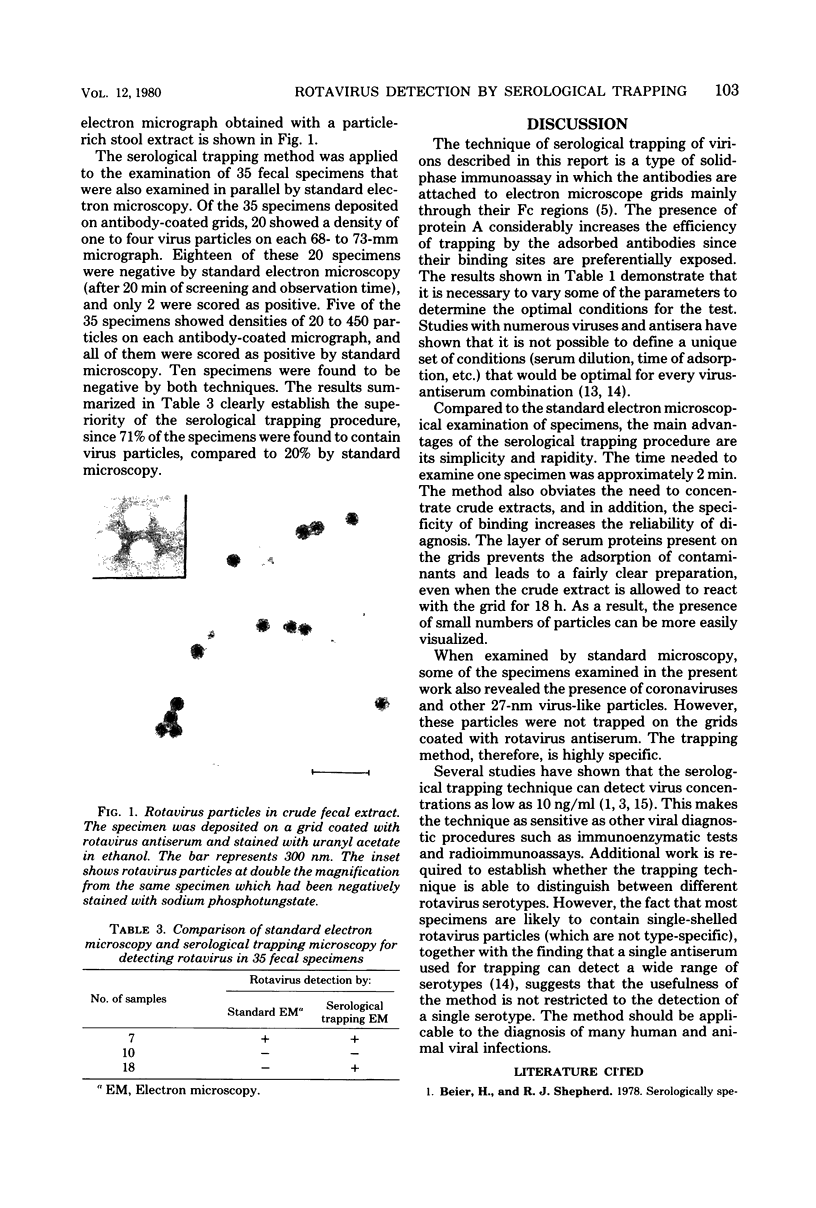
A serological trapping technique for detecting rotaviruses is described which involves coating electron microscope grids with protein A and specific rotavirus antiserum. The presence of a layer of antibodies on the grid increases the number of rotavirus particles that can be visualized. Thirty-five crude fecal extracts from infants suffering from diarrhea were examined by the serological trapping technique and by standard electron-microscopy. When the specimens were deposited on antibody-coated girds, 71% of them were found to contain virus particles, compared with 20% on standard uncoated grids. The method is simple and rapid and does away with the need to concentrate the specimens.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bradburne A. F., Almeida J. D., Gardner P. S., Moosai R. B., Nash A. A., Coombs R. R. A solid-phase system (SPACE) for the detection and quantification of rotavirus in faeces. J Gen Virol. 1979 Sep;44(3):615–623. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-44-3-615. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derrick K. S. Quantitative assay for plant viruses using serologically specific electron microscopy. Virology. 1973 Dec;56(2):652–653. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90068-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellens D. J., de Leeuw P. W. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for diagnosis of rotavirus infections in calves. J Clin Microbiol. 1977 Nov;6(5):530–532. doi: 10.1128/jcm.6.5.530-532.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forsgren A., Sjöquist J. "Protein A" from S. aureus. I. Pseudo-immune reaction with human gamma-globulin. J Immunol. 1966 Dec;97(6):822–827. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grauballe P. C., Genner J., Meyling A., Hornsleth A. Rapid diagnosis of rotavirus infections: comparison of electron microscopy and immunoelectroosmophoresis for the detection of rotavirus in human infantile gastroenteritis. J Gen Virol. 1977 May;35(2):203–218. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-35-2-203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes I. H. Viral gastroenteritis. Prog Med Virol. 1979;25:1–36. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalica A. R., Purcell R. H., Sereno M. M., Wyatt R. G., Kim H. W., Chanock R. M., Kapikian A. Z. A microtiter solid phase radioimmunoassay for detection of the human reovirus-like agent in stools. J Immunol. 1977 Apr;118(4):1275–1279. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapikian A. Z., Kim H. W., Wyatt R. G., Rodriguez W. J., Ross S., Cline W. L., Parrott R. H., Chanock R. M. Reoviruslike agent in stools: association with infantile diarrhea and development of serologic tests. Science. 1974 Sep 20;185(4156):1049–1053. doi: 10.1126/science.185.4156.1049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNulty M. S. Rotaviruses. J Gen Virol. 1978 Jul;40(1):1–18. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-40-1-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Middleton P. J., Holdaway M. D., Petric M., Szymanski M. T., Tam J. S. Solid-phase radioimmunoassay for the detection of rotavirus. Infect Immun. 1977 May;16(2):439–444. doi: 10.1128/iai.16.2.439-444.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milne R. G., Lesemann D. E. An immunoelectron microscopic investigation of oat sterile dwarf and related viruses. Virology. 1978 Oct 15;90(2):299–304. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90314-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodger S. M., Schnagl R. D., Holmes I. H. Biochemical and biophysical characteristics of diarrhea viruses of human and calf origin. J Virol. 1975 Nov;16(5):1229–1235. doi: 10.1128/jvi.16.5.1229-1235.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scherrer R., Bernard S. Application d'une technique immunoenzymologique (ELISA) a la détection du rotavirus bovin et des anticorps dirigés contre lui. Ann Microbiol (Paris) 1977 May-Jun;128A(4):499–510. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spence L., Fauvel M., Petro R., Bloch S. Comparison of Counterimmunoelectrophoresis and electron microscopy for laboratory diagnosis of human reovirus-like agent-associated infantile gastroenteritis. J Clin Microbiol. 1977 Feb;5(2):248–249. doi: 10.1128/jcm.5.2.248-249.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yolken R. H., Stopa P. J. Enzyme-linked fluorescence assay: Ultrasensitive solid-phase assay for detection of human rotavirus. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Sep;10(3):317–321. doi: 10.1128/jcm.10.3.317-321.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]