Abstract
All feces samples (n = 2,390) sent to the Bacteriological Laboratory, Göteborg, Sweden over 43 days were, in addition to the standard procedure, cultivated to detect Clostridium difficile by using a special selective medium. C. difficile was found in 81 of the 2,390 samples (3%). These 81 samples represented 56 patients. Fifty of the 56 patients had diarrhea. In 20 of the 56 patients (36%), Salmonella, Campylobacter, or Yersinia were also found. Of the 2,390 samples 252 (11%) from 132 patients revealed positive isolations of Salmonella, Shigella, Campylobacter, or Yersinia in comparison to 3% for C. difficile alone. This result suggests that C. difficile can easily be isolated with proper techniques. Concomitant isolations of more than one bacterial pathogen in cases of gastroenteritis were often found for C. difficile. The theory presented here is that any change of the normal bacterial fecal flora due to such causes as antimicrobial treatment or enteric infections like Salmonella increases the possibilities of isolating C. difficile. The causative significance of C. difficile might in most cases be doubtful. The majority of cases with diarrhea and C. difficile were self-healing and not severe. Only 2 cases of 56 had severe diarrhea with extended engagement of the colonic mucous membrane, but with no signs of pseudomembranes.
Full text
PDF
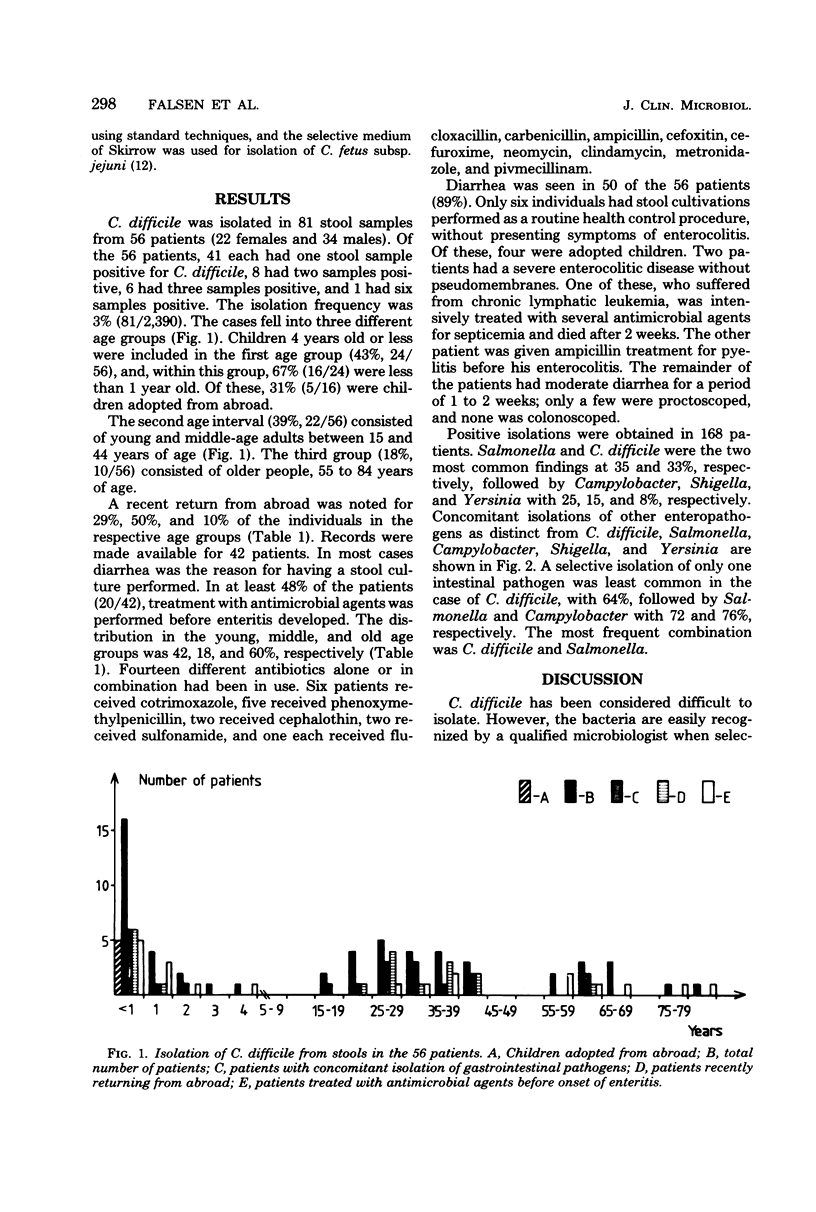


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bartlett J. G., Chang T. W., Gurwith M., Gorbach S. L., Onderdonk A. B. Antibiotic-associated pseudomembranous colitis due to toxin-producing clostridia. N Engl J Med. 1978 Mar 9;298(10):531–534. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197803092981003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartlett J. G., Chang T., Taylor N. S., Onderdonk A. B. Colitis induced by Clostridium difficile. Rev Infect Dis. 1979 Mar-Apr;1(2):370–378. doi: 10.1093/clinids/1.2.370. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartlett J. G., Gorbach S. L. Pseudomembranous enterocolitis (antibiotic-related colitis). Adv Intern Med. 1977;22:455–476. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- George W. L., Sutter V. L., Citron D., Finegold S. M. Selective and differential medium for isolation of Clostridium difficile. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Feb;9(2):214–219. doi: 10.1128/jcm.9.2.214-219.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gästrin B., Kallings L. O., Marcetic A. The survival time for different bacteria in various transport media. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1968;74(3):371–380. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1968.tb03490.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heimdahl A., Nord C. E. Effect of phenoxymethylpenicillin and clindamycin on the oral, throat and faecal microflora of man. Scand J Infect Dis. 1979;11(3):233–242. doi: 10.3109/inf.1979.11.issue-3.11. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keighley M. R., Burdon D. W., Arabi Y., Williams J. A., Thompson H., Youngs D., Johnson M., Bentley S., George R. H., Mogg G. A. Randomised controlled trial of vancomycin for pseudomembranous colitis and postoperative diarrhoea. Br Med J. 1978 Dec 16;2(6153):1667–1669. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.6153.1667. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larson H. E., Price A. B., Honour P., Borriello S. P. Clostridium difficile and the aetiology of pseudomembranous colitis. Lancet. 1978 May 20;1(8073):1063–1066. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(78)90912-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lusk R. H., Fekety F. R., Jr, Silva J., Jr, Bodendorfer T., Devine B. J., Kawanishi H., Korff L., Nakauchi D., Rogers S., Siskin S. B. Gastrointestinal side effects of clindamycin and ampicillin therapy. J Infect Dis. 1977 Mar;135 (Suppl):S111–S119. doi: 10.1093/infdis/135.supplement.s111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skirrow M. B. Campylobacter enteritis: a "new" disease. Br Med J. 1977 Jul 2;2(6078):9–11. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.6078.9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]