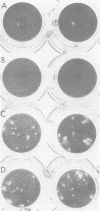
Abstract
An improved human interferon (IF) assay is described. This procedure is based on the ability of encephalomyocarditis virus to replicate in WISH cell microcultures with the production of discrete plaques in the presence of a liquid tissue culture medium. Performance of 50% plaque reduction endpoint assays in micro-culture required only 0.1 ml of specimen for determinations using duplicate dilutions beginning at 1:3. Semiautomated equipment facilitated simultaneous in situ dilution and distribution of multiple IF samples in cultures containing preformed WISH cell monolayers. An incubation period of 5 to 6 h was adequate for development of maximal antiviral activity by both virus- and immune-induced IF. Sensitivity of the encephalomyocarditis microplaque reduction assay was comparable to that of other commonly used techniques. The method is rapid, can be completed within 30 h from the beginning of the IF assay, and is able to accommodate as many as 40 to 50 samples at a single time. Encephalomyocarditis microplaque reduction is suitable for the quantitation of IF as an antiviral agent or a lymphokine.
Full text
PDF
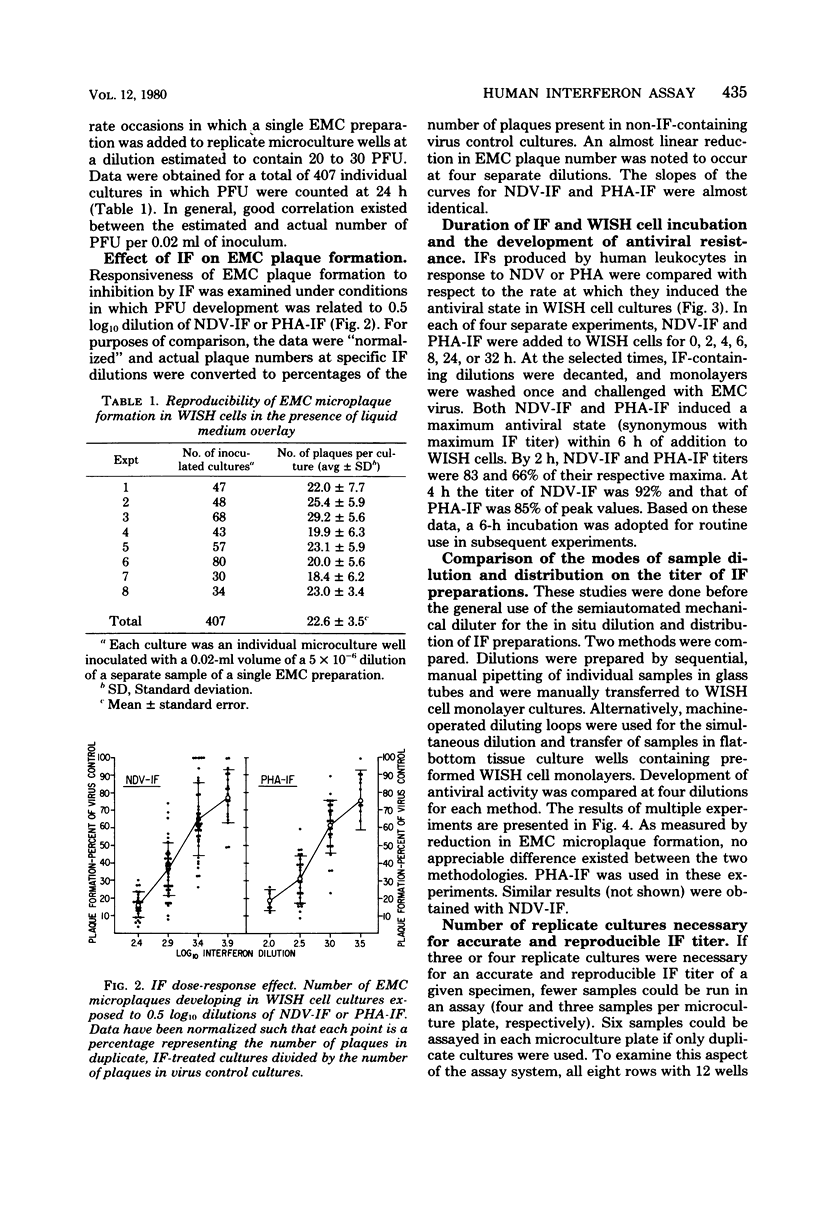
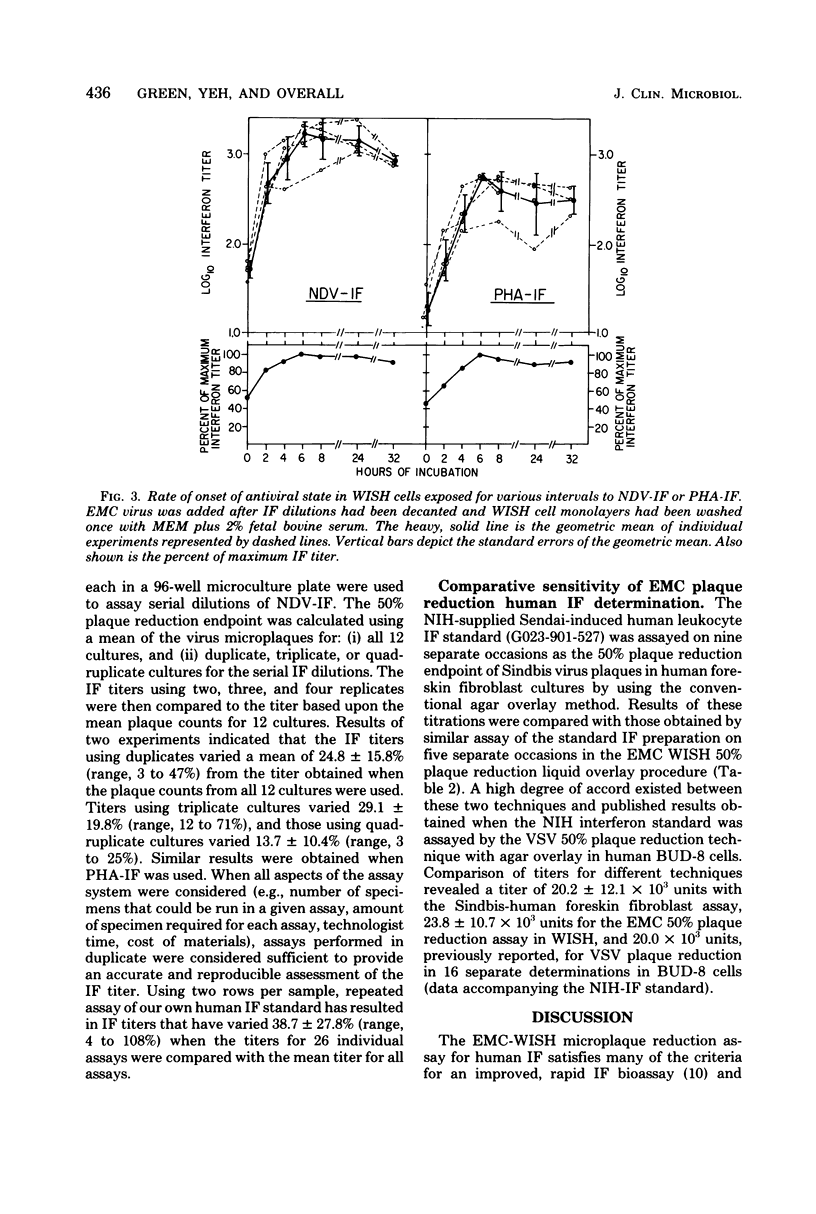
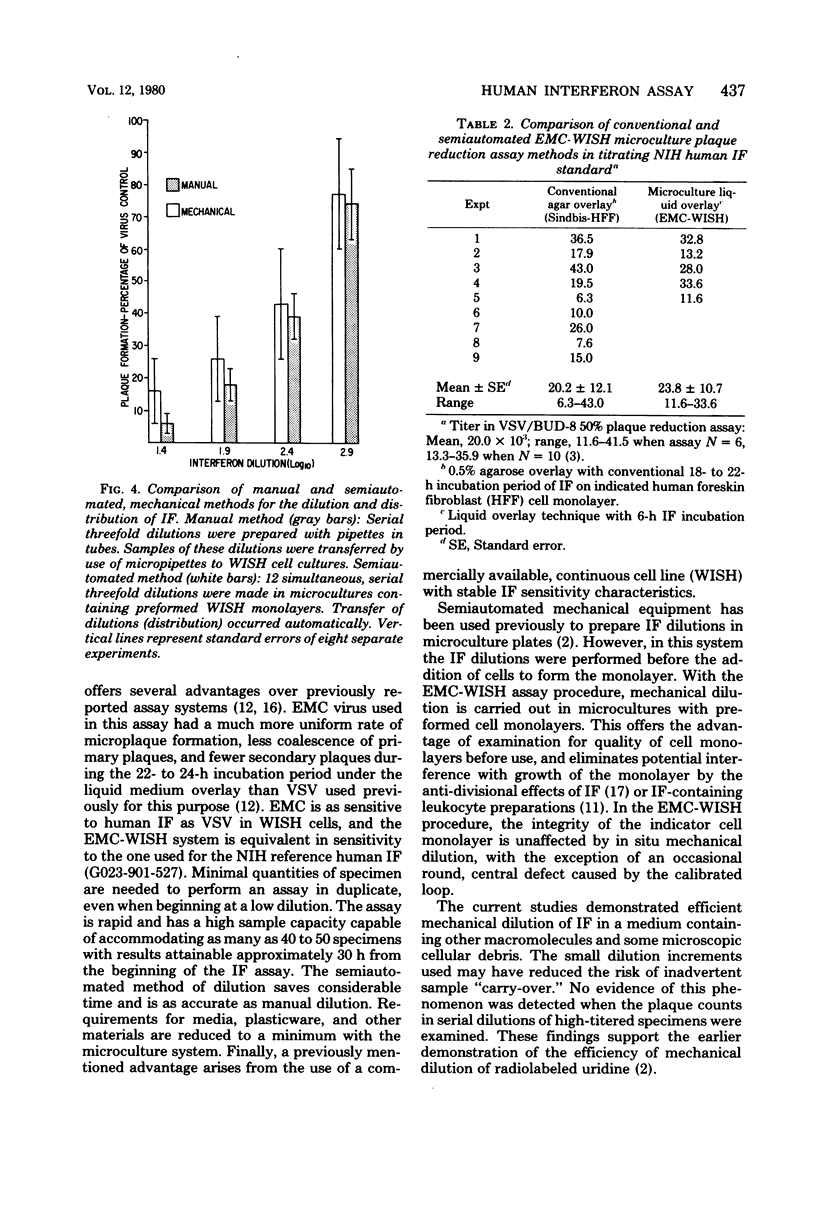

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Armstrong J. A. Semi-micro, dye-binding assay for rabbit interferon. Appl Microbiol. 1971 Apr;21(4):723–725. doi: 10.1128/am.21.4.723-725.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell J. B., Grunberger T., Kochman M. A., White S. L. A microplaque reduction assay for human and mouse interferon. Can J Microbiol. 1975 Aug;21(8):1247–1253. doi: 10.1139/m75-186. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Maeyer E., De Maeyer-Guignard J. Effect of interferon on cell-mediated immunity. Tex Rep Biol Med. 1977;35:370–374. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dianzani F., Baron S. Unexpectedly rapid action of human interferon in physiological conditions. Nature. 1975 Oct 23;257(5528):682–684. doi: 10.1038/257682a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dianzani F., Salter L., Fleischmann W. R., Jr, Zucca M. Immune interferon activates cells more slowly than does virus-induced interferon. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1978 Oct;159(1):94–97. doi: 10.3181/00379727-159-40291. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleischmann W. R., Jr, Georgiades J. A., Osborne L. C., Johnson H. M. Potentiation of interferon activity by mixed preparations of fibroblast and immune interferon. Infect Immun. 1979 Oct;26(1):248–253. doi: 10.1128/iai.26.1.248-253.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galasso G. J., Dunnick J. K. Interferon, an antiviral drug for use in man. Tex Rep Biol Med. 1977;35:478–485. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gifford G. E., Tobey M. Effect of interferon and lymphokines on lymphocytes. Tex Rep Biol Med. 1977;35:375–380. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green J. A., Cooperband S. R., Rutstein J. A., Kibrick S. Inhibition of target cell proliferation by supernatants from cultures of human peripheral lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1970 Jul;105(1):48–54. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green J. A. Rapid assay of interferon. Tex Rep Biol Med. 1977;35:167–172. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green J. A., Stanton G. J., Goode J., Baron S. Vesicular stomatitis virus plaque production in monolayer cultures with liquid overlay medium: description and adaptation to a one-day, human interferon-plaque. J Clin Microbiol. 1976 Dec;4(6):479–485. doi: 10.1128/jcm.4.6.479-485.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAYFLICK L. The establishment of a line (WISH) of human amnion cells in continuous cultivation. Exp Cell Res. 1961 Feb;23:14–20. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(61)90059-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hooks J. J., Moutsopoulos H. M., Geis S. A., Stahl N. I., Decker J. L., Notkins A. L. Immune interferon in the circulation of patients with autoimmune disease. N Engl J Med. 1979 Jul 5;301(1):5–8. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197907053010102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson H. M. Effect of interferon on antibody formation. Tex Rep Biol Med. 1977;35:357–369. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oie H. K. Conventional assay systems for interferon. Tex Rep Biol Med. 1977;35:154–160. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strander H. Anti-tumor effects of interferon and its possible use as an anti-neoplastic agent in man. Tex Rep Biol Med. 1977;35:429–435. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]