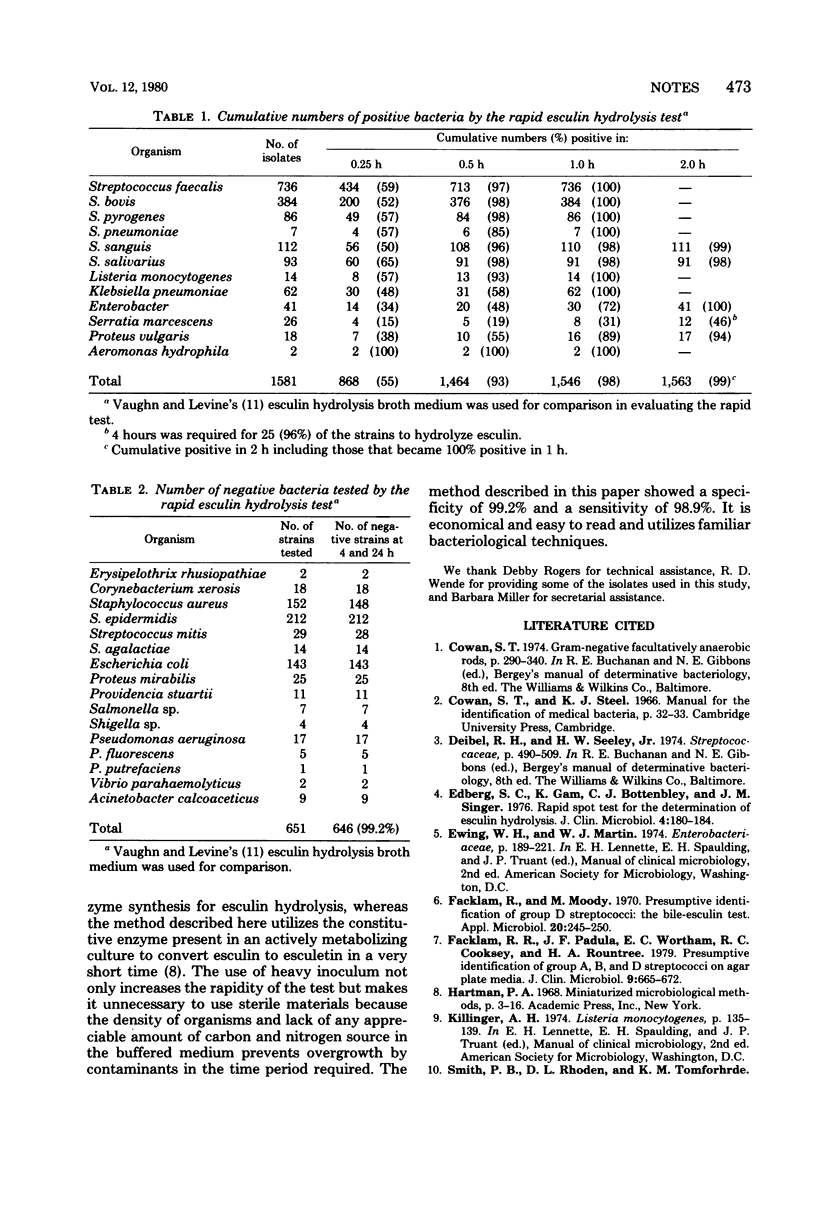
Abstract
An esculin hydrolysis test is described which distinguishes over 97% of bacteria that can convert esculin to esculetin in a buffered solution, from those that cannot, within an hour.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Edberg S. C., Gam K., Bottenbley C. J., Singer J. M. Rapid spot test for the determination of esculin hydrolysis. J Clin Microbiol. 1976 Aug;4(2):180–184. doi: 10.1128/jcm.4.2.180-184.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Facklam R. R., Moody M. D. Presumptive identification of group D streptococci: the bile-esculin test. Appl Microbiol. 1970 Aug;20(2):245–250. doi: 10.1128/am.20.2.245-250.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Facklam R. R., Padula J. F., Wortham E. C., Cooksey R. C., Rountree H. A. Presumptive identification of group A, B, and D streptococci on agar plate media. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Jun;9(6):665–672. doi: 10.1128/jcm.9.6.665-672.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasilauskas B. L. Preliminary observations on the rapid differentiation of the Klebsiella-Enterobacter-Serratia group on bile-esculin-agar. Appl Microbiol. 1971 Jan;21(1):162–163. doi: 10.1128/am.21.1.162-163.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



