Abstract
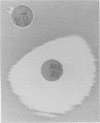
Development of resistance during therapy with cefamandole contributes to treatment failure. A simple cefoxitin disk test was recently described which detects a cefamandole-active inducible beta-lactamase not otherwise detectable with cefamandole as the inducer. A case of breakthrough Enterobacter bacteremia due to selection of a resistant subpopulation is reported in an immunocompromised patient. The use of this simple disk test in selected clinical cases is advocated.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson E. T., Young L. S., Hewitt W. L. Simultaneous antibiotic levels in "breakthrough" gram-negative rod bacteremia. Am J Med. 1976 Oct;61(4):493–497. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(76)90328-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beckwith D. G. Simultaneous recovery of ampicillin-sensitive and ampicillin-resistant H. influenzae from blood. J Pediatr. 1980 May;96(5):954–954. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(80)80597-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bodey G. P., Ketchel S., Rodriguez V. Carbenicillin plus cefamandole in the treatment of infections in patients with cancer. J Infect Dis. 1978 May;137 (Suppl):S139–S143. doi: 10.1093/infdis/137.supplement.s139. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Findell C. M., Sherris J. C. Susceptibility of Enterobacter to cefamandole: evidence for a high mutation rate to resistance. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976 Jun;9(6):970–974. doi: 10.1128/aac.9.6.970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gentry L. O. Efficacy and safety of cefamandole plus either gentamicin or tobramycin in therapy of severe gram-negative bacterial infections. J Infect Dis. 1978 May;137 (Suppl):S144–S149. doi: 10.1093/infdis/137.supplement.s144. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goering R. V., Sanders C. C., Sanders W., Jr Comparison of BL-S786 with cephalothin, cefamandole and cefoxitin in vitro and in treatment of experimental infections in mice. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1978 Apr;31(4):363–372. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.31.363. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris J. A., Cobbs C. G. Persistent gram-negative bacteremia. Observations in twenty patients. Am J Surg. 1973 Jun;125(6):705–717. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(73)90169-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine L. R., McCain E. Cefamandole in the treatment of infections due to Enterobacter and indole-positive Proteus. J Infect Dis. 1978 May;137 (Suppl):S125–S132. doi: 10.1093/infdis/137.supplement.s125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahoney D. F., Koppel G. A., Turner J. R. Substrate inhibition of beta-lactamases, a method for predicting enzymatic stability of cephalosporins. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976 Sep;10(3):470–475. doi: 10.1128/aac.10.3.470. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McHenry M. C., Gavan T. L., Hawk W. A., Van Ommen R. A., Ma C. A. Gram-negative bacteremia of long duration. Clinical study of 29 patients. Cleve Clin Q. 1973 Summer;40(2):47–56. doi: 10.3949/ccjm.40.2.47. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray P. R. Standardization of the Analytab Enteric (API 20E) system to increase accuracy and reproducibility of the test for biotype characterization of bacteria. J Clin Microbiol. 1978 Jul;8(1):46–49. doi: 10.1128/jcm.8.1.46-49.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ott J. L., Turner J. R., Mahoney D. F. Lack of correlation between beta-lactamase production and susceptibility to cefamandole or cefoxitin among spontaneous mutants of Enterobacteriaceae. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1979 Jan;15(1):14–19. doi: 10.1128/aac.15.1.14. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perkins R. L., Fass R. J., Warner J. F., Prior R. B., File T. M., Tight R. R., Gardner W. G., Ruiz D. E., Slama T. G. Cefamandole nafate therapy of respiratory tract, skin, and soft tissue infections in 74 patients. J Infect Dis. 1978 May;137 (Suppl):S110–S118. doi: 10.1093/infdis/137.supplement.s110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanders C. C., Sanders W. E., Jr Emergence of resistance to cefamandole: possible role of cefoxitin-inducible beta-lactamases. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1979 Jun;15(6):792–797. doi: 10.1128/aac.15.6.792. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]