Abstract
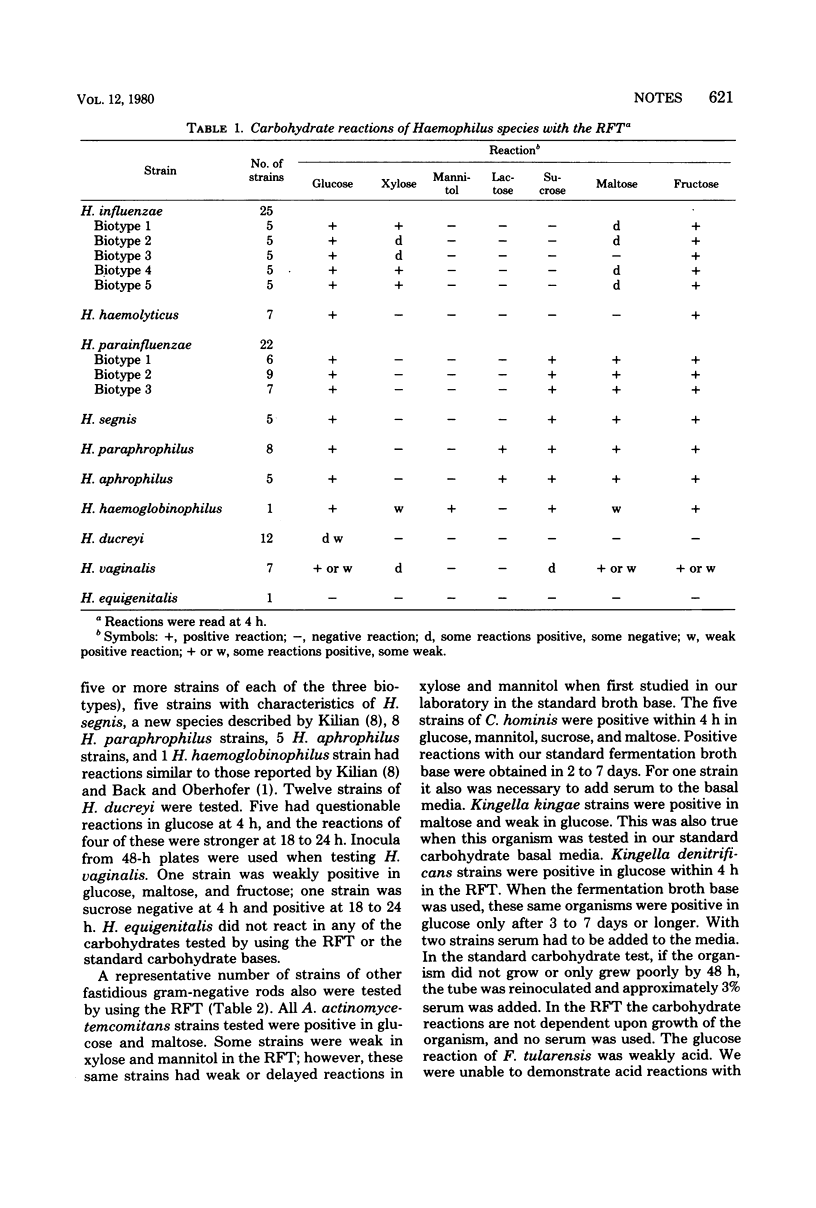
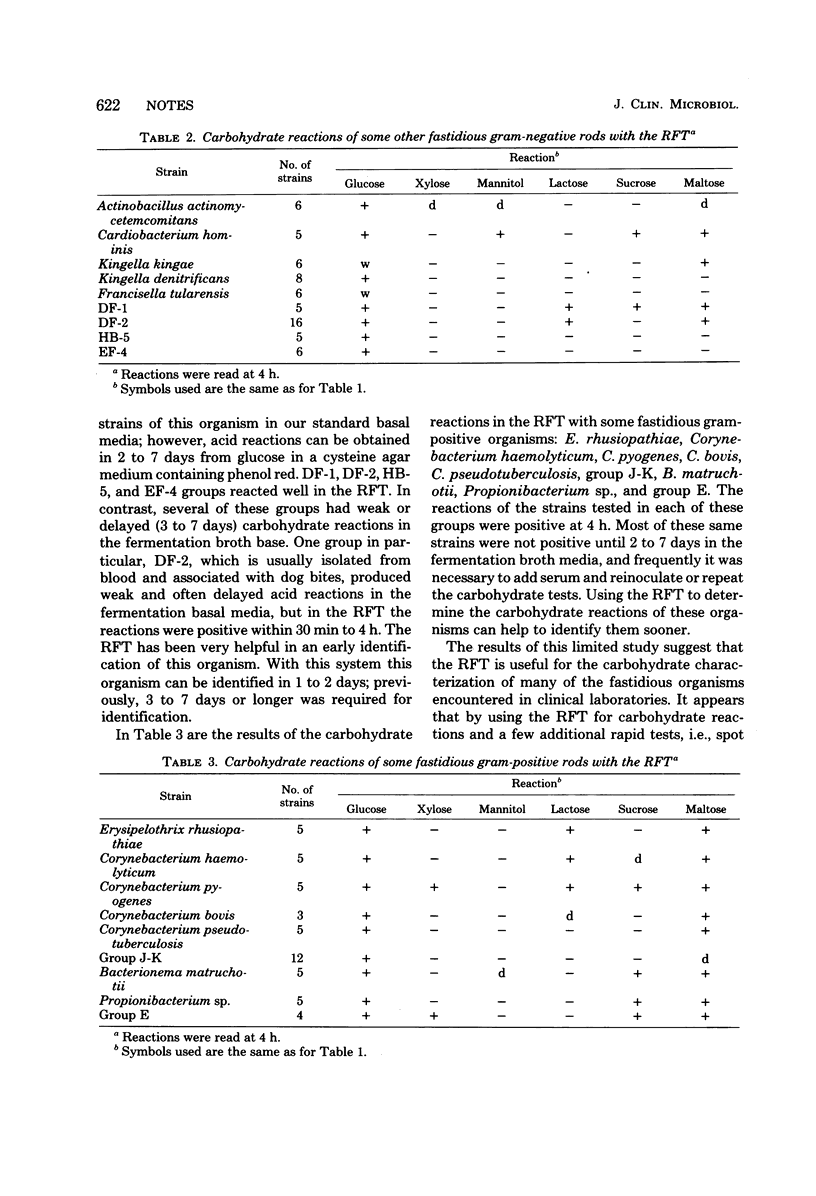
The rapid fermentation test was used to determine the carbohydrate reactions of some of the fastidious bacteria encountered in clinical laboratories, such as: Haemophilus species, including Haemophilus vaginalis; Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans; Cardiobacterium hominis; Kingella species; Corynebacterium species; Propionibacterium species; and Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae. Results were usually obtained within 4 h by using inocula from 24- or 48-h blood or chocolate agar media.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Back A. E., Oberhofer T. R. Use of the Minitek system for biotyping Haemophilus species. J Clin Microbiol. 1978 Mar;7(3):312–313. doi: 10.1128/jcm.7.3.312-313.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown W. J. A comparison of three fermentation methods for the confirmation of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Health Lab Sci. 1976 Jan;13(1):54–58. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown W. J. Modification of the rapid fermentation test for Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Appl Microbiol. 1974 Jun;27(6):1027–1030. doi: 10.1128/am.27.6.1027-1030.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown W. J. Stability of working reagents for the Modified Rapid Fermentation Test (MRFT). Health Lab Sci. 1977 Jul;14(3):172–176. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kellogg D. S., Jr, Turner E. M. Rapid fermentation confirmation of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Appl Microbiol. 1973 Apr;25(4):550–552. doi: 10.1128/am.25.4.550-552.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilian M. A taxonomic study of the genus Haemophilus, with the proposal of a new species. J Gen Microbiol. 1976 Mar;93(1):9–62. doi: 10.1099/00221287-93-1-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riley P. S., Tatum H. W., Weaver R. E. Pseudomonas putrefaciens isolates from clinical specimens. Appl Microbiol. 1972 Nov;24(5):798–800. doi: 10.1128/am.24.5.798-800.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



