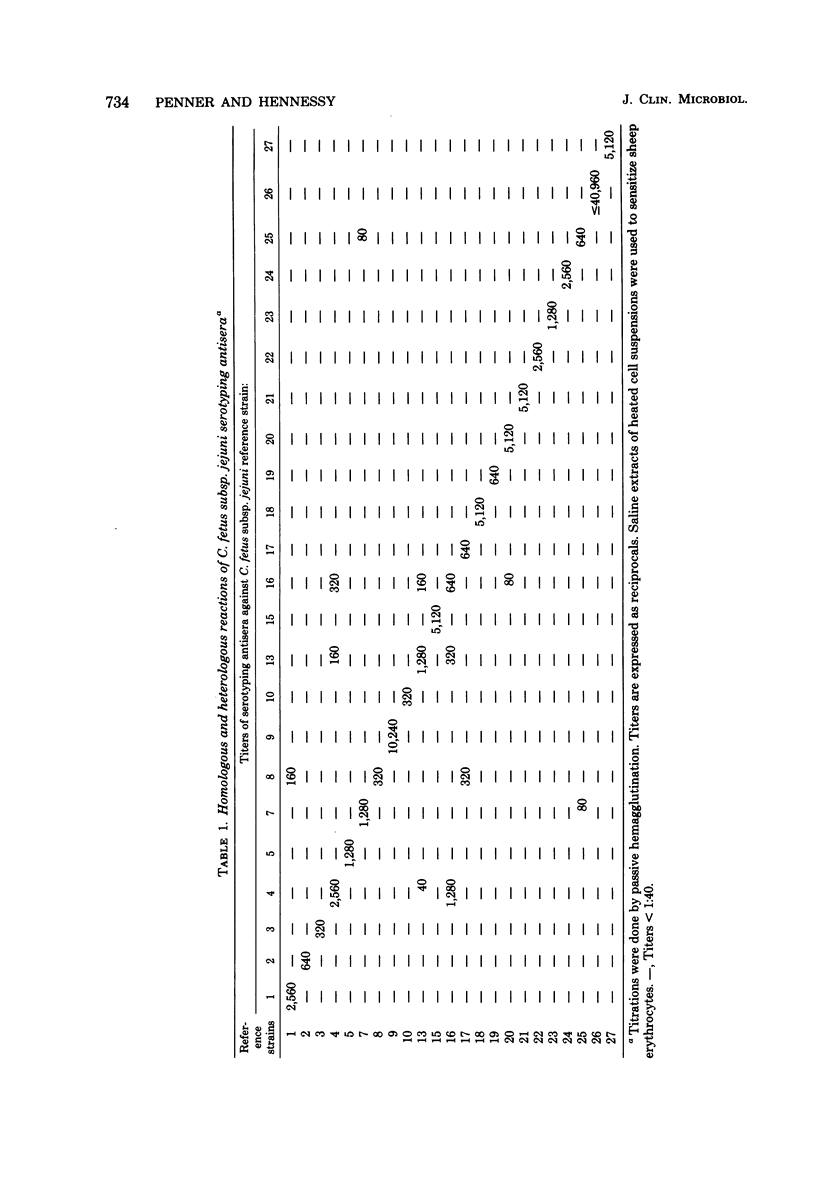
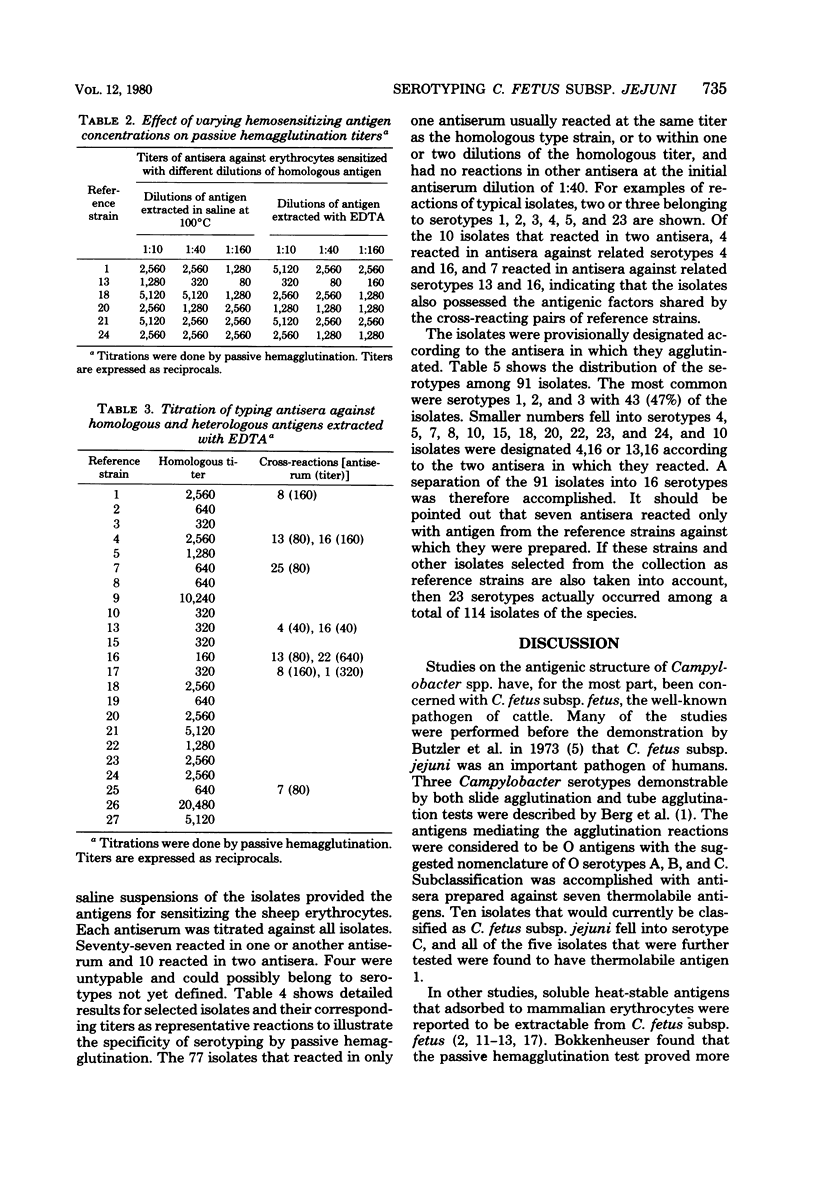
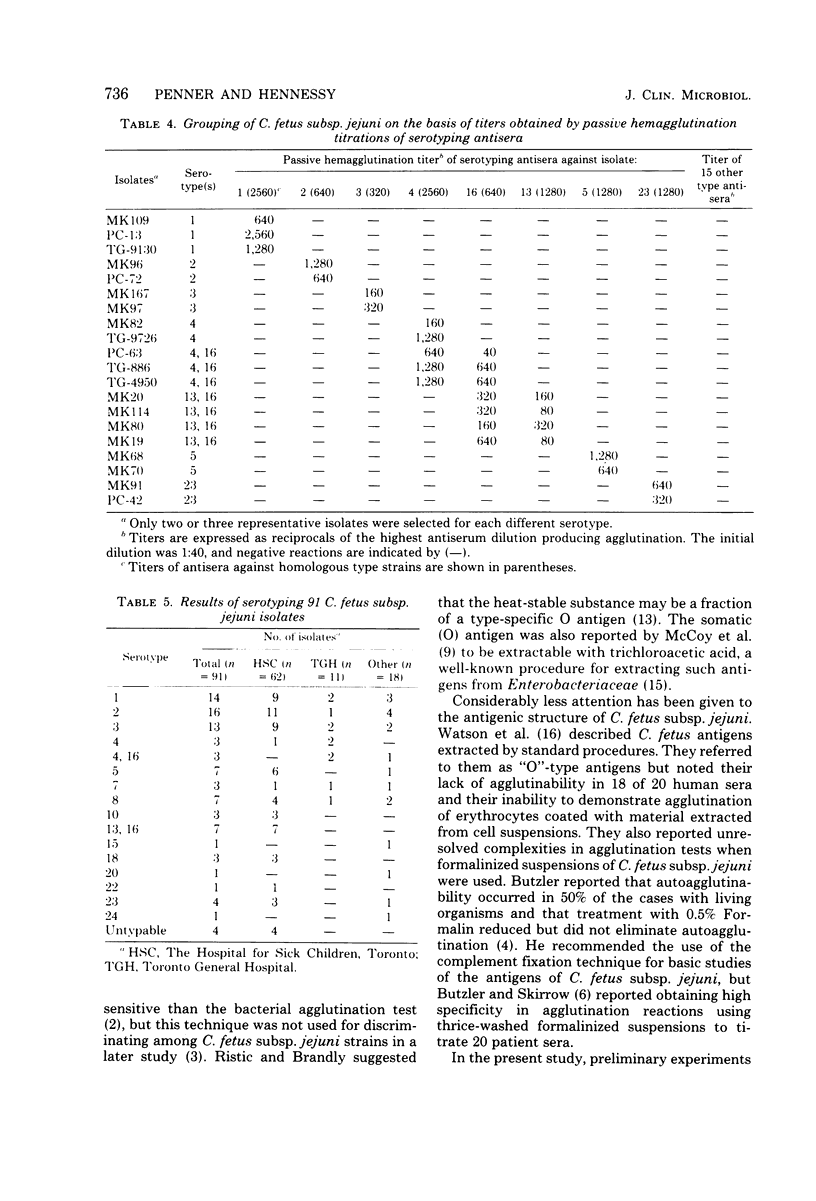
Abstract
Antigenic materials were extracted from Campylobacter fetus subsp. jejuni strains by heating bacterial suspensions in saline at 100 degrees C and by exposure to ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid. The antigens were heat stable at 100 degrees C, capable of sensitizing sheep erythrocytes for agglutination in antisera, and able to elicit production of specific antibody in rabbits; they occurred with different immunological specificities in 23 strains. Antisera against the 23 strains could be used for discriminating among isolates of the species when the passive hemagglutination technique was used for serotyping. Three serotypes were more common than others among a collection of human isolates.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berg R. L., Jutila J. W., Firehammer B. D. A revised classification of Vibrio fetus. Am J Vet Res. 1971 Jan;32(1):11–22. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bokkenheuser V. D., Richardson N. J., Bryner J. H., Roux D. J., Schutte A. B., Koornhof H. J., Freiman I., Hartman E. Detection of enteric campylobacteriosis in children. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Feb;9(2):227–232. doi: 10.1128/jcm.9.2.227-232.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bokkenheuser V. Vibrio fetus infection in man: a serological test. Infect Immun. 1972 Feb;5(2):222–226. doi: 10.1128/iai.5.2.222-226.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butzler J. P., Dekeyser P., Detrain M., Dehaen F. Related vibrio in stools. J Pediatr. 1973 Mar;82(3):493–495. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(73)80131-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butzler J. P., Skirrow M. B. Campylobacter enteritis. Clin Gastroenterol. 1979 Sep;8(3):737–765. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karmali M. A., Fleming P. C. Campylobacter enteritis in children. J Pediatr. 1979 Apr;94(4):527–533. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(79)80004-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leive L., Shovlin V. K., Mergenhagen S. E. Physical, chemical, and immunological properties of lipopolysaccharide released from Escherichia coli by ethylenediaminetetraacetate. J Biol Chem. 1968 Dec 25;243(24):6384–6391. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCoy E. C., Doyle D., Burda K., Corbeil L. B., Winter A. J. Superficial antigens of Campylobacter (Vibrio) fetus: characterization of antiphagocytic component. Infect Immun. 1975 Mar;11(3):517–525. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.3.517-525.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NETER E., WESTPHAL O., LUDERITZ O., GORZYNSKI E. A., EICHENBERGER E. Studies of enterobacterial lipopolysaccharides; effects of heat and chemicals on erythrocyte-modifying, antigenic, toxic and pyrogenic properties. J Immunol. 1956 May;76(5):377–385. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newsam I. D., George T. D. Diagnosis of bovine vibriosis. 3. Indirect haemagglutination using untanned sheep erythrocytes. Aust Vet J. 1967 Aug;43(8):283–285. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-0813.1967.tb08943.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RISTIC M., BRANDLY C. A. Characterization of Vibrio fetus antigens. I. Chemical properties and serological activities of a soluble antigen. Am J Vet Res. 1959 Jan;20:148–153. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RISTIC M., BRANDLY C. A. Characterization of Vibrio fetus antigens. II. Agglutination of polysaccharide-sensitized sheep erythrocytes by specific antiserums. Am J Vet Res. 1959 Jan;20:154–161. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skirrow M. B. Campylobacter enteritis: a "new" disease. Br Med J. 1977 Jul 2;2(6078):9–11. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.6078.9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winter A. J. An antigenic analysis of Vibrio fetus. 3. Chemical, biologic, and antigenic properties of the endotoxin. Am J Vet Res. 1966 May;27(118):653–658. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



