Abstract
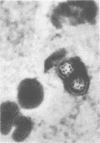
The recognition of Cryptococcus neoformans in Gram-stained smears of purulent exudates may be hampered by the presence of the large gelatinous capsule which apparently prevents definitive staining of the yeast-like cells. In such stained preparations, C. neoformans may appear either as round cells with gram-positive granular inclusions impressed upon a pale lavender cytoplasmic background or as gram-negative lipoid bodies.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Damsker B., Bottone E. D. Recovery of Cryptococcus neoformans from modified Dubos liquid medium utilized for isolation of mycobacteria. J Clin Microbiol. 1975 Apr;1(4):393–395. doi: 10.1128/jcm.1.4.393-395.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodman J. S., Kaufman L., Koenig M. G. Diagnosis of cryptococcal meningitis. Value of immunologic detection of cryptococcal antigen. N Engl J Med. 1971 Aug 19;285(8):434–436. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197108192850804. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornfeld S. J., Wormser G. P., Blum D., Singer C. Purulent cryptococcal meningitis. Mt Sinai J Med. 1979 May-Jun;46(3):326–327. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]