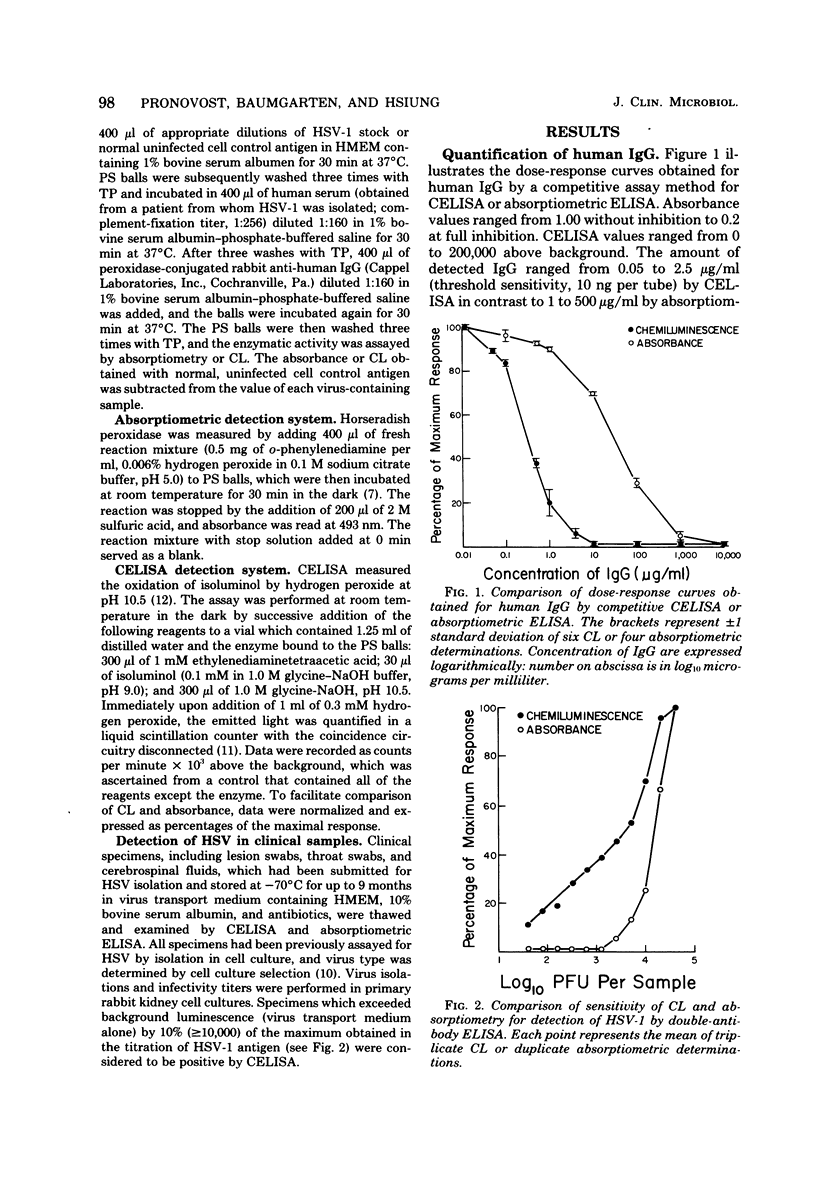
Abstract
A chemiluminescent enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (CELISA) was developed for detecting human immunoglobulin G and herpes simplex viral antigen. A comparison of CELISA with a conventional absorptiometric detection system showed that CELISA was 100 times more sensitive than absorptiometry for the measurement of human immunglobulin G. Similarly, CELISA detected as few as 40 plaque-forming units of herpes simplex virus in contrast to 2,500 plaque-forming units detected by absorptiometry. Of 18 specimens which were positive for herpes simplex virus type 1 by isolation in tissue culture, 15 (83%) were detected by CELISA within a few hours; in certain cases, several days were necessary for detection of virus by isolation techniques.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baumgarten A. Viral immunodiagnosis. Yale J Biol Med. 1980 Jan-Feb;53(1):71–83. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forghani B., Schmidt N. J., Lennette E. H. Solid phase radioimmunoassay for identification of Herpesvirus hominis types 1 and 2 from clinical materials. Appl Microbiol. 1974 Oct;28(4):661–667. doi: 10.1128/am.28.4.661-667.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forghani B., Schmidt N. J., Lennette E. H. Solid phase radioimmunoassay for typing herpes simplex viral antibodies in human sera. J Clin Microbiol. 1975 Nov;2(5):410–418. doi: 10.1128/jcm.2.5.410-418.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorus F., Schram E. Applications of bio- and chemiluminescence in the clinical laboratory. Clin Chem. 1979 Apr;25(4):512–519. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grauballe P. C., Vestergaard B. F. ELISA for herpes simplex virus type 2 antibodies. Lancet. 1977 Nov 12;2(8046):1038–1039. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(77)92948-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hersh L. S., Vann W. P., Wilhelm S. A. A luminol-assisted, competitive-binding immunoassay of human immunoglobulin G. Anal Biochem. 1979 Mar;93(2):267–271. doi: 10.1016/s0003-2697(79)80150-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madore H. P., Baumgarten A. Enzyme-linked protein A: an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay reagent for detection of human immunoglobulin G and virus-specific antibody. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Oct;10(4):529–532. doi: 10.1128/jcm.10.4.529-532.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathiesen L. R., Feinstone S. M., Wong D. C., Skinhoej P., Purcell R. H. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for detection of hepatitis A antigen in stool and antibody to hepatitis A antigen in sera: comparison with solid-phase radioimmunoassay, immune electron microscopy, and immune adherence hemagglutination assay. J Clin Microbiol. 1978 Feb;7(2):184–193. doi: 10.1128/jcm.7.2.184-193.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mills K. W., Gerlach E. H., Bell J. W., Farkas M. E., Taylor R. J. Serotyping herpes simplex virus isolated by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays. J Clin Microbiol. 1978 Jan;7(1):73–76. doi: 10.1128/jcm.7.1.73-76.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nordlund J. J., Anderson C., Hsiung G. D., Tenser R. B. The use of temperature sensitivity and selective cell culture systems for differentiation of herpes simplex virus types 1 and 2 in a clinical laboratory. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1977 May;155(1):118–123. doi: 10.3181/00379727-155-39757. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuurs A. H., Van Weemen B. K. Enzyme-immunoassay. Clin Chim Acta. 1977 Nov 15;81(1):1–40. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(77)90410-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vestergaard B. F., Grauballe P. C., Spanggaard H. Titration of herpes simplex virus antibodies in human sera by the enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B. 1977 Dec;85B(6):466–468. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1977.tb02004.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voller A., Bartlett A., Bidwell D. E. Enzyme immunoassays with special reference to ELISA techniques. J Clin Pathol. 1978 Jun;31(6):507–520. doi: 10.1136/jcp.31.6.507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitehead T. P., Kricka L. J., Carter T. J., Thorpe G. H. Analytical luminescence: its potential in the clinical laboratory. Clin Chem. 1979 Sep;25(9):1531–1546. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yolken R. H. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA): a practical tool for rapid diagnosis of viruses and other infectious agents. Yale J Biol Med. 1980 Jan-Feb;53(1):85–92. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yolken R. H., Stopa P. J. Enzyme-linked fluorescence assay: Ultrasensitive solid-phase assay for detection of human rotavirus. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Sep;10(3):317–321. doi: 10.1128/jcm.10.3.317-321.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


