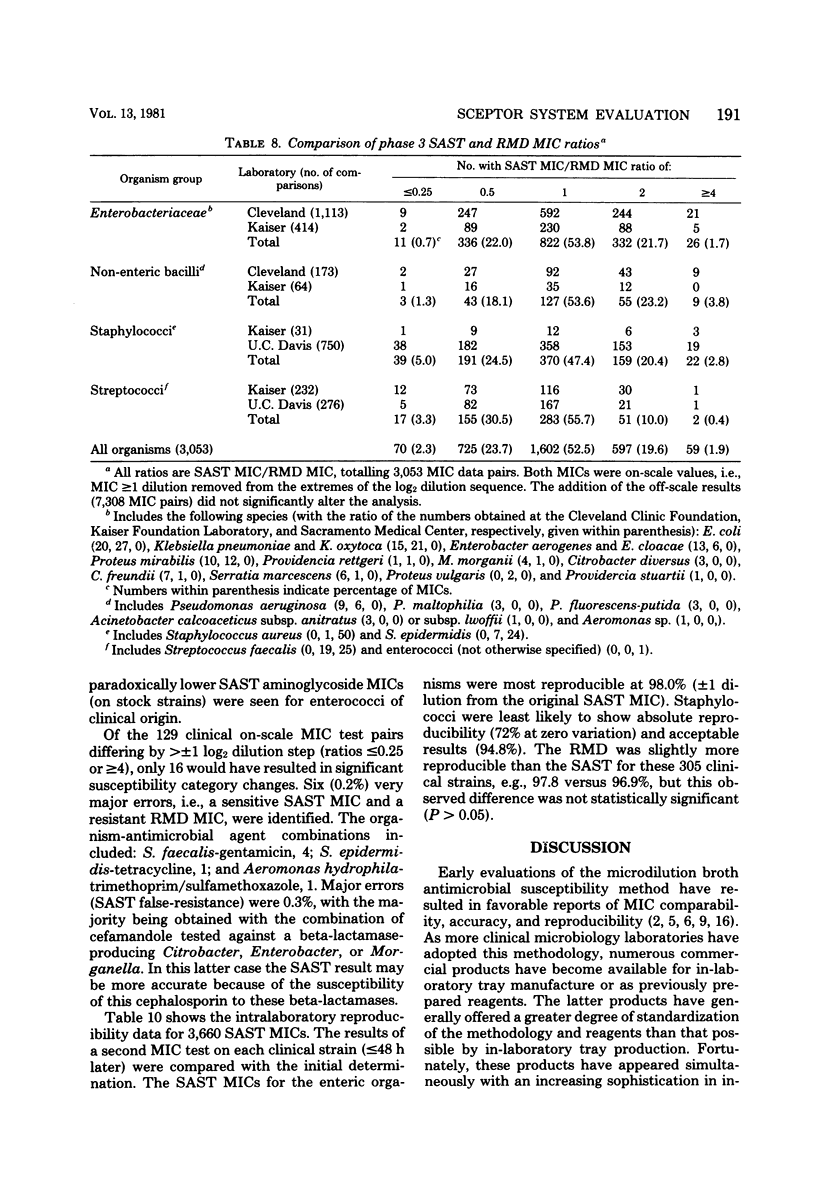
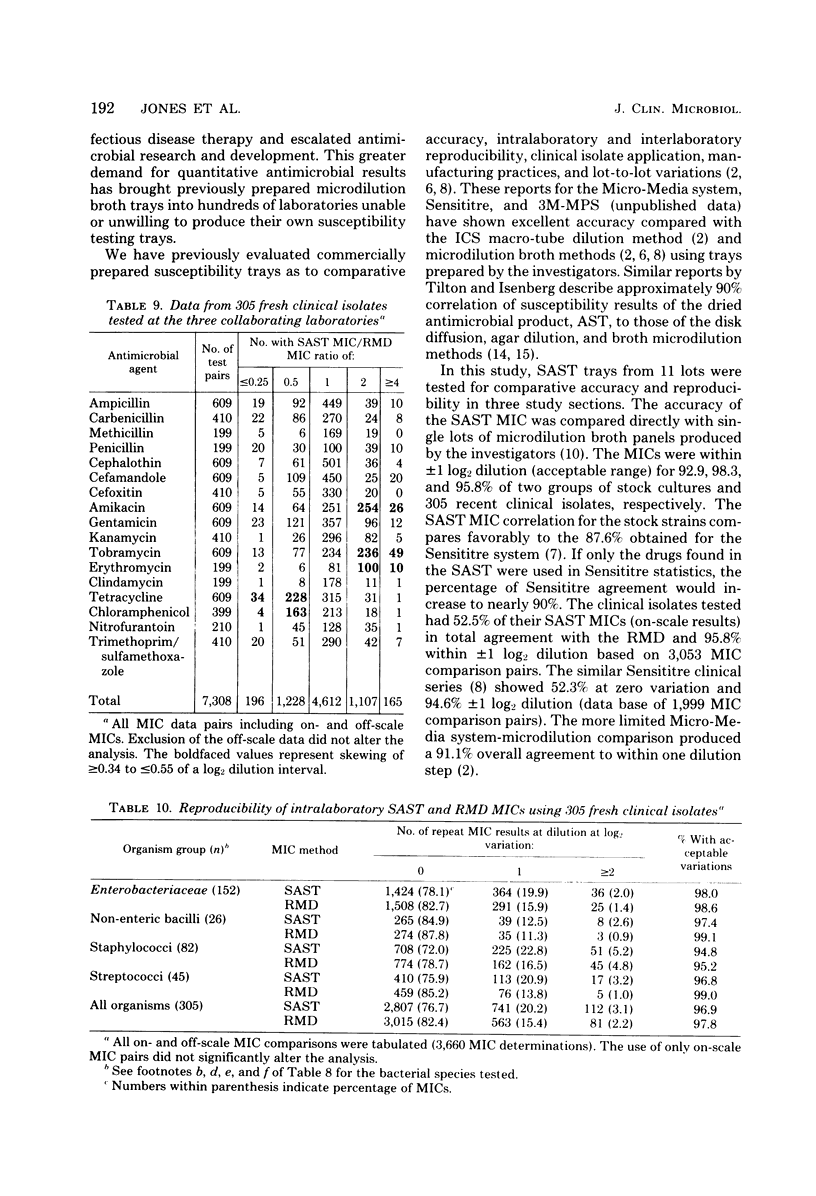
Abstract
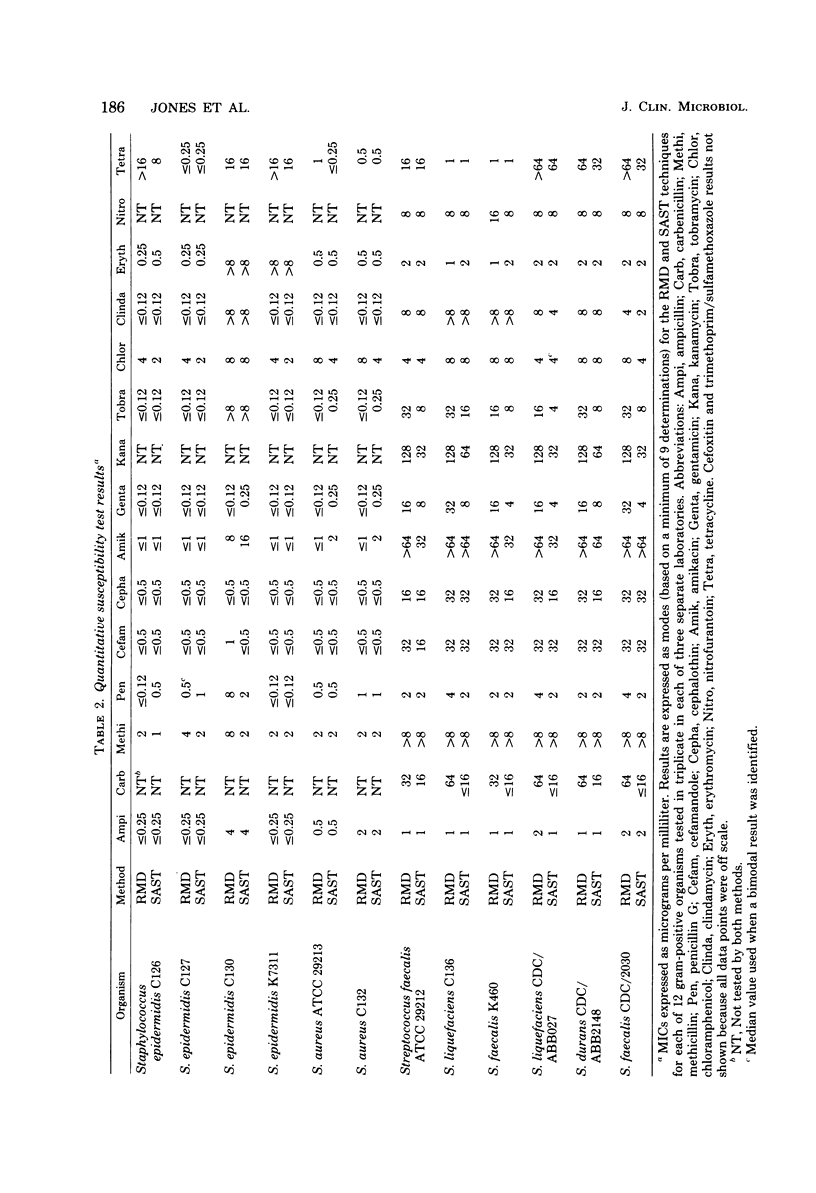
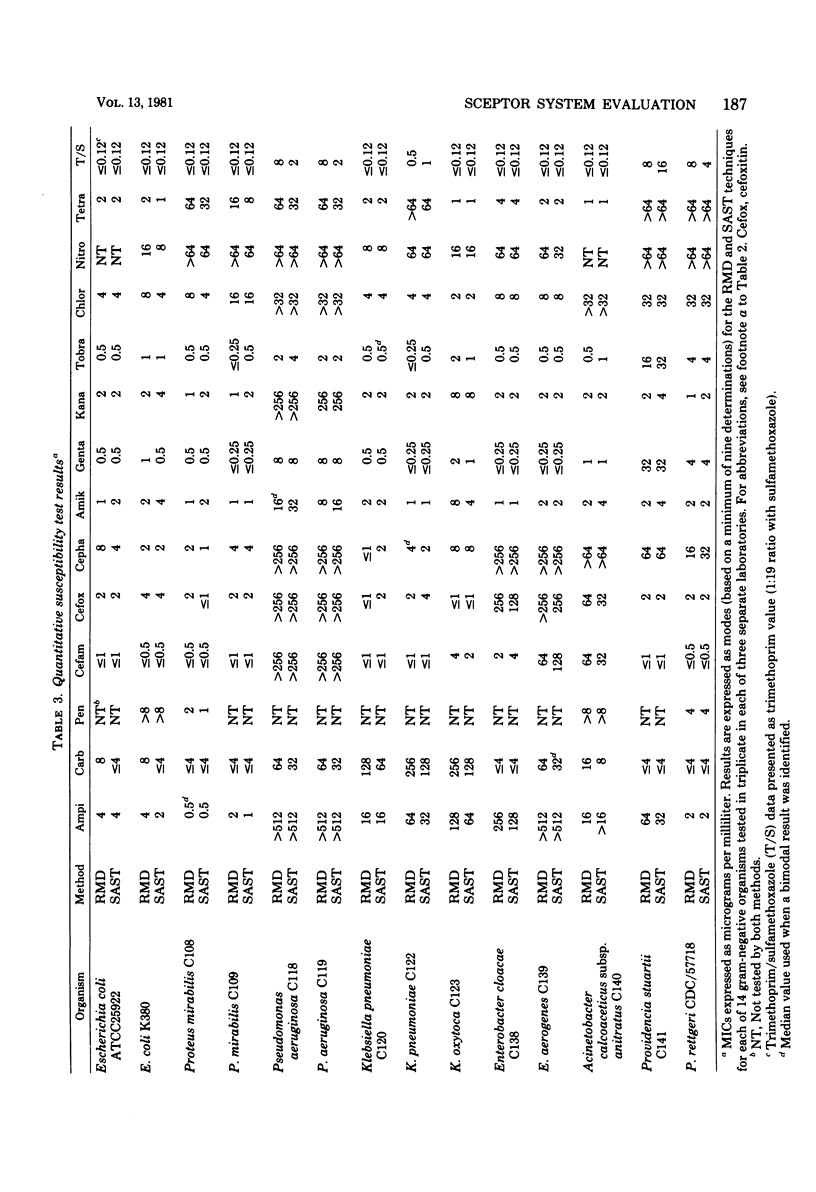
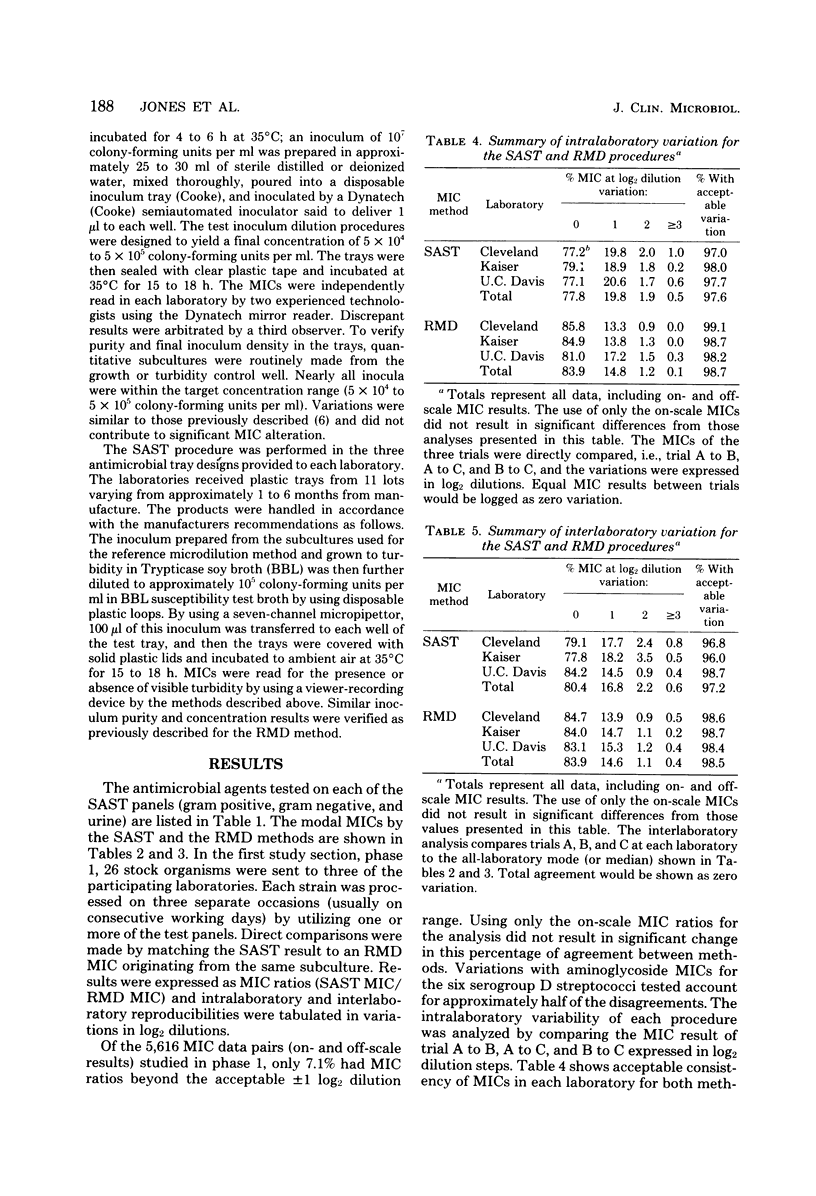
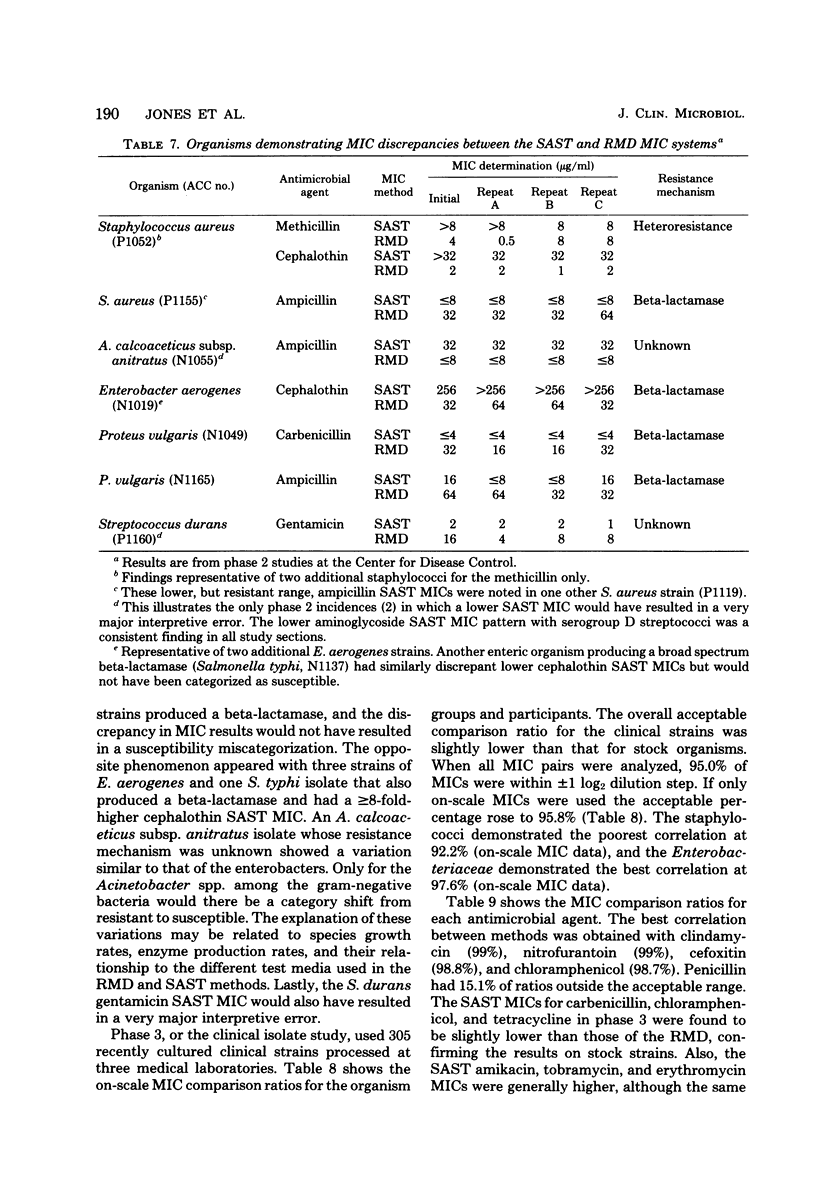
A multiwell, dried antimicrobial agent susceptibility test system, Sceptor (BBL Microbiology Systems, Cockeysville, Md.), was tested. The system was compared directly with a reference microdilution method by using two collections of stock cultures and 305 fresh clinical isolates. Sceptor was found to be in agreement (+/- log2 dilution) with the reference microdilution method in 96.9 to 98.3% of 9,840 minimal inhibitory concentration determinations performed on stock strains and 95.0% of 7,308 minimal inhibitory concentrations obtained from the clinical isolates. The intralaboratory and interlaboratory reproducibility on stock strains was 97.6 and 97.2%, respectively. The intralaboratory reproducibility for the clinical isolates was 96.9%. Sceptor accurately categorized representative challenge strains of methicillin-resistant staphylococci, beta-lactamase-producing bacteria, organisms producing other antimicrobial agent-inactivating enzymes, and permeability mutants as resistant. Only 0.2% very major errors (false-sensitive minimal inhibitory concentrations by Sceptor) were identified among the clinical isolate test results, the majority being clinically insignificant. The product is accurate and reliable, has a long shelf life, and seems applicable for routine use in clinical laboratories.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barry A. L., Jones R. N., Gavan T. L. Evaluation of the micro-media system for quantitative antimicrobial drug susceptibility testing: a collaborative study. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1978 Jan;13(1):61–69. doi: 10.1128/aac.13.1.61. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gavan T. L., Jones R. N., Barry A. L. Evaluation of the Sensititre system for quantitative antimicrobial drug susceptibility testing: a collaborative study. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Mar;17(3):464–469. doi: 10.1128/aac.17.3.464. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gavan T. L., Town M. A. A microdilution method for antibiotic susceptibility testing: an evaluation. Am J Clin Pathol. 1970 Jun;53(6):880–885. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/53.6.880. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones R. N., Gavan T. L., Barry A. L. Evaluation of the sensititre microdilution antibiotic susceptibility system against recent clinical isolates: three-laboratory collaborative study. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Apr;11(4):426–429. doi: 10.1128/jcm.11.4.426-429.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacLowry J. D., Marsh H. H. Semiautomatic microtechnique for serial dilution-antibiotic sensitivity testing in the clinical laboratory. J Lab Clin Med. 1968 Oct;72(4):685–687. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips I., Warren C., Waterworth P. M. Determination of antibiotic sensitivities by the Sensititre system. J Clin Pathol. 1978 Jun;31(6):531–535. doi: 10.1136/jcp.31.6.531. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thornsberry C., Gavan T. L., Sherris J. C., Balows A., Matsen J. M., Sabath L. D., Schoenknecht F., Thrupp L. D., Washington J. A., 2nd Laboratory evaluation of a rapid, automatic susceptibility testing system: report of a collaborative study. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1975 Apr;7(4):466–480. doi: 10.1128/aac.7.4.466. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tilton R. C., Isenberg H. D. Evaluation of the performance parameters of a prediluted, quantitative antibiotic susceptibility test device. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1977 Feb;11(2):271–276. doi: 10.1128/aac.11.2.271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tilton R. C., Isenberg H. D. In-use evaluation of a prediluted quantitative antibiotic susceptibility test device. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1977 Oct;12(4):470–473. doi: 10.1128/aac.12.4.470. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tilton R. C., Lieberman L., Gerlach E. H. Microdilution antibiotic susceptibility test: examination of certain variables. Appl Microbiol. 1973 Nov;26(5):658–665. doi: 10.1128/am.26.5.658-665.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



