Abstract
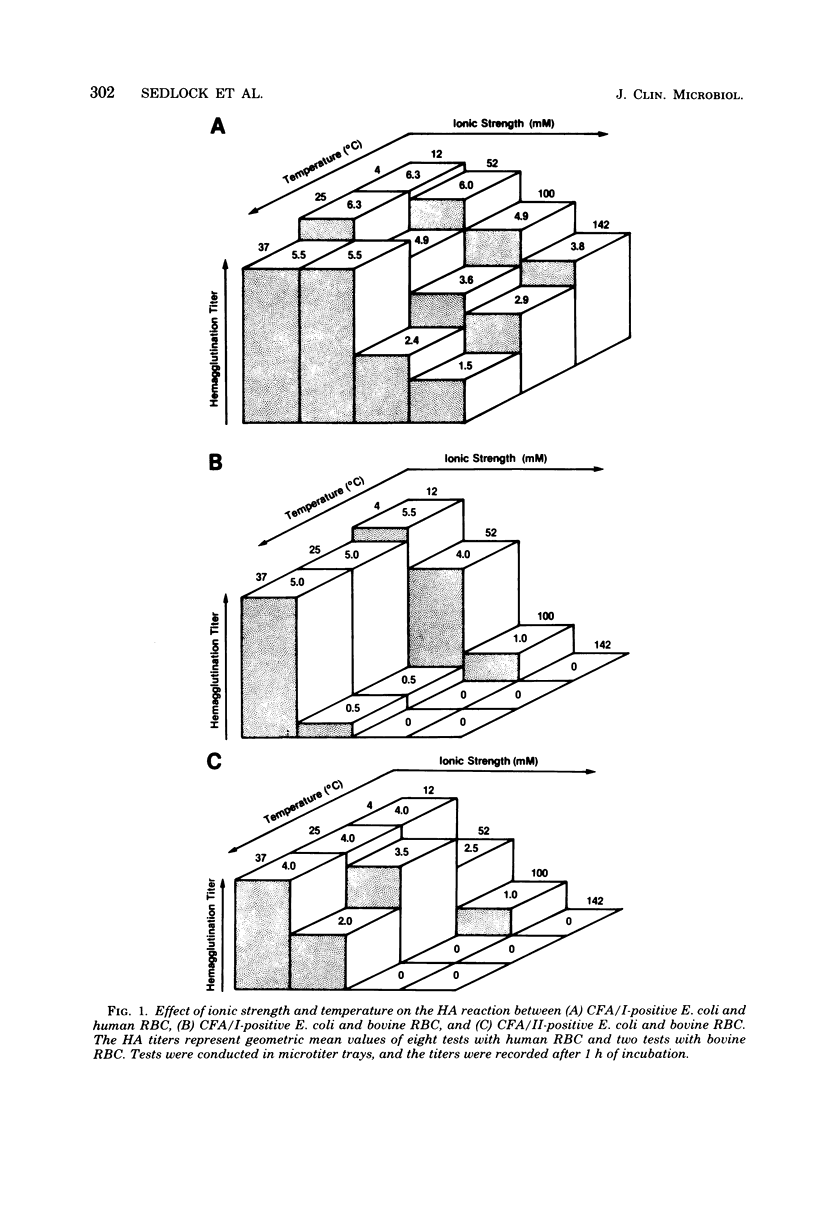
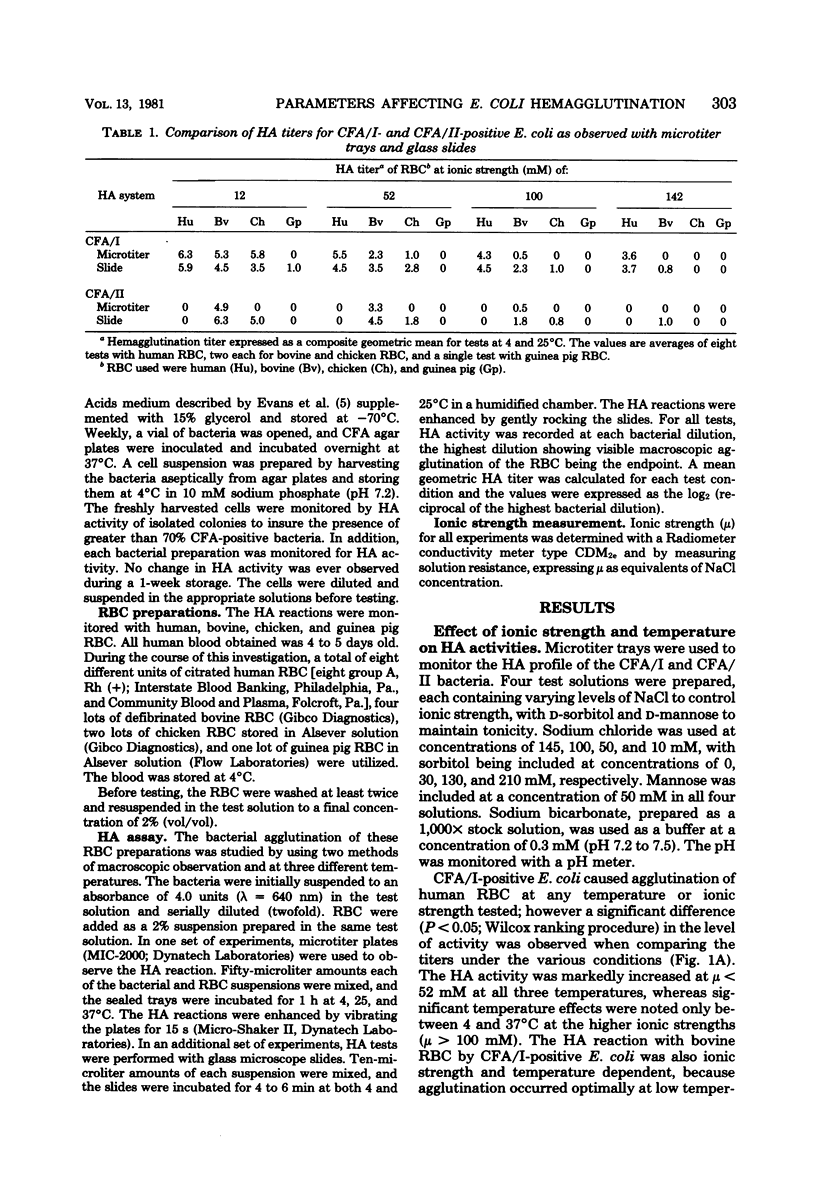
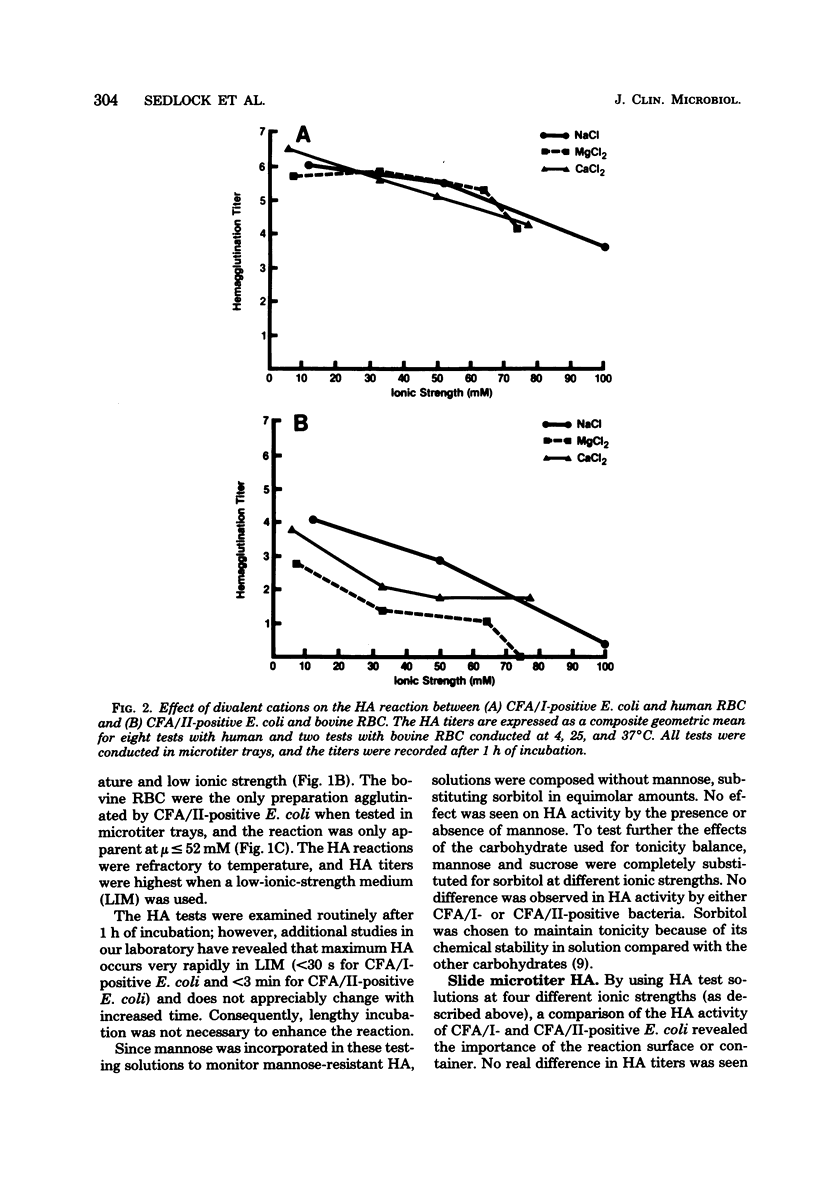
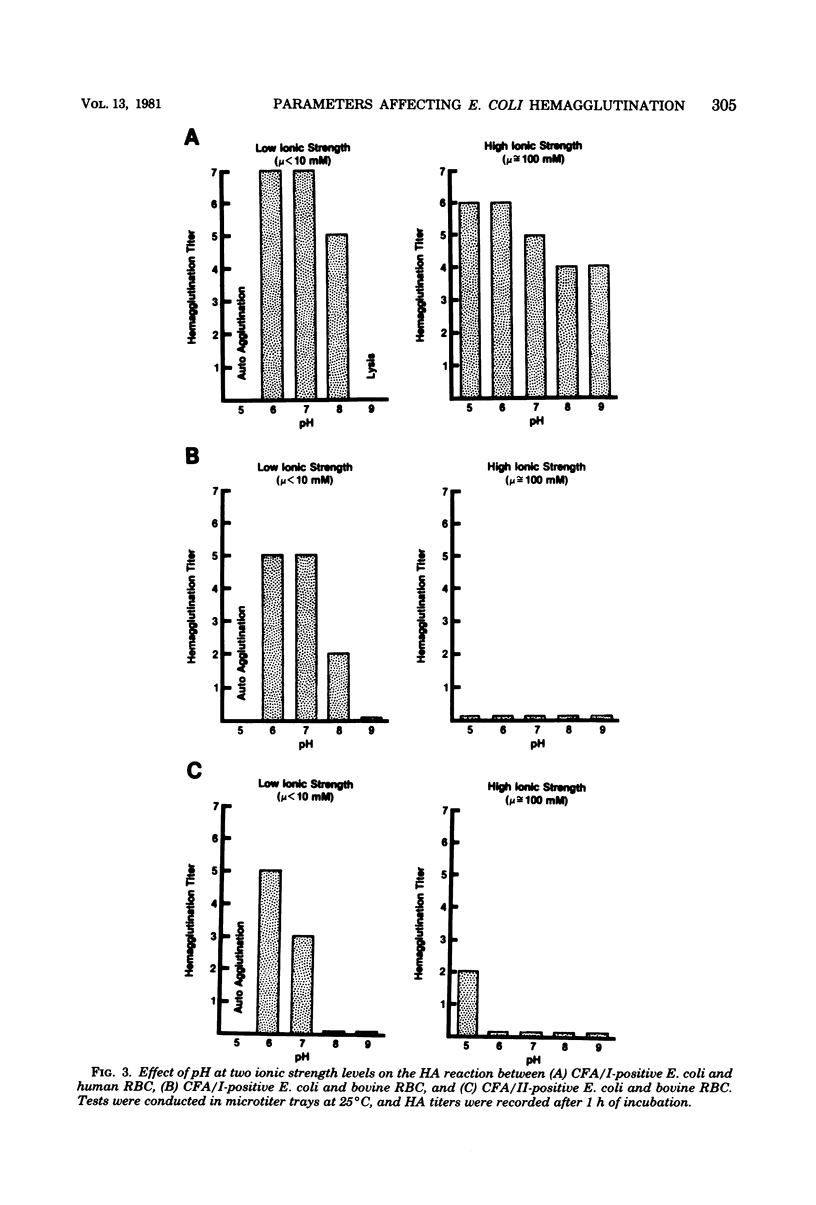
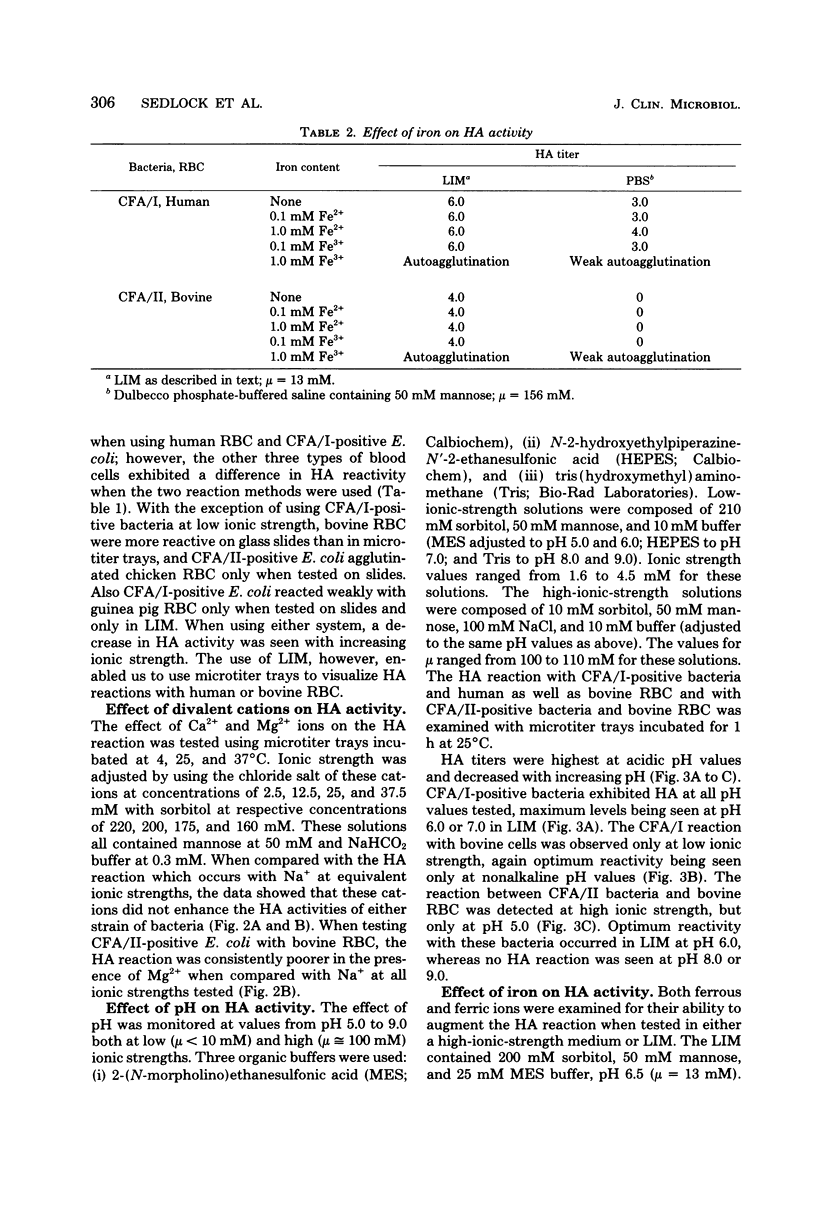
The hemagglutination (HA) activity of two strains of Escherichia coli, each possessing different colonization factor antigens (CFA), was examined under different test conditions. The effects of ionic strength, temperature, pH, cations, and reaction surface on erythrocyte (RBC) agglutination were analyzed. Strain H-10407 (CFA/I) caused the agglutination of human, bovine, and chicken RBC, whereas strain CL-9699 (CFA/II) agglutinated only bovine and chicken RBC. The HA activity of both strains increased with decreasing ionic strength, pH, and temperature, the effects of temperature being negligible at low ionic strength. When accounting for ionic strength, the presence of Ca2+, Mg2+, Fe2+, or Fe3+ ions did not increase the HA activity of these bacteria. Optimum conditions for HA of reactive RBC by bacteria included low ionic strength (less than 50 mM) and slightly acidic pH (6.0 to 7.0). Use of a low-ionic-strength medium permitted application of microtitration methods to visualize the HA reactions. Storage of RBC in low-ionic-strength medium did not change their HA properties, and the use of this medium proved superior to saline in overcoming HA variation observed with different preparations of RBC.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Deneke C. F., Thorne G. M., Gorbach S. L. Attachment pili from enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli pathogenic for humans. Infect Immun. 1979 Oct;26(1):362–368. doi: 10.1128/iai.26.1.362-368.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duguid J. P., Clegg S., Wilson M. I. The fimbrial and non-fimbrial haemagglutinins of Escherichia coli. J Med Microbiol. 1979 May;12(2):213–227. doi: 10.1099/00222615-12-2-213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans D. G., Evans D. J., Jr New surface-associated heat-labile colonization factor antigen (CFA/II) produced by enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli of serogroups O6 and O8. Infect Immun. 1978 Aug;21(2):638–647. doi: 10.1128/iai.21.2.638-647.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans D. G., Evans D. J., Jr, Tjoa W. Hemagglutination of human group A erythrocytes by enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli isolated from adults with diarrhea: correlation with colonization factor. Infect Immun. 1977 Nov;18(2):330–337. doi: 10.1128/iai.18.2.330-337.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans D. G., Silver R. P., Evans D. J., Jr, Chase D. G., Gorbach S. L. Plasmid-controlled colonization factor associated with virulence in Esherichia coli enterotoxigenic for humans. Infect Immun. 1975 Sep;12(3):656–667. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.3.656-667.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans D. J., Jr, Evans D. G. Three characteristics associated with enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli isolated from man. Infect Immun. 1973 Sep;8(3):322–328. doi: 10.1128/iai.8.3.322-328.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HEARD D. H., SEAMAN G. V. The influence of pH and ionic strength on the electrokinetic stability of the human erythrocyte membrane. J Gen Physiol. 1960 Jan;43:635–654. doi: 10.1085/jgp.43.3.635. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hahon N., Booth J. A., Eckert H. L. Cell attachment and penetration by influenza virus. Infect Immun. 1973 Mar;7(3):341–351. doi: 10.1128/iai.7.3.341-351.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heckels J. E., Blackett B., Everson J. S., Ward M. E. The influence of surface charge on the attachment of Neisseria gonorrhoeae to human cells. J Gen Microbiol. 1976 Oct;96(2):359–364. doi: 10.1099/00221287-96-2-359. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James A. N., Knox J. M., Williams R. P. Attachment of gonococci to sperm. Influence of physical and chemical factors. Br J Vener Dis. 1976 Apr;52(2):128–135. doi: 10.1136/sti.52.2.128. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jan K. M., Chien S. Influence of the ionic composition of fluid medium on red cell aggregation. J Gen Physiol. 1973 May;61(5):655–668. doi: 10.1085/jgp.61.5.655. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones G. W., Rutter J. M. The association of K88 antigen with haemagglutinating activity in porcine strains of Escherichia coli. J Gen Microbiol. 1974 Sep;84(1):135–144. doi: 10.1099/00221287-84-1-135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jørgensen J., Nielsen M., Nielsen C. B., Nørmark J. The influence of ionic strength, albumin and incubation time on the sensitivity of the indirect Coombs' test. Vox Sang. 1979;36(3):186–191. doi: 10.1111/j.1423-0410.1979.tb04422.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore H. C., Mollison P. L. Use of a low-ionic-strength medium in manual tests for antibody detection. Transfusion. 1976 Jul-Aug;16(4):291–296. doi: 10.1046/j.1537-2995.1976.16476247048.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ochoa J. L. The mechanisms of lectin-mediated cell agglutination. Pathol Biol (Paris) 1979 Feb;27(2):103–113. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orskov I., Orskov F. Special O:K:H serotypes among enterotoxigenic E. coli strains from diarrhea in adults and children. Occurrence of the CF (colonization factor) antigen and of hemagglutinating abilities. Med Microbiol Immunol. 1977 Jul 18;163(2):99–110. doi: 10.1007/BF02121825. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierce J. S., Strauss E. G., Strauss J. H. Effect of ionic strength on the binding of Sindbis virus to chick cells. J Virol. 1974 May;13(5):1030–1036. doi: 10.1128/jvi.13.5.1030-1036.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg M. L., Koplan J. P., Wachsmuth I. K., Wells J. G., Gangarosa E. J., Guerrant R. L., Sack D. A. Epidemic diarrhea at Crater Lake from enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. A large waterborne outbreak. Ann Intern Med. 1977 Jun;86(6):714–718. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-86-6-714. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenfield R. E., Shaikh S. H., Innella F., Kaczera Z., Kochwa S. Augmentation of hemagglutination by low ionic conditions. Transfusion. 1979 Sep-Oct;19(5):499–510. doi: 10.1046/j.1537-2995.1979.19580059800.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnebli H. P., Roeder C., Tarcsay L. Reaction of lectins with human erythrocytes. III. Surface charge density and agglutination. Exp Cell Res. 1976 Mar 15;98(2):273–276. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(76)90438-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schott H., Young C. Y. Electrokinetic studies of bacteria. I. Effect of nature, ionic strength, and pH of buffer solutions on electrophoretic mobility of Streptococcus faecalis and Escherichia coli. J Pharm Sci. 1972 Feb;61(2):182–187. doi: 10.1002/jps.2600610208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Oss C. J., Mohn J. F., Cunningham R. K. Influence of various physicochemical factors on hemagglutination. Vox Sang. 1978;34(6):351–361. doi: 10.1111/j.1423-0410.1978.tb02890.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


