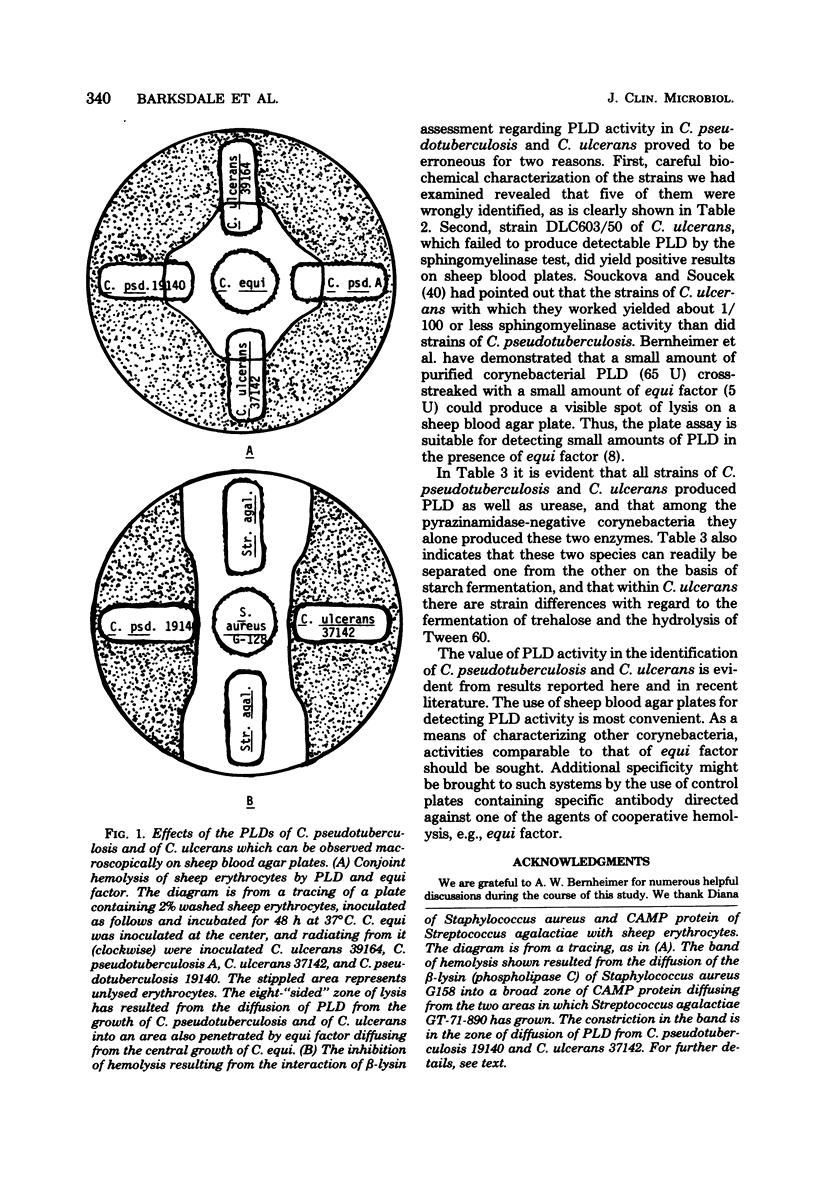
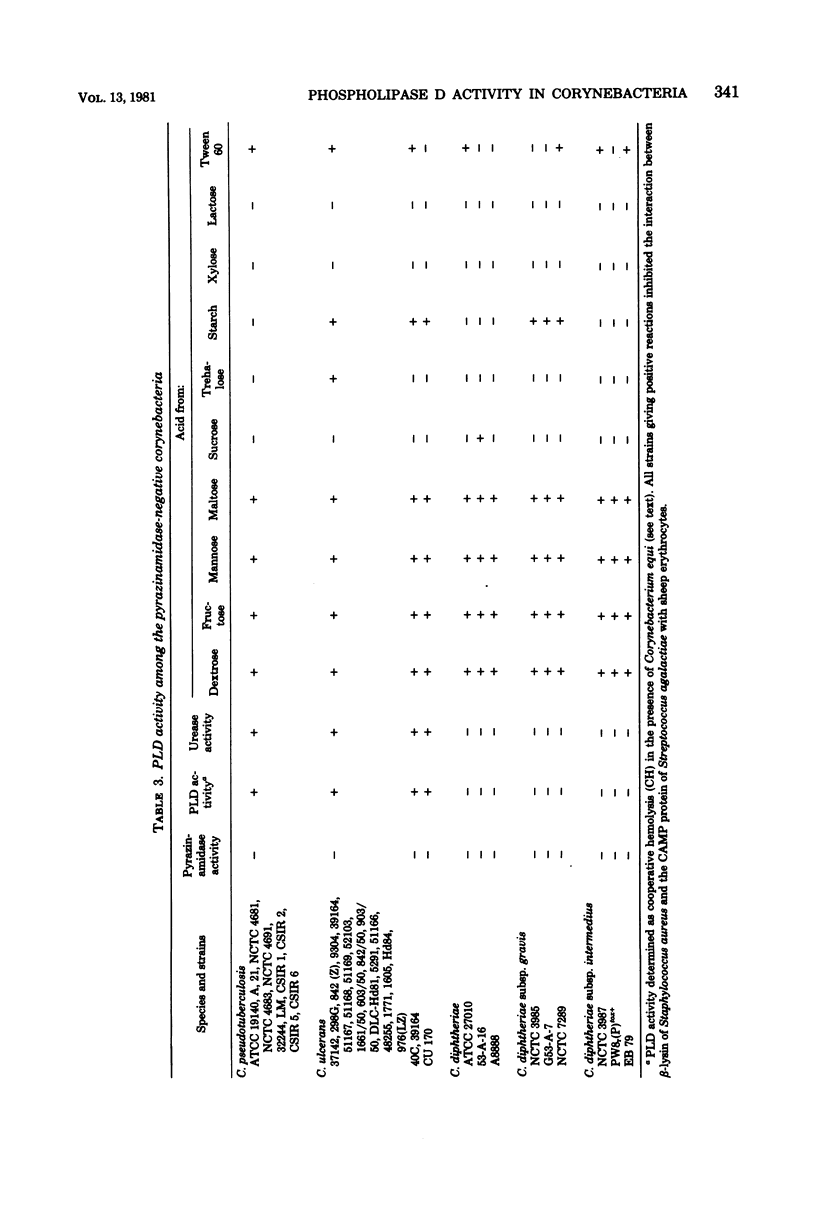
Abstract
A search has been made for corynebacterial phospholipase D, "ovis toxin," a sphingomyelinase (phosphatidylcholine phosphohydrolase, EC 3.1.4.4), among a wide variety of corynebacteria. Phospholipase D activity has been found in strains exhibiting the biochemical properties characteristic of Corynebacterium pseudotuberculosis or of Corynebacterium ulcerans and in no other species of Corynebacterium. Methods for the assay of phospholipase D as a sphingomyelinase and methods for screening for phospholipase D in the presence of Corynebacterium equi on washed sheep blood agar are discussed.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BARKSDALE W. L., LI K., CUMMINS C. S., HARRIS H. The mutation of Corynebacterium pyogenes to Corynebacterium haemolyticum. J Gen Microbiol. 1957 Jun;16(3):749–758. doi: 10.1099/00221287-16-3-749. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BERNHEIMER A. W., SCHWARTZ L. L. Isolation and composition of staphylococcal alpha toxin. J Gen Microbiol. 1963 Mar;30:455–468. doi: 10.1099/00221287-30-3-455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barksdale L. Corynebacterium diphtheriae and its relatives. Bacteriol Rev. 1970 Dec;34(4):378–422. doi: 10.1128/br.34.4.378-422.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernheimer A. W., Avigad L. S., Kim K. S. Staphylococcal sphingomyelinase (beta-hemolysin). Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1974 Jul 31;236(0):292–306. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1974.tb41499.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernheimer A. W., Linder R., Avigad L. S. Stepwise degradation of membrane sphingomyelin by corynebacterial phospholipases. Infect Immun. 1980 Jul;29(1):123–131. doi: 10.1128/iai.29.1.123-131.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown J., Farnsworth R., Wannamaker L. W., Johnson D. W. CAMP factor of group B streptococci: production, assay, and neutralization by sera from immunized rabbits and experimentally infected cows. Infect Immun. 1974 Feb;9(2):377–383. doi: 10.1128/iai.9.2.377-383.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRASER G. Haemolytic activity of Corynebacterium ovis. Nature. 1961 Jan 21;189:246–246. doi: 10.1038/189246a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRASER G. THE EFFECT ON ANIMAL ERYTHROCYTES OF COMBINATIONS OF DIFFUSIBLE SUBSTANCES PRODUCED BY BACTERIA. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1964 Jul;88:43–53. doi: 10.1002/path.1700880105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furness G., Evangelista A. T. A diagnostic key employing biological reactions for differentiating pathogenic Corynebacterium genitalium (NSU corynebacteria) from commensals of the urogenital tract. Invest Urol. 1978 Jul;16(1):1–4. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goel M. C., Singh I. P. Purification and characterization of Corynebacterium ovis exotoxin. J Comp Pathol. 1972 Jul;82(3):345–353. doi: 10.1016/0021-9975(72)90016-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HARTWIGK H. ANTIHAEMOLYSINBILDUNG BEIM TIER VORKOMMENDER BETA-HAEMOLYTISCHER CORYNEBAKTERIEN. Zentralbl Bakteriol Orig. 1963 Dec;191:274–280. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HENRIKSEN S. D., GRELLAND R. Toxigenicity, serological reactions and relationships of the diphtheria-like Corynebacteria. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1952 Jul;64(3):503–511. doi: 10.1002/path.1700640310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOWARD D. H., JANN G. J. The isolation and characterization of bacteriophage active against the diphtheria-like corynebacteria. J Bacteriol. 1954 Sep;68(3):316–319. doi: 10.1128/jb.68.3.316-319.1954. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumazawa N., Yanagawa R. DNA base compositions of the three types of Coryneb-acterium renale. Jpn J Vet Res. 1969 Dec;17(4):115–120. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lampidis T., Barksdale L. Park-Williams number 8 strain of Corynebacterium diphtheriae. J Bacteriol. 1971 Jan;105(1):77–85. doi: 10.1128/jb.105.1.77-85.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanéelle M. A., Asselineau J. Glycolipids of brevibacterium vitarumen. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Jan 18;486(1):205–208. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(77)90085-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linder R., Bernheimer A. W. Effect on sphingomyelin-containing liposomes of phospholipase D from Corynebacterium ovis and the cytolysin from Stoichactis helianthus. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Aug 25;530(2):236–246. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(78)90009-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linder R., Bernheimer A. W., Kim K. S. Interaction between sphingomyelin and a cytolysin from the sea anemone Stoichactis helianthus. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Jun 16;467(3):290–300. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(77)90306-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lovell R., Zaki M. M. Studies on growth products of Corynebacterium ovis. I. The exotoxin and its lethal action on white mice. Res Vet Sci. 1966 Jul;7(3):302–306. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lovell R., Zaki M. M. Studies on growth products of Corynebacterium ovis. II. Other activities and their relationship. Res Vet Sci. 1966 Jul;7(3):307–311. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maximesco P., Pop A., Oprişan A., Potorac E. Relations biologiques entre Corynebacterium ulcerans, Corynebacterium ovis et Corynebacterium diphtheriae. (Etude expérimentale) Arch Roum Pathol Exp Microbiol. 1968 Dec;27(4):733–750. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maximescu P., Oprişan A., Pop A., Potorac E. Further studies on Corynebacterium species capable of producing diphtheria toxin (C. diphtheriae, C. ulcerans, C. ovis). J Gen Microbiol. 1974 May;82(1):49–56. doi: 10.1099/00221287-82-1-49. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meitert E., Saragea A., Petrovici A., Ionescu M. Studies on the host phage systems of Corynebacterium hofmanni species. Arch Roum Pathol Exp Microbiol. 1972 Mar;31(1):31–37. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson J. B. Response of mice to Corynebacterium kutscheri on footpad injection. Lab Anim Sci. 1973 Jun;23(3):370–372. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PARSONS E. I. Induction of toxigenicity in non-toxigenic strains of C. diphtheriae with bacteriophages derived from non-toxigenic strains. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1955 Oct;90(1):91–93. doi: 10.3181/00379727-90-21948. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saragea A., Maximescu P., Meitert E., Stuparu I., Vieru E., Petruş V., Bălteanu C. Incidenţa şi distribuţia geografică a tipurilor fagice DE Corynebacterium diphtheriae în dinamica procesului epidemic al difteriei în republica socialistă România. Microbiol Parazitol Epidemiol (Bucur) 1966 Jul-Aug;11(4):351–362. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soucek A., Michalec C., Soucková A. Identification and characterization of a new enzyme of the group "phospholipase D" isolated from Corynebacterium ovis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Jan 13;227(1):116–128. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(71)90173-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soucek A., Soucková A., Patocka F. Inhibition of the activity of alpha-toxin of Clostridium perfringens by toxic filtrates of corynebacteria. J Hyg Epidemiol Microbiol Immunol. 1967;11(1):123–124. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soucek A., Soucková A. Toxicity of bacterial sphingomyelinases D. J Hyg Epidemiol Microbiol Immunol. 1974;18(3):327–335. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soucková A., Soucek A. Inhibition of the hemolytic action of and lysins of Staphylococcus pyogenes by Corynebacterium hemolyticum, C. ovis and C. ulcerans. Toxicon. 1972 Aug;10(5):501–509. doi: 10.1016/0041-0101(72)90176-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soucková A., Soucek A. Two distinct toxic proteins in Corynebacterium ulcerans. J Hyg Epidemiol Microbiol Immunol. 1974;18(3):336–341. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toshach S., Valentine A., Sigurdson S. Bacteriophage typing of Corynebacterium diphtheriae. J Infect Dis. 1977 Nov;136(5):655–660. doi: 10.1093/infdis/136.5.655. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welby-Gieusse M., Lanéelle M. A., Asselineau J. Structure des acides corynomycoliqes de Corynebacterium hofmanii et leur implication biogénétique. Eur J Biochem. 1970 Mar 1;13(1):164–167. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1970.tb00913.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanagawa R. A numerical taxonomic study of the strains of three types of Corynebacterium renale. Can J Microbiol. 1975 Jun;21(6):824–827. doi: 10.1139/m75-122. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ZAKI M. M. PRODUCTION OF A SOLUBLE SUBSTANCE BY CORYNEBACTERIUM OVIS. Nature. 1965 Feb 27;205:928–929. doi: 10.1038/205928a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


