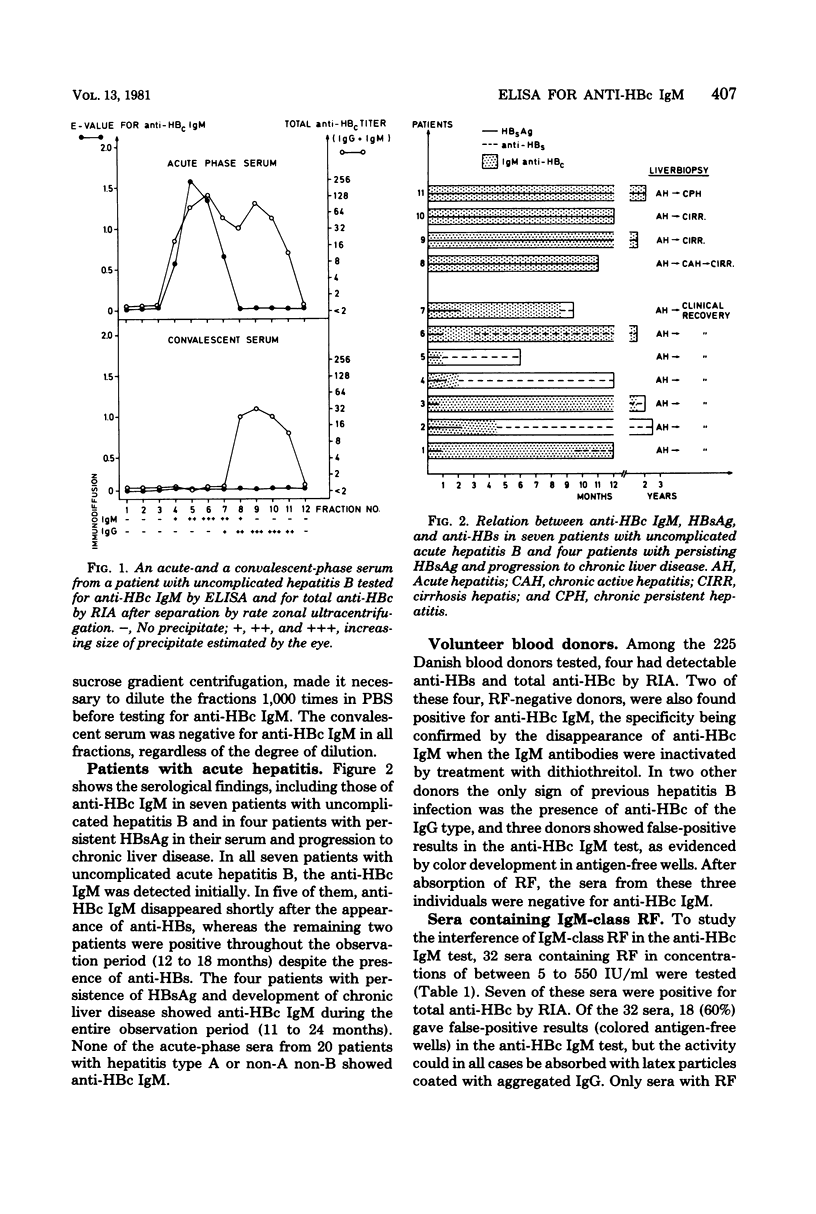
Abstract
An enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for detection of specific immunoglobulin M (IgM) antibodies against the core antigen of the hepatitis B virus (anti-HBc IgM) is described. The interference of IgM rheumatoid factor was evaluated quantitatively. In the anti-HBc IgM test, the rheumatoid factor gave false-positive results when the concentration exceeded 20 IU/ml. The rheumatoid-positive sera were disclosed by a control and retested for anti-HBc IgM after absorption of rheumatoid factor with latex particles aggregated with human IgG. In five of seven selected patients with acute hepatitis B followed to biochemical and clinical recovery, anti-HBc IgM was present transiently until antibodies against hepatitis B surface antigen (anti-HBs) appeared. Two patients had persistent anti-HBc IgM during the follow-up period. Four patients with hepatitis B surface antigenemia and progression to chronic liver disease did not clear their anti-HBc IgM in the period of observation (11 to 24 months). Anti-HBc IgM could not be demonstrated in 223 of 225 Danish blood donors. The two donors found positive for anti-HBc IgM also had anti-HBs. Twenty patients with acute A or non-A non-B hepatitis were negative for anti-HBc IgM. The enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for anti-HBc IgM described here has a high specificity and sensitivity. The diagnostic relevance needs further evaluation, including quantitation of anti-HBc IgM, but the results presented indicate that anti-HBc IgM may be helpful in differentiating between prior and recent or ongoing hepatitis B infection.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cohen B. J. The IgM antibody responses to the core antigen of hepatitis B virus. J Med Virol. 1978;3(2):141–149. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890030208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duermeyer W., Wielaard F., van der Veen J. A new principle for the detection of specific IgM antibodies applied in an ELISA for hepatitis A. J Med Virol. 1979;4(1):25–32. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890040104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerlich W. H., Lüer W. Selective detection of IgM-antibody against core antigen of the hepatitis B virus by a modified enzyme immune assay. J Med Virol. 1979;4(3):227–238. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890040308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansson B. G. Age- and sex-related distribution of antibodies to hepatitis B surface and core antigens in a Swedish population. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B. 1976 Dec;84B(6):342–346. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1976.tb01951.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoofnagle J. H., Gerety R. J., Ni L. Y., Barker L. F. Antibody to hepatitis B core antigen. A sensitive indicator of hepatitis B virus replication. N Engl J Med. 1974 Jun 13;290(24):1336–1340. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197406132902402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoofnagle J. H., Seeff L. B., Bales Z. B., Zimmerman H. J. Type B hepatitis after transfusion with blood containing antibody to hepatitis B core antigen. N Engl J Med. 1978 Jun 22;298(25):1379–1383. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197806222982502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Locarnini S. A., Coulepis A. G., Stratton A. M., Kaldor J., Gust I. D. Solid-phase enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for detection of hepatitis A-specific immunoglobulin M. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Apr;9(4):459–465. doi: 10.1128/jcm.9.4.459-465.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathiesen L. R., Feinstone S. M., Wong D. C., Skinhoej P., Purcell R. H. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for detection of hepatitis A antigen in stool and antibody to hepatitis A antigen in sera: comparison with solid-phase radioimmunoassay, immune electron microscopy, and immune adherence hemagglutination assay. J Clin Microbiol. 1978 Feb;7(2):184–193. doi: 10.1128/jcm.7.2.184-193.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Møller A. M., Mathiesen L. R. Detection of immunoglobulin M antibodies to hepatitis A virus by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Nov;10(5):628–632. doi: 10.1128/jcm.10.5.628-632.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niermeiier P., Gips C. H., Huizenga J. R., Ringers J., Verkerk S., Houthuff H. J., Houwen B., Snijder J. A., Nielsen J. O. IgM-anti-HBc as a marker of persistent and IgG-anti-HBc as a marker of past hepatitis B infection. A longitudinal study over 5 years. Acta Hepatogastroenterol (Stuttg) 1978 Oct;25(5):360–364. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Omata M., Afroudakis A., Liew C. T., Ashcavai M., Peters R. L. Comparison of serum hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg) and serum anticore with tissue HBsAg and hepatitis B core antigen (HBcAg). Gastroenterology. 1978 Dec;75(6):1003–1009. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schrohenloher R. E. Copper-catalysed reoxidation of human monoclonal IgM. Scand J Immunol. 1978;8(5):443–449. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1978.tb00540.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vejtorp M., Fanøe E., Leerhoy J. Diagnosis of postnatal rubella by the enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for rubella IgM and IgG antibodies. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B. 1979 Jun;87B(3):155–160. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1979.tb02419.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vejtorp M., Høier-Madsen M., Halberg P. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for determination of IgM rheumatoid factor. Scand J Rheumatol. 1979;8(2):65–70. doi: 10.3109/03009747909105338. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yolken R. H., Wyatt R. G., Kim H. W., Kapikian A. Z., Chanock R. M. Immunological response to infection with human reovirus-like agent: measurement of anti-human reovirus-like agent immunoglobulin G and M levels by the method of enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Infect Immun. 1978 Feb;19(2):540–546. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.2.540-546.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


