Abstract
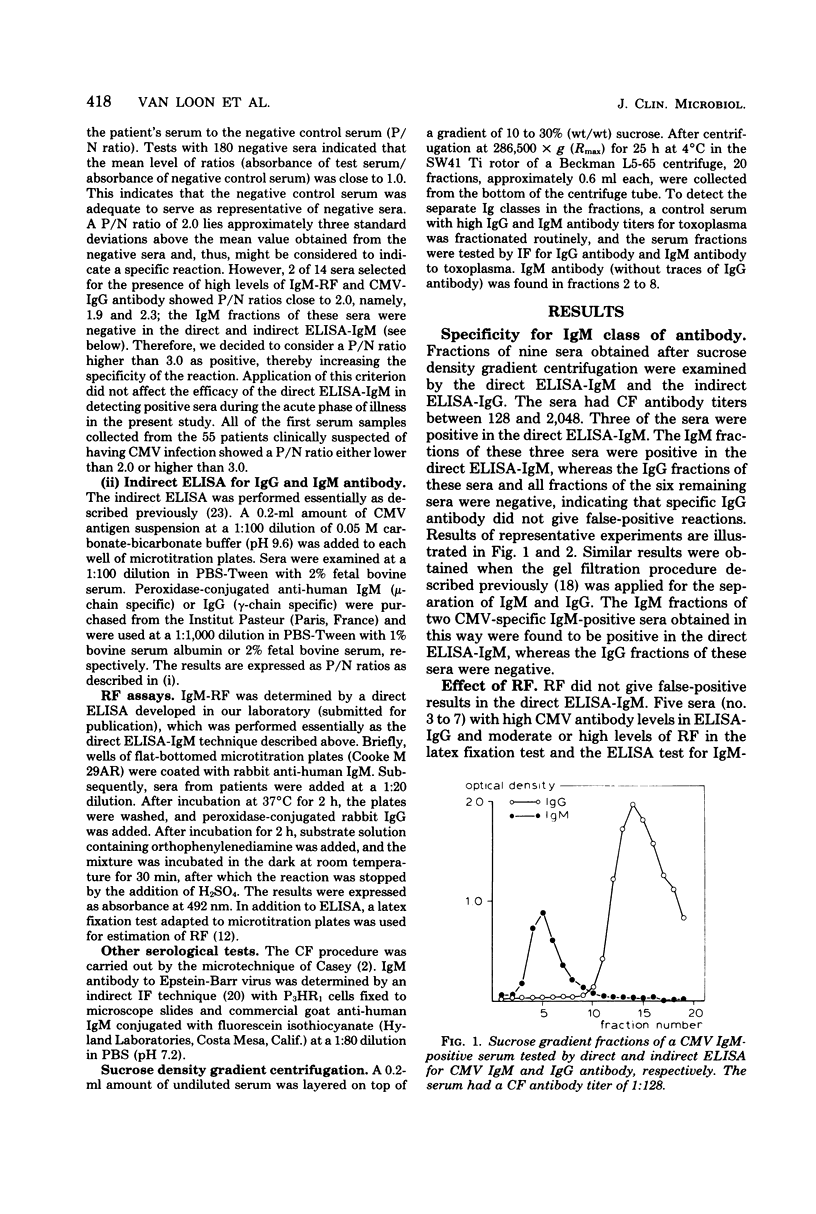
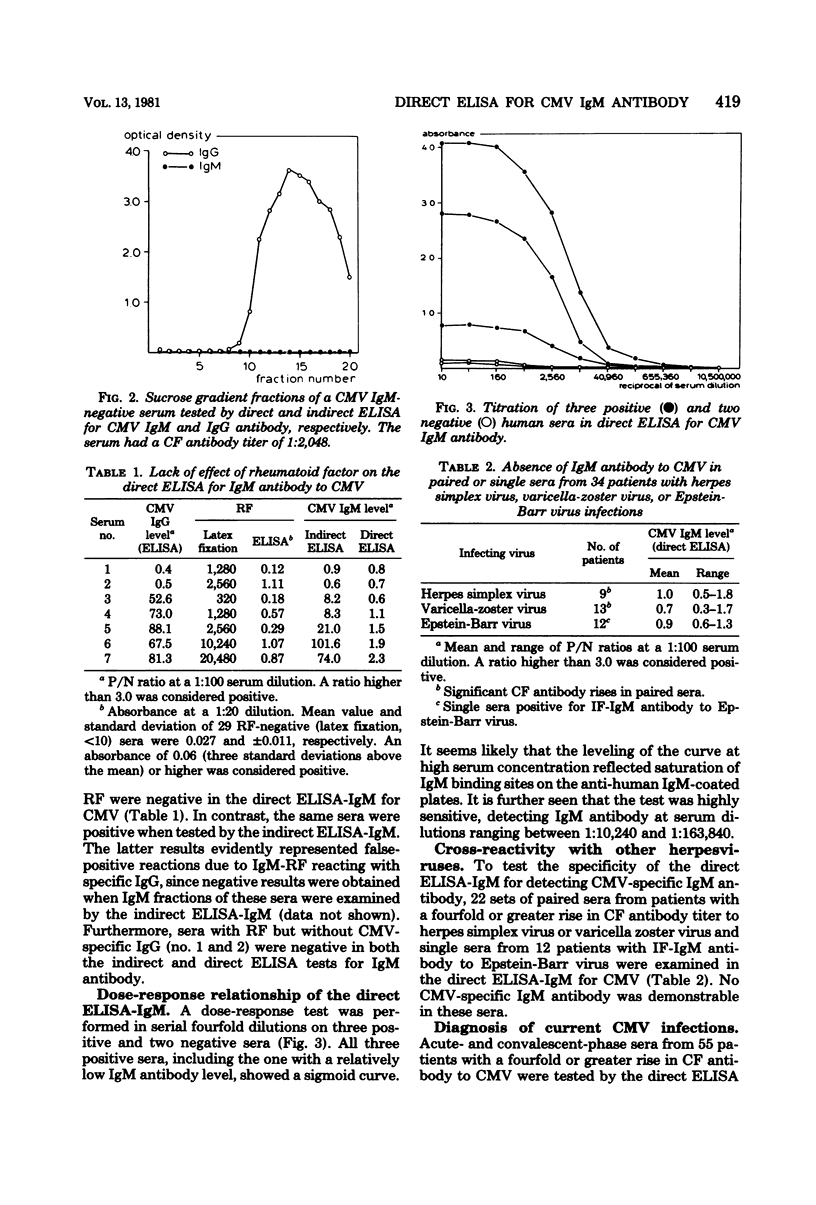
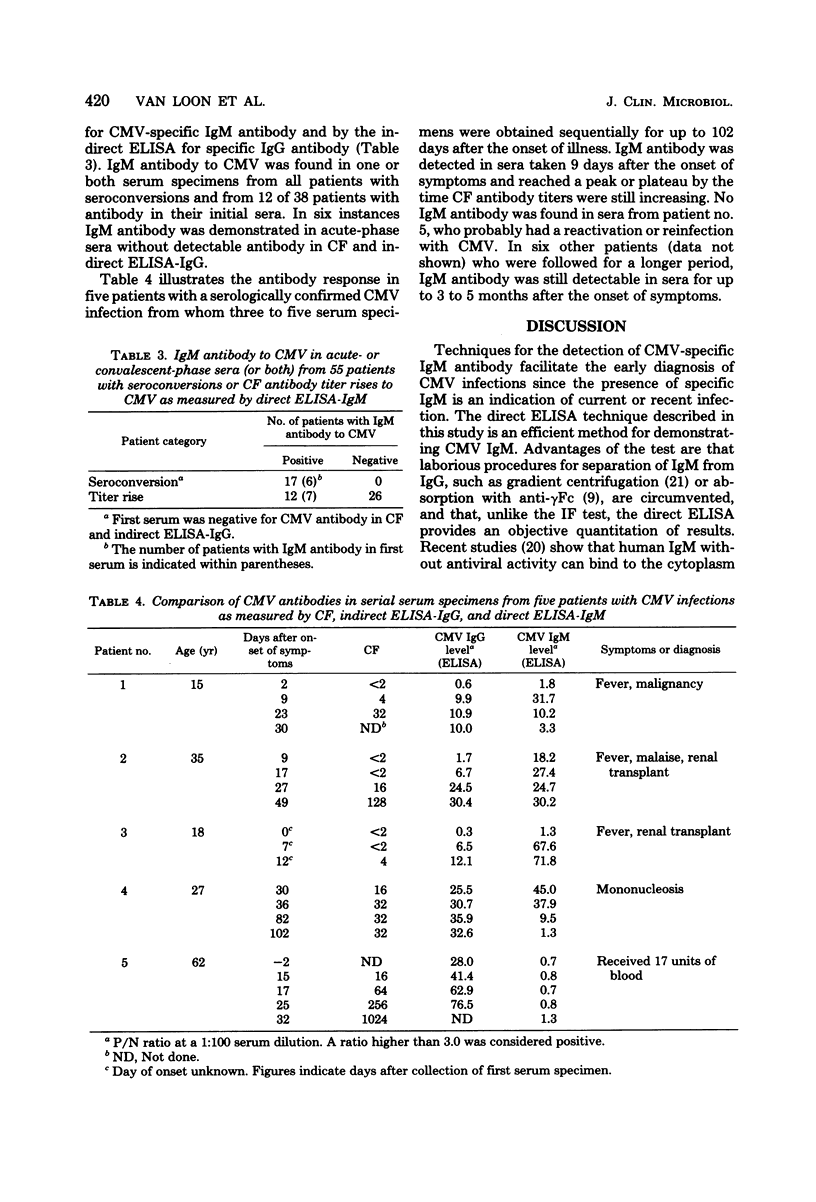
A direct enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay was developed for the measurement of immunoglobulin M (IgM) antibody to cytomegalovirus (CMV). Wells of microtiter plates were coated with anti-human IgM. Each patient's serum was added at a dilution of 1:100, and IgM from the serum was allowed to react with anti-human IgM. The amount of CMV-specific IgM antibody bound was determined by measuring the intensity of color change after the addition of peroxidase-labeled CMV antigen and substrate. Nuclei of infected cells served as an antigen source. CMV IgM could be detected only in IgM fractions of sera from patients with a recent CMV infection. Rheumatoid factor did not cause false-positive results. No cross-reactions were observed when paired sera from 22 patients with herpes simplex or varicella and single sera from 12 patients with suspected infectious mononucleosis were tested by the direct enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Each of 17 patients with a seroconversion for CMV antibody showed CMV-specific IgM antibody. In six of these patients the antibody was detected in the initial serum. The direct enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for CMV IgM is a specific and sensitive test for the diagnosis of recent CMV infections and possesses distinct advantages over indirect tests.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cappel R., de Cuyper F., de Braekeleer J. Rapid detection of IgG and IgM antibodies for cytomegalovirus by the enzyme linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Arch Virol. 1978;58(3):253–258. doi: 10.1007/BF01317608. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cremer N. E., Hoffman M., Lennette E. H. Role of rheumatoid factor in complement fixation and indirect hemagglutination tests for immunoglobulin M antibody to cytomegalovirus. J Clin Microbiol. 1978 Aug;8(2):160–165. doi: 10.1128/jcm.8.2.160-165.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duermeyer W., van der Veen J. Specific detection of IgM-antibodies by ELISA, applied in hepatitis-A. Lancet. 1978 Sep 23;2(8091):684–685. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(78)92802-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flehmig B., Ranke M., Berthold H., Gerth H. J. A solid-phase radioimmunoassay for detection of IgM antibodies to hepatitis A virus. J Infect Dis. 1979 Aug;140(2):169–175. doi: 10.1093/infdis/140.2.169. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanshaw J. B., Niederman J. C., Chessin L. N. Cytomegalovirus macroglobulin in cell-associated herpesvirus infections. J Infect Dis. 1972 Mar;125(3):304–306. doi: 10.1093/infdis/125.3.304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanshaw J. B., Steinfeld H. J., White C. J. Fluorescent-antibody test for cytomegalovirus macroglobulin. N Engl J Med. 1968 Sep 12;279(11):566–570. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196809122791102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hekker A. C., Brand-Saathof B., Vis J., Meijers R. C. Indirect immunofluorescence test for detection of IgM antibodies to cytomegalovirus. J Infect Dis. 1979 Oct;140(4):596–600. doi: 10.1093/infdis/140.4.596. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heni N., Glogner P., Schmitz H. Klinik und Diagnostik der akuten Cytomegalie-Infektion bei primär gesunden Erwachsenen. Klin Wochenschr. 1976 Dec 1;54(23):1117–1124. doi: 10.1007/BF01469255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kettering J. D., Schmidt N. J., Lennette E. H. Improved glycine-extracted complement-fixing antigen for human cytomegalovirus. J Clin Microbiol. 1977 Dec;6(6):647–649. doi: 10.1128/jcm.6.6.647-649.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein F., Bronsveld W., Norde W., Van Romunde L. K., Singer J. M. A modified latex-fixation test for the detection of rheumatoid factors. J Clin Pathol. 1979 Jan;32(1):90–92. doi: 10.1136/jcp.32.1.90. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knez V., Stewart J. A., Ziegler D. W. Cytomegalovirus specific IgM and IgG response in humans studied by radioimmunoassay. J Immunol. 1976 Nov;117(5 PT2):2006–2013. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krech U., Wilhelm J. A. A solid-phase immunosorbent technique for the rapid detection of rubella IgM by haemagglutination inhibition. J Gen Virol. 1979 Aug;44(2):281–286. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-44-2-281. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langenhuysen M. M., The T. H., Nieweg H. O., Kapsenberg J. G. Demonstration of IgM cytomegalovirus-antibodies as an aid to early diagnosis in adults. Clin Exp Immunol. 1970 Mar;6(3):387–393. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagington J. Cytomegalovirus antibody production in renal transplant patients. J Hyg (Lond) 1971 Dec;69(4):645–660. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400021926. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price P. C. Direct radioimmunoassay for the detection of IgM antibodies against Mycoplasma pneumoniae. J Immunol Methods. 1980;32(3):261–273. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(80)90191-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pyndiah N., Krech U., Price P., Wilhelm J. Simplified chromatographic separation of immunoglobulin M from G and its application to toxoplasma indirect immunofluorescence. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Feb;9(2):170–174. doi: 10.1128/jcm.9.2.170-174.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roggendorf M., Frösner G. G., Deinhardt F., Scheid R. Comparison of solid phase test systems for demonstrating antibodies against hepatitis A virus (anti-Hav) of the IgM-class. J Med Virol. 1980;5(1):47–62. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890050107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmitz H., Doerr H. W., Kampa D., Vogt A. Solid-phase enzyme immunoassay for immunoglobulin M antibodies to cytomegalovirus. J Clin Microbiol. 1977 Jun;5(6):629–634. doi: 10.1128/jcm.5.6.629-634.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmitz H. Improved detection of virus-specific IgM antibodies. Elimination of non-specific IgM binding. J Gen Virol. 1978 Aug;40(2):459–463. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-40-2-459. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stagno S., Reynolds D. W., Smith R. J. Use of isolated nuclei in the indirect fluorescent-antibody test for human cytomegalovirus infection: comparison with microneutralization, anticomplement, and conventional indirect fluorescent-antibody assays. J Clin Microbiol. 1978 May;7(5):486–489. doi: 10.1128/jcm.7.5.486-489.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Loon A. M., van der Veen J. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for quantitation of toxoplasma antibodies in human sera. J Clin Pathol. 1980 Jul;33(7):635–639. doi: 10.1136/jcp.33.7.635. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


