Abstract
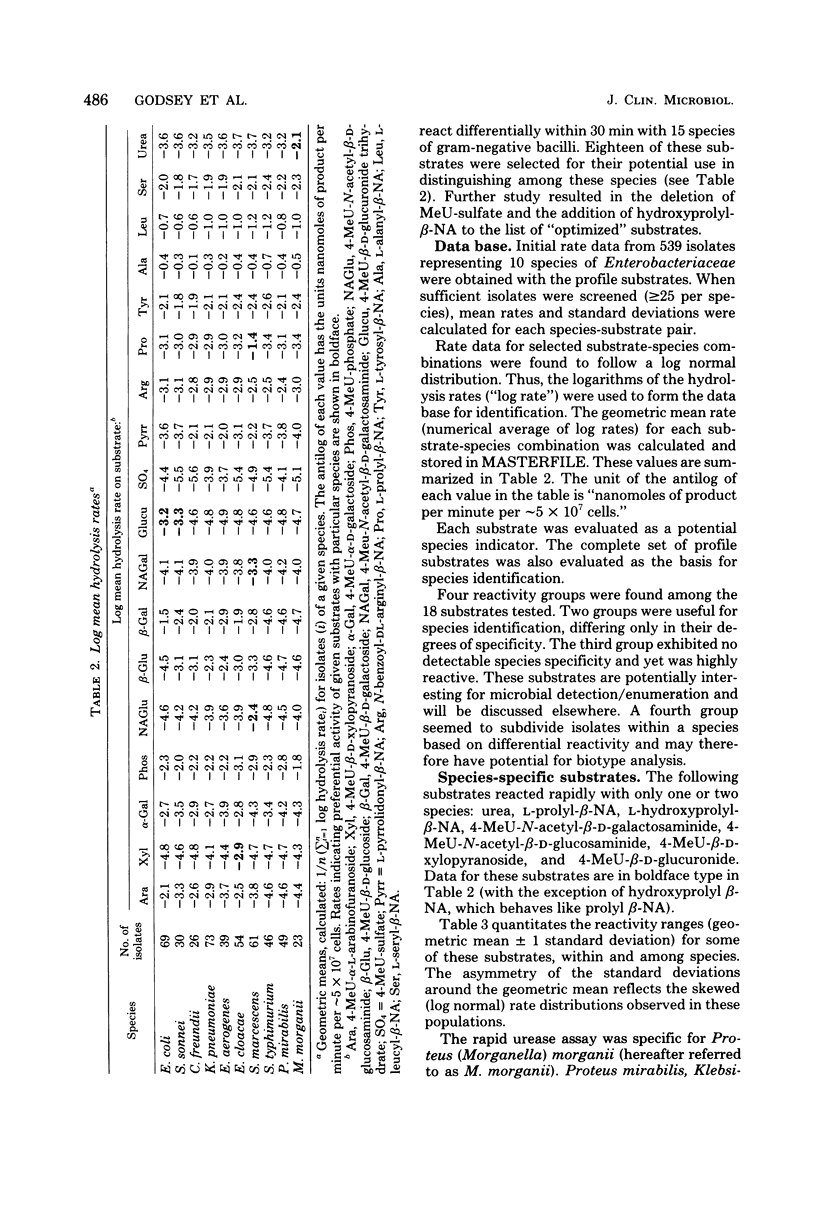
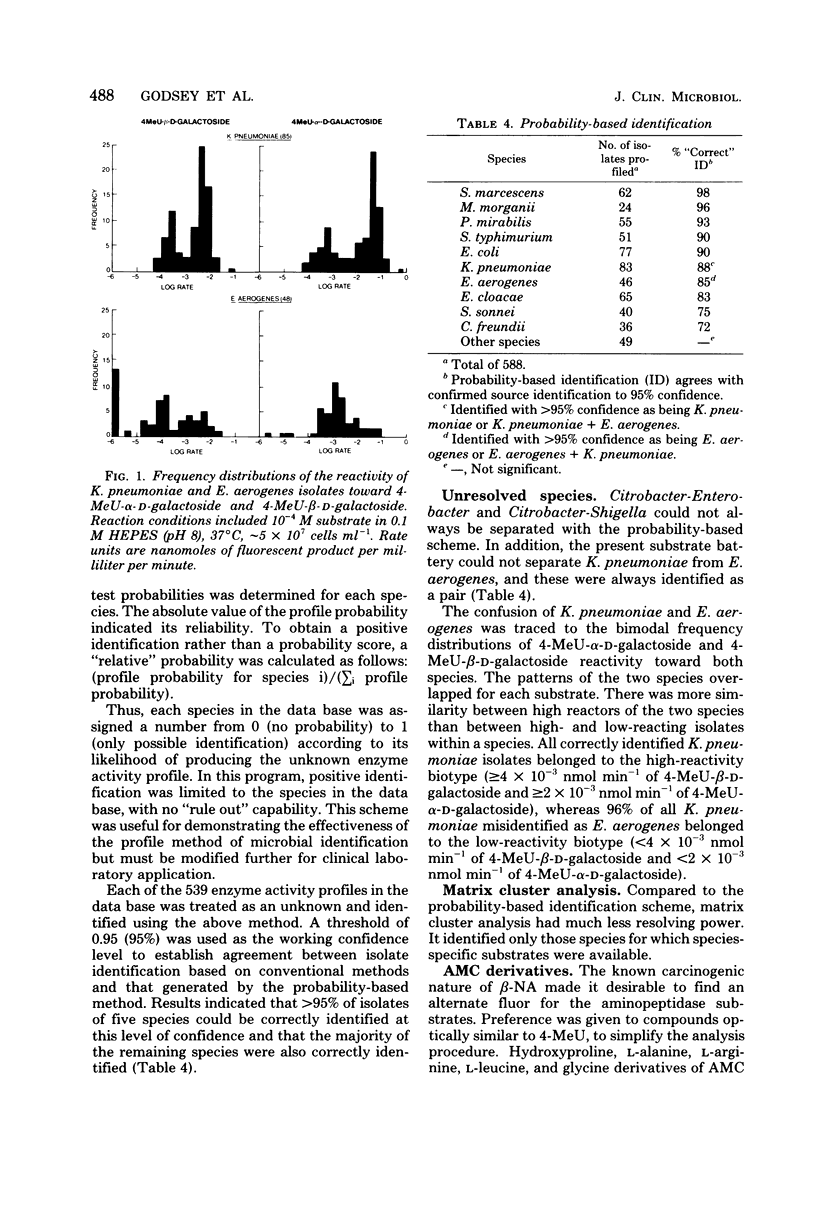
A total of 539 clinical isolates belonging to 10 species of the Enterobacteriaceae family were identified by enzyme activity profiles within 30 min of test inoculation. Each isolate was grown at 37 degrees C for 18 h on Mueller-Hinton agar and suspended to an optical density of 200 Klett units on 0.85% saline. Enzyme activity profiles were obtained by inoculating 18 fluorogenic substrates with the standardized bacterial suspension and monitoring initial rates of hydrolysis over the first 30 min of analysis. Individual enzyme activity profiles were entered into a coded data bank, and identifications were based on the Bayesian theory of probabilities. At a confidence level of 95%, five species were identified with a greater than 90% efficiency, three species were identified between 83 and 88% efficiency, and two species demonstrated a 72 and 75% efficiency of identification. The enzyme activity profile method of bacterial identification is rapid, easily automated, and reproducible.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- D'Amato R. F., Eriquez L. A., Tomfohrde K. M., Singerman E. Rapid identification of Neisseria gonorrhoeae and Neisseria meningitidis by using enzymatic profiles. J Clin Microbiol. 1978 Jan;7(1):77–81. doi: 10.1128/jcm.7.1.77-81.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fink U., Möller U., Lutilsky A., Sauer E., Staber F., Sack W., Huber C., Rastetter J. Klassifizierung lymphoproliferativer Erkrankungen mit Hilfe von Lymphozytenmarkern. Verh Dtsch Ges Inn Med. 1975;81:1211–1212. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOLDSTEIN T. P., PLAPINGER R. E., NACHLAS M. M., SELIGMAN A. M. SYNTHESIS OF CHROMOGENIC SUBSTRATES FOR THE ASSAY OF AMINOPEPTIDASE ACTIVITY. J Med Pharm Chem. 1962 Jul;91:852–857. doi: 10.1021/jm01239a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilian M., Bülow P. Rapid diagnosis of Enterobacteriaceae. I. Detection of bacterial glycosidases. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B. 1976 Oct;84B(5):245–251. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1976.tb01933.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muftić M. Application of chromogenic substrates to the determination of peptidases in mycobacteria. Folia Microbiol (Praha) 1967;12(6):500–507. doi: 10.1007/BF02875711. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulczyk M., Szewczuk A. Pyrrolidonyl peptidase in bacteria: a new colorimetric test for differentiation of enterobacteriaceae. J Gen Microbiol. 1970 Apr;61(1):9–13. doi: 10.1099/00221287-61-1-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westley J. W., Anderson P. J., Close V. A., Halpern B., Lederberg E. M. Aminopeptidase profiles of various bacteria. Appl Microbiol. 1967 Jul;15(4):822–825. doi: 10.1128/am.15.4.822-825.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerman M., Ashe B., Yurewicz E. C., Patel G. Sensitive assays for trypsin, elastase, and chymotrypsin using new fluorogenic substrates. Anal Biochem. 1977 Mar;78(1):47–51. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(77)90006-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerman M., Yurewicz E., Patel G. A new fluorogenic substrate for chymotrypsin. Anal Biochem. 1976 Jan;70(1):258–262. doi: 10.1016/s0003-2697(76)80066-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


