Abstract
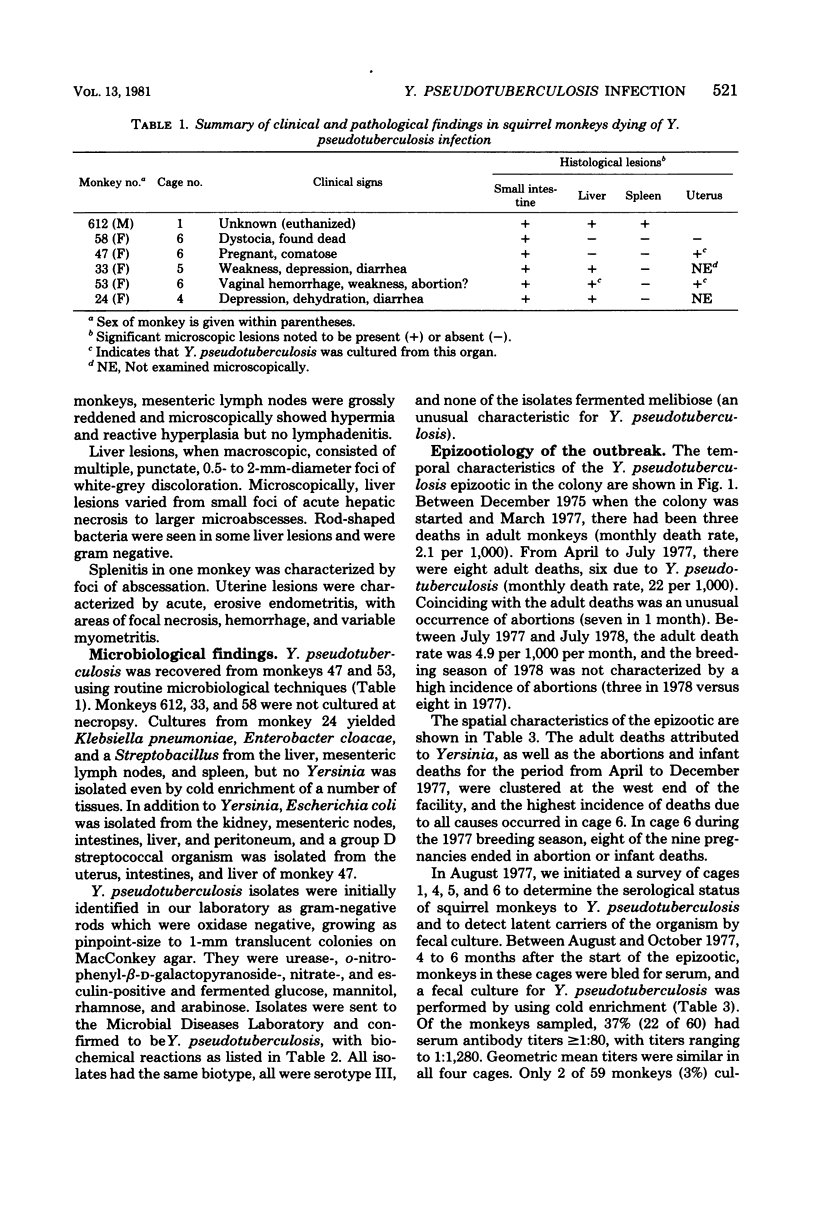
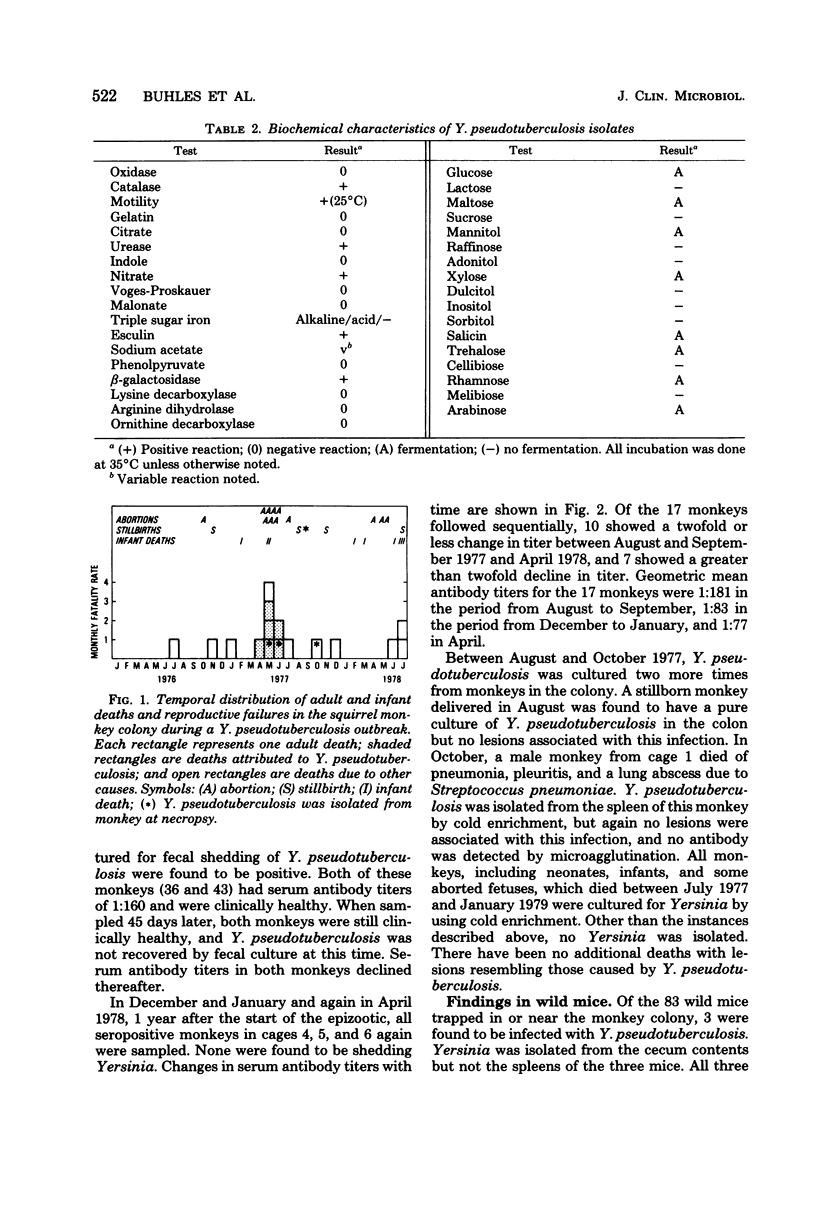
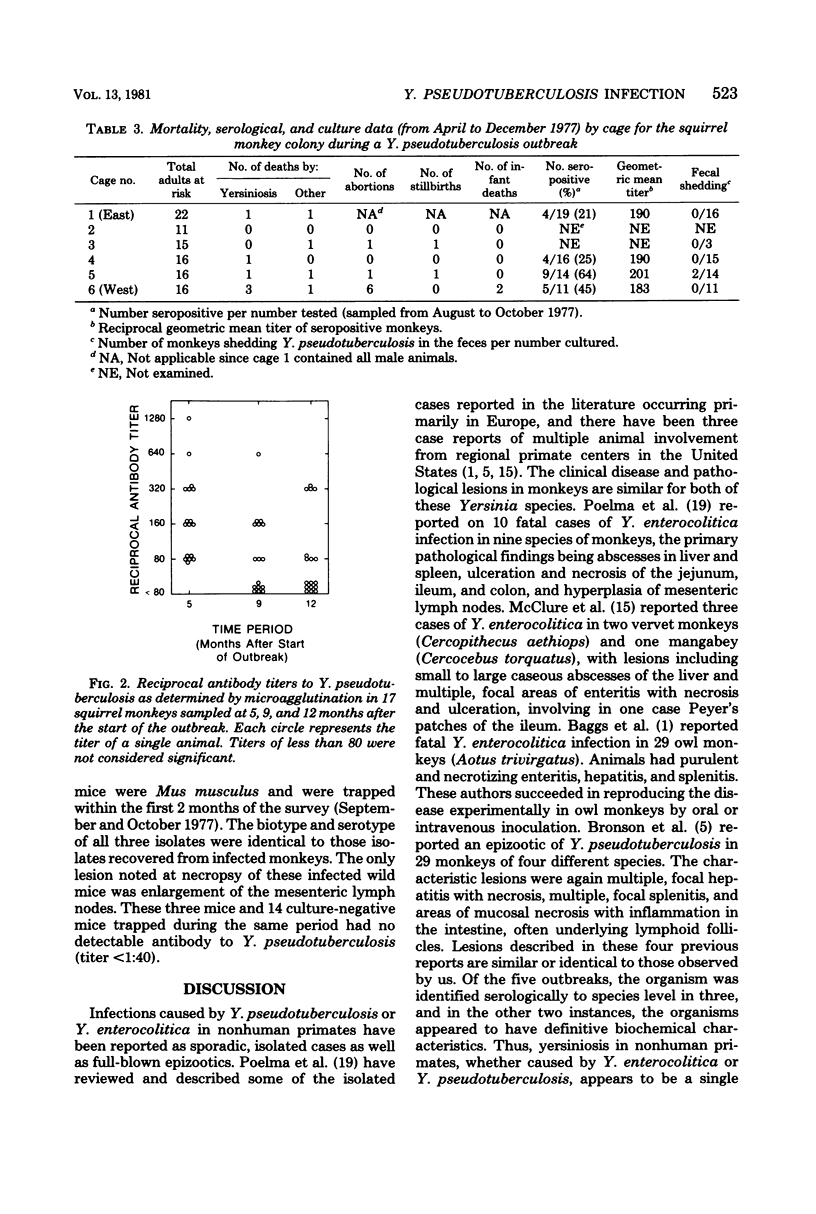
An epizootic of an acutely fatal enteric disease in a colony of squirrel monkeys (Saimiri sciureus) was attributed to infection by Yersinia pseudotuberculosis serotype III. Of a total adult population of 96 animals at risk, there were six fatal cases of yersiniosis. Serological evaluation of the colony just after the outbreak ended revealed that 22 of 60 monkeys tested (37%) had significant antibody to Y. pseudotuberculosis (microagglutination titer of greater than or equal to 1:80) but did not have clinical disease. The outstanding pathological lesions noted in dying monkeys were acute, purulent, necrotic and focal enteritis primarily affecting the jejunum and ileum and focal hepatic necrosis and abscessation. Y. pseudotuberculosis was isolated from the organs of two of the dying monkeys. Using cold enrichment techniques, Yersinia was also isolated from the feces of two apparently healthy monkeys (both seropositive), from the spleen of a monkey dying of other causes, and from the colon contents of a stillborn squirrel monkey baby. All isolates had the same biotype and serotype. An episode of abortions was associated both temporally and spatially with the fatal cases of yersiniosis, and Y. pseudotuberculosis was cultured from the uterus of two of the dying monkeys, suggesting that yersinia infection may be associated with abortion, as well as with enteric infection, in these animals.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baggs R. B., Hunt R. D., Garcia F. G., Hajema E. M., Blake B. J., Fraser C. E. Pseudotuberculosis (Yersinia enterocolitica) in the owl monkey (Aotus trivirgatus). Lab Anim Sci. 1976 Dec;26(6 Pt 2):1079–1083. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baskin G. B., Montali R. J., Bush M., Quan T. J., Smith E. Yersiniosis in captive exotic mammals. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1977 Nov 1;171(9):908–912. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bissett M. L. Yersinia enterocolitica isolates from humans in California, 1968-1975. J Clin Microbiol. 1976 Aug;4(2):137–144. doi: 10.1128/jcm.4.2.137-144.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bottone E. J. Yersinia enterocolitica: a panoramic view of a charismatic microorganism. CRC Crit Rev Microbiol. 1977;5(2):211–241. doi: 10.3109/10408417709102312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bronson R. T., May B. D., Ruebner B. H. An outbreak of infection by Yersinia pseudotuberculosis in nonhuman primates. Am J Pathol. 1972 Nov;69(2):289–308. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eiss J. Selective culturing of Yersinia enterocolitica at a low temperature. Scand J Infect Dis. 1975;7(4):249–251. doi: 10.3109/inf.1975.7.issue-4.05. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenwood J. R., Flanigan S. M., Pickett M. J., Martin W. J. Clinical isolation of Yersinia enterocolitica: cold temperature enrichment. J Clin Microbiol. 1975 Dec;2(6):559–560. doi: 10.1128/jcm.2.6.559-560.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hacking M. A., Sileo L. Yersinia enterocolitica and Yersinia pseudotuberculosis from wildlife in Ontario. J Wildl Dis. 1974 Oct;10(4):452–457. doi: 10.7589/0090-3558-10.4.452. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hubbert W. T. Yersiniosis in mammals and birds in the United States: case reports and review. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1972 Jul;21(4):458–463. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1972.21.458. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapperud G. Yersinia enterocolitica and Yersinia like microbes isolated from mammals and water in Norway and Denmark. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B. 1977 Apr;85(2):129–135. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1977.tb01686.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langford E. V. Pasteurella pseudotuberculosis associated with abortion and pneumonia in the bovine. Can Vet J. 1969 Aug;10(8):208–211. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAIR N. S., MAIR H. J., STIRK E. M., CORSON J. G. Three cases of acute mesenteric lymphadenitis due to Pasteurella pseudotuberculosis. J Clin Pathol. 1960 Sep;13:432–439. doi: 10.1136/jcp.13.5.432. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mair N. S. Yersiniosis in wildlife and its public health implications. J Wildl Dis. 1973 Jan;9(1):64–71. doi: 10.7589/0090-3558-9.1.64. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClure H. M., Weaver R. E., Kaufmann A. F. Pseudotuberculosis in nonhuman primates: infection with organisms of the Yersinia enterocolitica group. Lab Anim Sci. 1971 Jun;21(3):376–382. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Obwolo M. J. The pathology of experimental yersiniosis in guinea pigs. J Comp Pathol. 1977 Apr;87(2):213–221. doi: 10.1016/0021-9975(77)90008-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PATERSON J. S., COOK R. A method for the recovery of Pateurella pseudotuberculosis from faeces. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1963 Jan;85:241–242. doi: 10.1002/path.1700850124. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poelma F. G., Borst G. H., Zwart P. Yersinia enterocolitica infections in non-human primates. Acta Zool Pathol Antverp. 1977 Dec;(69):3–9. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ricciardi I. D., Pearson A. D., Suckling W. G., Klein C. Long-term fecal excretion and resistance induced in mice infected with Yersinia enterocolitica. Infect Immun. 1978 Jul;21(1):342–344. doi: 10.1128/iai.21.1.342-344.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


