Abstract
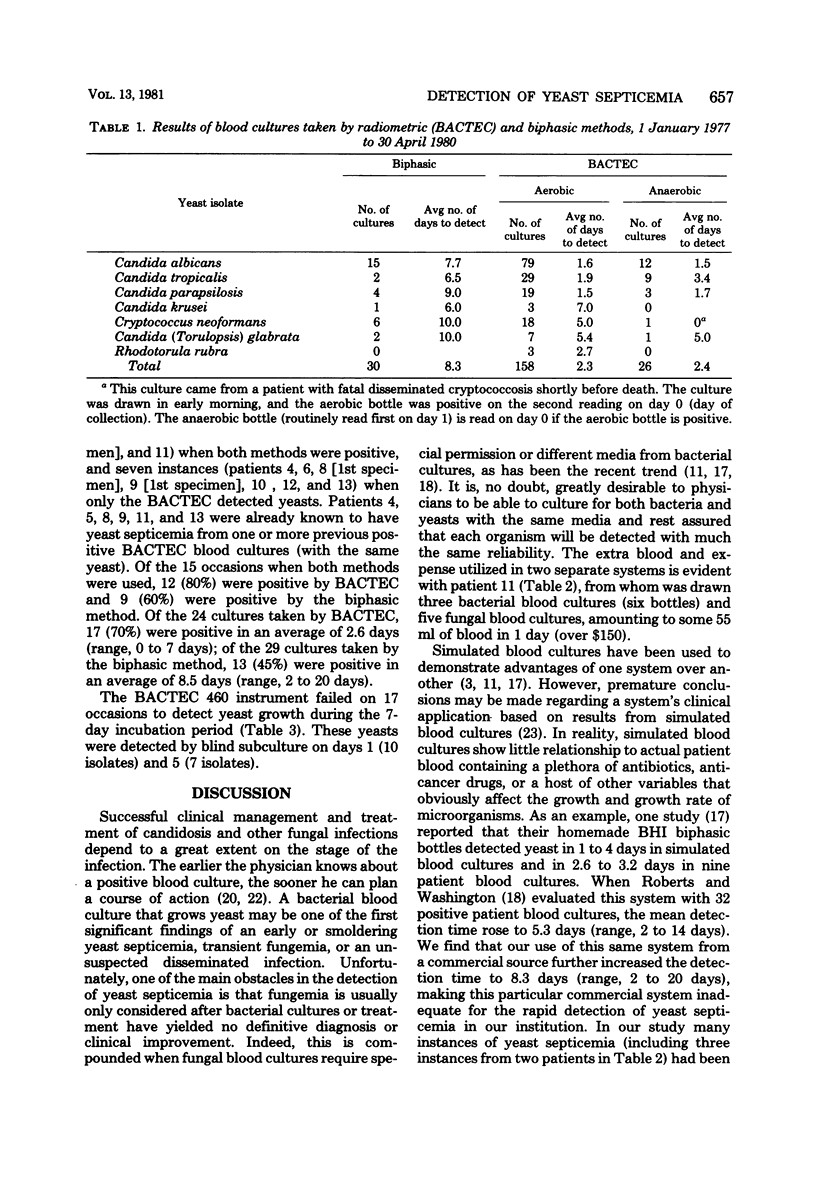
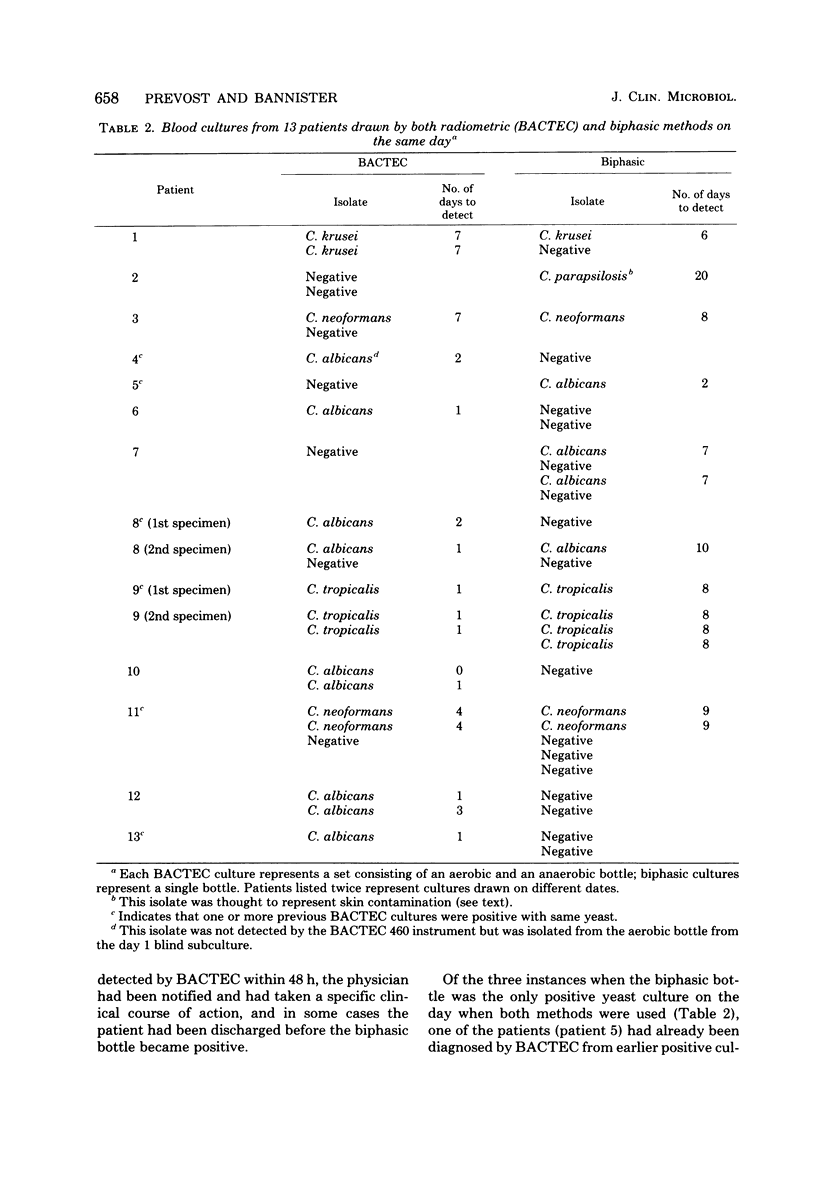
From January 1977 to April 1980 our microbiology laboratory used a commercial biphasic brain heart infusion vented culture method for fungal blood cultures and a commercial radiometric (BACTEC 460, Johnson Laboratories, Cockeysville, Md.) method for bacterial blood cultures. A total of 668 biphasic fungal blood cultures were processed, of which 30 grew yeasts from 19 patients. There were 38,324 BACTEC blood cultures processed for bacteria, of which 184 grew yeasts from 85 patients. The overall detection time for all yeasts averaged 8.3 days for the biphasic method and 2.4 days for the radiometric method. The BACTEC aerobic bottle detected over six times as many yeasts as did the anaerobic bottle. Candida albicans was the most frequently isolated yeast in both methods, being detected in an average of 7.7 days in the biphasic method and 1.6 days in the aerobic BACTEC bottle. It is concluded from this study that the radiometric method is far superior to the biphasic method, because (i) it has a shorter detection time, (ii) it can be used simultaneously with bacterial methods, saving blood and money, and (iii) it requires no special or separate media or instructions for yeasts, thus alleviating confusion in the blood collection process.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bodey G. P. Fungal infections complicating acute leukemia. J Chronic Dis. 1966 Jun;19(6):667–687. doi: 10.1016/0021-9681(66)90066-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braunstein H., Tomasulo M. A quantitative study of the growth of Candida albicans in vented and unvented blood-culture bottles. Am J Clin Pathol. 1976 Jul;66(1):87–90. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/66.1.87. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caplan L. M., Merz W. G. Evaluation of two commercially prepared biphasic media for recovery of fungi from blood. J Clin Microbiol. 1978 Oct;8(4):469–470. doi: 10.1128/jcm.8.4.469-470.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caslow M., Ellner P. D., Kiehn T. E. Comparison of the BACTEC system with blind subculture for the detection of bacteremia. Appl Microbiol. 1974 Sep;28(3):435–438. doi: 10.1128/am.28.3.435-438.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curry C. R., Quie P. G. Fungal septicemia in patients receiving parenteral hyperalimentation. N Engl J Med. 1971 Nov;285(22):1221–1225. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197111252852203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeBlanc H. J., Jr, DeLand F., Wagner H. N., Jr Automated radiometric detection of bacteria in 2,967 blood cultures. Appl Microbiol. 1971 Nov;22(5):846–849. doi: 10.1128/am.22.5.846-849.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis C. A., Spivack M. L. The significance of candidemia. Ann Intern Med. 1967 Sep;67(3):511–522. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-67-3-511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaines J. D., Remington J. S. Disseminated candidiasis in the surgical patient. Surgery. 1972 Nov;72(5):730–736. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gantz N. M., Medeiros A. A., Swain J. L., O'Brien T. F. Vacuum blood-culture bottles inhibiting growth of Candida and fostering growth of Bacteroides. Lancet. 1974 Nov 16;2(7890):1174–1176. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(74)90813-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopfer R. L., Mills K., Gröschel D. Improved blood culture medium for radiometric detection of yeasts. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Mar;9(3):448–449. doi: 10.1128/jcm.9.3.448-449.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopfer R. L., Orengo A., Chesnut S., Wenglar M. Radiometric detection of yeasts in blood cultures of cancer patients. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Sep;12(3):329–331. doi: 10.1128/jcm.12.3.329-331.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Komorowski R. A., Farmer S. G. Rapid detection of candidemia. Am J Clin Pathol. 1973 Jan;59(1):56–61. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/59.1.56. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Renner E. D., Gatheridge L. A., Washington J. A., 2nd Evaluation of radiometric system for detecting bacteremia. Appl Microbiol. 1973 Sep;26(3):368–372. doi: 10.1128/am.26.3.368-372.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts G. D., Horstmeier C., Hall M., Washington J. A., 2nd Recovery of yeast from vented blood culture bottles. J Clin Microbiol. 1975 Jul;2(1):18–20. doi: 10.1128/jcm.2.1.18-20.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts G. D., Washington J. A., 2nd Detection of fungi in blood cultures. J Clin Microbiol. 1975 Mar;1(3):309–310. doi: 10.1128/jcm.1.3.309-310.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose H. D. Venous catheter-associated candidemia. Am J Med Sci. 1978 May-Jun;275(3):265–269. doi: 10.1097/00000441-197805000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosner R. Comparison of macroscopic, microscopic, and radiometric examinations of clinical blood cultures in hypertonic media. Appl Microbiol. 1974 Oct;28(4):644–646. doi: 10.1128/am.28.4.644-646.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sande M. A., Bowman C. R., Calderone R. A. Experimental Candida albicans endocarditis: characterization of the disease and response to therapy. Infect Immun. 1977 Jul;17(1):140–147. doi: 10.1128/iai.17.1.140-147.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seelig M. S., Speth C. P., Kozinn P. J., Toni E. F., Taschdjian C. L. Candida endocarditis after cardiac surgery. Clues to earlier detection. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1973 Apr;65(4):583–601. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Washington J. A., 2nd, Yu P. K. Radiometric method for detection of bacteremia. Appl Microbiol. 1971 Jul;22(1):100–101. doi: 10.1128/am.22.1.100-101.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


