Abstract
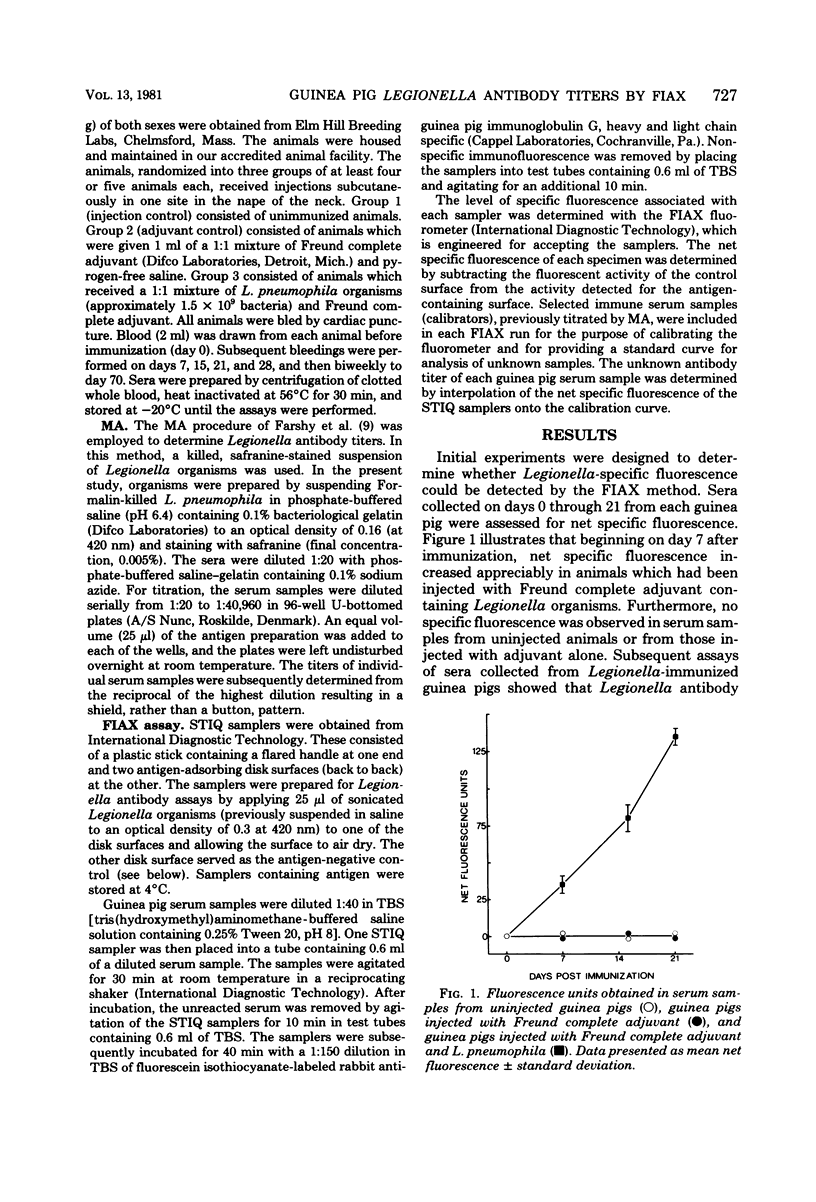
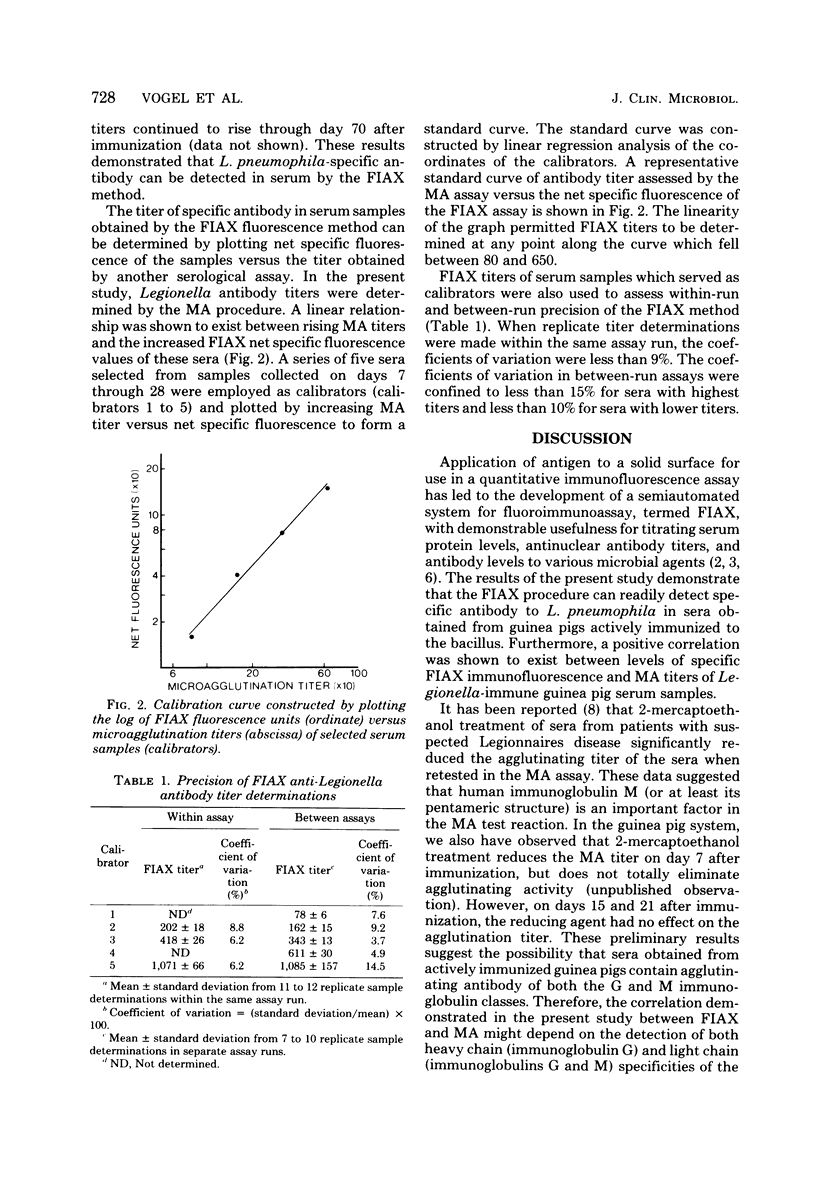
A semiautomated solid-phase immunofluorescence apparatus (FIAX; International Diagnostic Technology, Santa Clara, Calif.) was utilized to develop a rapid method for detection of antibody to Legionella pneumophila. The sera from guinea pigs immunized with a mixture of killed L. pneumophila and Freund complete adjuvant displayed markedly enhanced antibody activity as measured by FIAX when compared with that obtained from adjuvant-injected or unimmunized animals. A correlation was observed between FIAX net fluorescence units and microagglutination titers of serum samples obtained from immunized animals. Within-run and between-run coefficients of variation performed on selected immune serum samples were low. These results demonstrated that the FIAX method could readily and reproducibly detect Legionella-specific antibodies in the sera of actively immunized animals and suggest the possibility of a broader application of FIAX in the serological detection of exposure to L. pneumophila antigen.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benjamin W. R., Specter S. C., Klein T. W., Hitchings M., Friedman H. Evaluation of solid-phase immunofluorescence for quantitation of antibodies to herpes simplex virus and cytomegalovirus. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Oct;12(4):558–561. doi: 10.1128/jcm.12.4.558-561.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casavant C. H., Hart A. C., Stites D. P. Comparison of a semiautomated fluorescent immunoassay system and indirect immunofluorescence for detection of antinuclear antibodies in human serum. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Nov;10(5):712–718. doi: 10.1128/jcm.10.5.712-718.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cremer N. E., Hagens S. J., Cossen C. Comparison of the hemagglutination inhibition test and an indirect fluorescent-antibody test for detection of antibody to rubella virus in human sera. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Jun;11(6):746–747. doi: 10.1128/jcm.11.6.746-747.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edson D. C., Stiefel H. E., Wentworth B. B., Wilson D. L. Prevalence of antibodies to Legionnaires' disease. A seroepidemiologic survey of Michigan residents using the hemagglutination test. Ann Intern Med. 1979 Apr;90(4):691–693. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-90-4-691. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eickhoff T. C. Epidemiology of Legionnaires' disease. Ann Intern Med. 1979 Apr;90(4):499–502. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-90-4-499. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Estes G. B., Muñoz M., Burdash N. M., Virella G. A quantitative immunofluorescence test for the detection of anti-Candida antibodies. J Immunol Methods. 1980;35(1-2):105–113. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(80)90155-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fallon R. J., Abraham W. H. Scottish experience with the serologic diagnosis of Legionnaires' disease. Ann Intern Med. 1979 Apr;90(4):684–686. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-90-4-684. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farshy C. E., Cruce D. D., Klein G. C., Wilkinson H. W., Feeley J. C. Immunoglobulin specificity of the microagglutination test for the Legionnaires' disease bacterium. Ann Intern Med. 1979 Apr;90(4):690–690. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-90-4-690. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farshy C. E., Klein G. C., Feeley J. C. Detection of antibodies to legionnaires disease organism by microagglutination and micro-enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay tests. J Clin Microbiol. 1978 Apr;7(4):327–331. doi: 10.1128/jcm.7.4.327-331.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDade J. E., Shepard C. C., Fraser D. W., Tsai T. R., Redus M. A., Dowdle W. R. Legionnaires' disease: isolation of a bacterium and demonstration of its role in other respiratory disease. N Engl J Med. 1977 Dec 1;297(22):1197–1203. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197712012972202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai T. F., Fraser D. W. The diagnosis of Legionnaires' disease. Ann Intern Med. 1978 Sep;89(3):413–414. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-89-3-413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


