Abstract
Soluble epoxide hydrolase (sEH) is a novel target for the treatment of hypertension and vascular inflammation. A new class of potent non-urea sEH inhibitors was identified via high throughput screening (HTS) and chemical modification. IC50s of the most potent compounds range from micromolar to low nanomolar.
A Class of potent non-Urea inhibitors of soluble epoxide hydrolase was discovered via high throughput screening and SARs-guided modification.
Keywords: sEH, non-urea, HTS, nanomolar
Soluble epoxide hydrolase (sEH) plays an important role in the metabolism of lipid epoxides. Endogenous substrates of sEH include epoxides of arachidonic acid and the epoxyeicosatrienoic acids or EETs, the latter are effective regulators of blood pressure and inflammation. Hydrolysis by sEH converts EETs to the corresponding diols with diminished vasodilatory and anti-inflammation effects.1,2 Inhibition of sEH leads to accumulation of active EETs and thus provides a novel approach to the treatment of hypertension and vascular inflammation.3 To date, the most successful sEH inhibitors are 1,3-disubstituted ureas, which display anti-hypertension and anti-inflammatory effects through inhibition of EET hydrolysis. However, urea-based inhibitors often suffer from poor solubility and bioavailability4 and new scaffolds are needed for therapeutic applications. Here we describe the HTS, design and synthesis of a series of potent non-urea sEH inhibitors.
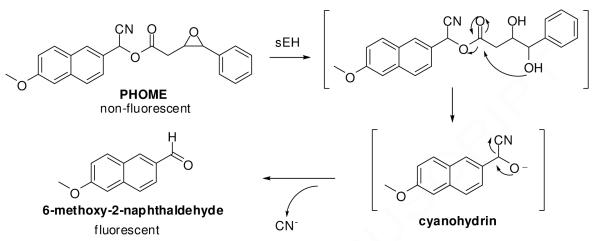
A fluorescent assay5 was employed for HTS using recombinant human sEH and a water soluble α-cyanocarobonate epoxide (PHOME) as the substrate. As shown in Figure 1, sEH-catalyzed hydrolysis of the non-fluorescent substrate is followed by spontaneous cyclization to a cyanohydrin that under basic conditions, rapidly decomposes to a highly fluorescent naphthaldehyde. Fluorescence with excitation at 320nm and emission at 460nm was recorded at the endpoint of the reaction cascade.
Figure 1.
Reaction mechanism of the fluorescent assay used for the HTS.
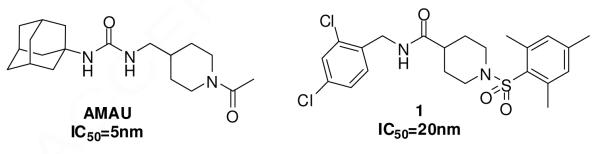
From the compound collection provided by the NIH Roadmap project, a variety of hits were identified with low micromolar to nanomolar potency.6 A large proportion of hits were ureas, but several non-urea compounds showed substantial activities. The most potent compound among these non-ureas was the sulfonyl isonipecotamide 1, a nanomolar inhibitor (IC50=20.0nm) with some structural similarity to the previously reported piperidine-containing urea AMAU (Figure 2).7
Figure 2.
The structures of Compounds AMAU and 1
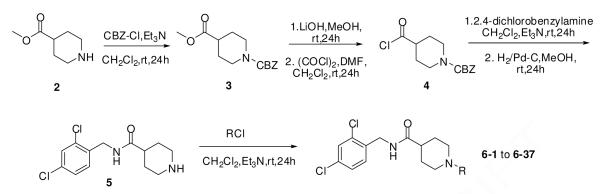
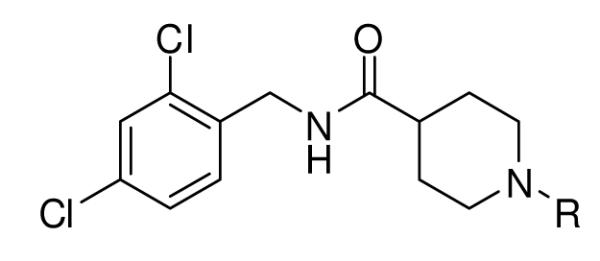
A secondary library based on 1 was prepared by modifying either the amide head group or the sulfonamide tail group. The synthesis of the sulfonamide-modified analogs is outlined Scheme 1. Methyl isonipecotate 2 was first protected with benzyl chloroformate, and then converted to the acid chloride 4 by hydrolyzing the methyl ester and then treating with oxalyl chloride. Coupling of 4 with 2,4-dichlorobenzylamine followed by palladium catalyzed hydrogenation afforded amine 5, which was reacted with a variety of sulfonyl chlorides, carbonyl chlorides and chloroformates to yield products 6-1 to 6-37.
Scheme 1.
The synthesis of compounds 6-1 to 6-37
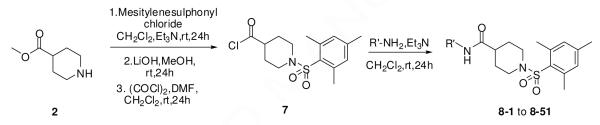
Modification of the amide head is shown in Scheme 2. Thus, 2 was treated with mesitylenesulphonyl chloride and similarly converted into the acid chloride 7. In parallel, reaction of 7 with various amines led to the products 8-1 to 8-51.
Scheme 2.
The synthesis of compounds 8-1 to 8-51
The secondary library8 was screened at concentration 200nm using the fluorescence assay as above. The IC50 values were determined for those compounds displaying greater than 50% inhibition at 200nm. The results for the tail and head modification are summarized in Tables 1 and 2, respectively.
Table 1.
The biological results for the tail modification.
 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Comp | R | Inhibition(%) at 200nm |
IC50(nm)a | Comp | R | Inhibition(%) at 200nm |
IC50(nm)a |
| 1 |  |
97 | 20.0b | 6-19 |  |
37 | ND |
| 6-1 | 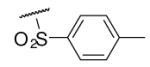 |
15 | NDc | 6-20 | 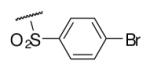 |
32 | ND |
| 6-2 | 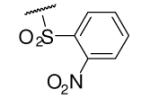 |
47 | ND | 6-21 | 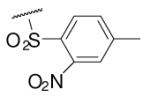 |
28 | ND |
| 6-3 | 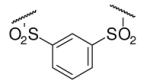 |
45 | ND | 6-22 | 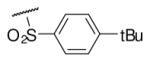 |
85 | 164.0 |
| 6-4 | 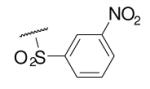 |
21 | ND | 6-23 | 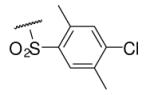 |
97 | 52.1 |
| 6-5 | 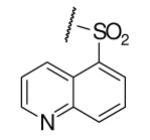 |
34 | ND | 6-24 | 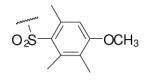 |
98 | 23.9 |
| 6-6 | 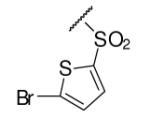 |
43 | ND | 6-25 | 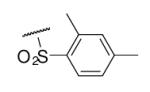 |
97 | 46.9 |
| 6-7 | 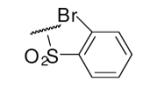 |
63 | 91.1 | 6-26 | 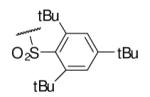 |
88 | 44.5 |
| 6-8 |  |
31 | ND | 6-27 |  |
34 | ND |
| 6-9 | 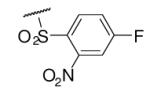 |
63 | 150.0 | 6-28 | 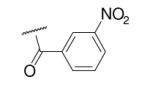 |
18 | ND |
| 6-10 | 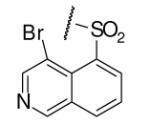 |
37 | ND | 6-29 | 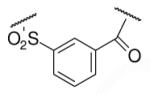 |
45 | ND |
| 6-11 | 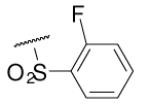 |
66 | 87.6 | 6-30 | 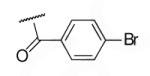 |
0 | ND |
| 6-12 | 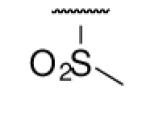 |
45 | ND | 6-31 | 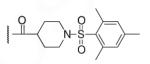 |
33 | ND |
| 6-13 | 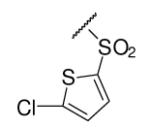 |
52 | 200.0 | 6-32 | 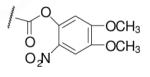 |
71 | 75.3 |
| 6-14 | 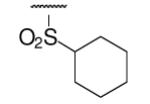 |
27 | ND | 6-33 | 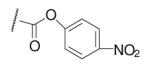 |
41 | ND |
| 6-15 | 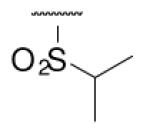 |
13 | ND | 6-34 | 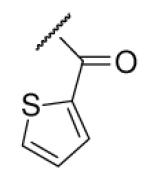 |
16 | ND |
| 6-16 | 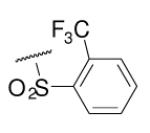 |
39 | ND | 6-35 | 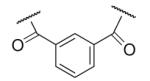 |
55 | 200.0 |
| 6-17 | 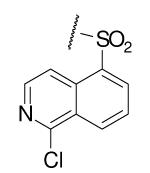 |
30 | ND | 6-36 | 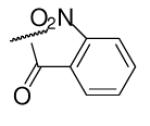 |
44 | ND |
| 6-18 | 53 | ND | 6-37 | 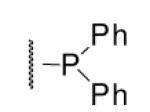 |
3 | ND | |
IC50 values are determined from a single experiment performed in triplicate.
IC50 values are determined from two independent experiments performed in triplicate.
ND: not determined.
Table 2.
The biological results for the head modification.
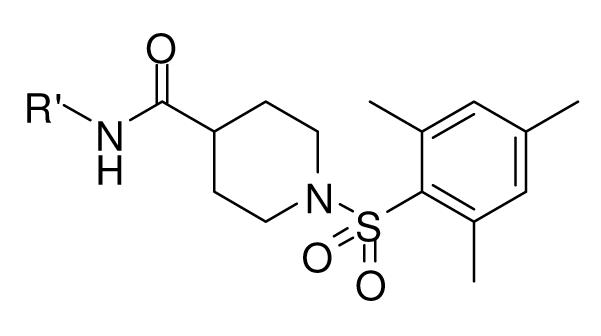 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Comp | R’ | Inhibition(%) at 200nm |
IC50(nm) | Comp | R’ | Inhibition(%) at 200nm |
IC50(nm)a |
| 8-1 | 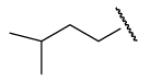 |
87 | 25.1 | 8-26 | 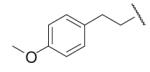 |
44 | ND |
| 8-2 | 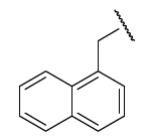 |
55 | 39.4 | 8-27 | 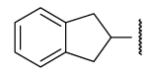 |
62 | 49.1 |
| 8-3 | 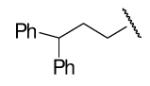 |
78 | 35 | 8-28 | 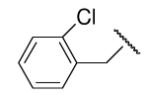 |
90 | 27.4 |
| 8-4 | 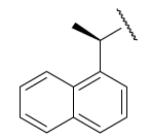 |
-4 | NDc | 8-29 | 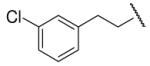 |
65 | 64.0 |
| 8-5 | 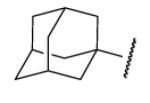 |
-1 | ND | 8-30 | 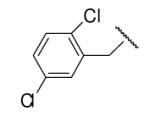 |
98 | 59.1 |
| 8-6 | 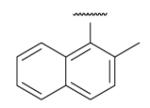 |
-16 | ND | 8-31 | 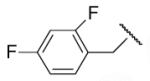 |
97 | 32.2 |
| 8-7 | 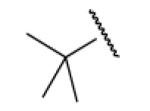 |
3 | ND | 8-32 | 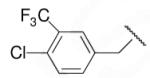 |
96 | 173.0 |
| 8-8 | 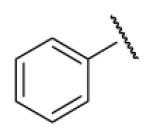 |
48 | ND | 8-33 | 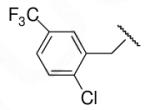 |
94 | 28.7 |
| 8-9 | 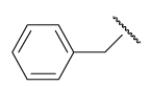 |
65 | 42.0 | 8-34 | 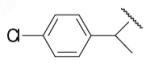 |
94 | 29.1 |
| 8-10 | 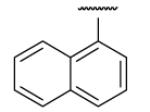 |
50 | 200.0 | 8-35 | 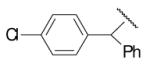 |
7 | ND |
| 8-11 | 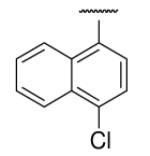 |
44 | ND | 8-36 | 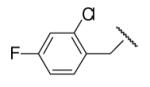 |
98 | 54.1 |
| 8-12 | 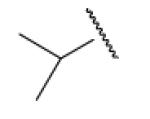 |
-7 | ND | 8-37 | 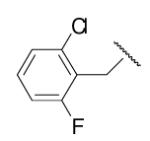 |
97 | 12.7b |
| 8-13 | 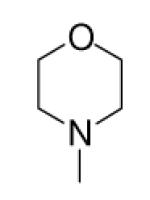 |
-29 | ND | 8-38 | 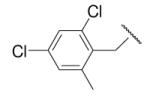 |
95 | 128.0 |
| 8-14 | 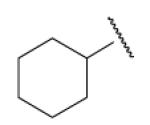 |
87 | 16.4 | 8-39 | 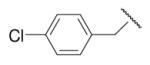 |
97 | 50.0 |
| 8-15 | 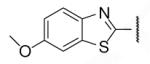 |
-17 | ND | 8-40 | 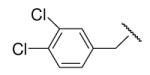 |
97 | 32.0 |
| 8-16 | 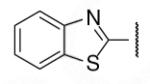 |
-18 | ND | 8-41 | 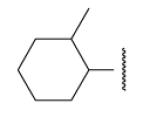 |
77 | 37.2b |
| 8-17 | 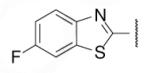 |
-6 | ND | 8-42 | 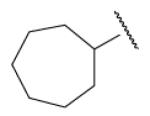 |
90 | 7.9b |
| 8-18 | 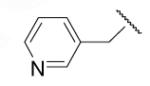 |
23 | ND | 8-43 | 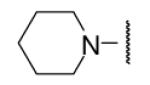 |
55 | 200.0 |
| 8-19 | 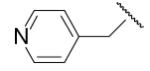 |
49 | ND | 8-44 | 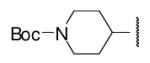 |
88 | 11.0b |
| 8-20 | 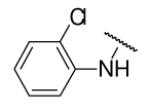 |
62 | 33.6 | 8-45 | 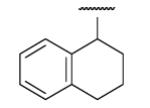 |
79 | 20.1 |
| 8-21 | 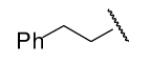 |
67 | 43.3 | 8-46 | 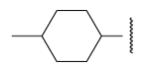 |
86 | 39.6b |
| 8-22 | 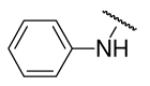 |
16 | ND | 8-47 | 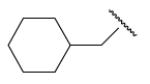 |
92 | 12.6b |
| 8-23 | 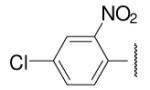 |
-25 | ND | 8-48 | 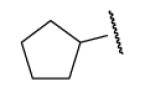 |
75 | 37.3b |
| 8-24 | 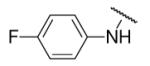 |
9 | ND | 8-49 | 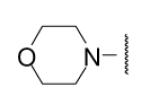 |
14 | ND |
| 8-25 | 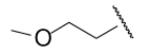 |
-6 | ND | 8-50 | 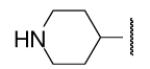 |
15 | ND |
IC50 values are determined from a single experiment performed in triplicate.
IC50 values are determined from two independent experiments performed in triplicate.
ND: not determined.
As illustrated in Table 1, the diverse tail modifications did not lead to improved potency over the original mesitylenesulfonamide. However, several structure activity relationships can be observed in this series. First, the sulfonamide moiety is important for potent inhibition. Great loss of activities was observed for amides (6-27 and 6-30) compared with the corresponding sulfonamides. Aromatic sulfonamides appeared to be more favorable as all tested alkylsulfonamides were poor inhibitors. Substituents on the aromatic ring modulated activities synergistically. Hydrophobic alkyl groups and halides were generally preferred with a positive effect more pronounced at the ortho position. For example, bromo or fluoro substitution at the ortho position (6-7, 6-10) confered nonamolar potency in contrast to para substitution (6-20). Deletion of one or both of the ortho methyl groups in 1 led to less active compounds 6-1 and 6-25.
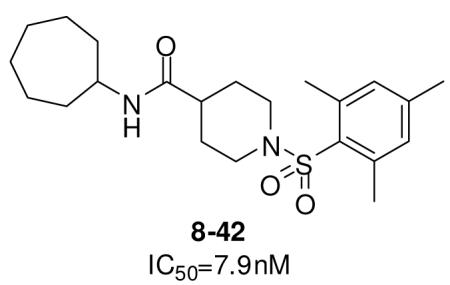
In the optimization of the head group, we first screened a set of structurally diversified amides. All disubstituted amides tested were inactive (results not shown), suggesting the proton in NH could be important to sEH inhibition. Previous studies with urea-based inhibitors have shown that one NH of the urea, forming a salt bridge with the catalytic nucleophile Asp333 in the active site of sEH, is absolutely required for the activity.9 Hypothesizing that the amide in our hit corresponded to the urea functionality serving as the primary pharmacophore, we selected a variety of primary amines to replace 2,4-dichloride benzylamine moiety, including those frequently found in urea-based inhibitors. As shown in Table 2, the primary amide was quite tolerant to modification and nanomolar potency was retained with various substitutions. N-benzylamide 8-9 (IC50=42.0nm) and N-cyclohexylamide 8-14, (IC50=16.4nm) were selected for further optimization. Extensive modification of the benzyl group led to 8-37 with a significant improvement of potency (IC50=12.7nm). The most noticeable SAR illustrated by this modification is that halides such as chloride and Fluoride seem favored for the substitution on the benzyl group. The modification of cyclohexylamide 8-14 yielded the most potent compounds 8-42 (IC50=7.9nm) and 8-47 (IC50=12.6nm). As demonstrated by this result, adding an extra methylene to the cyclohexyl ring significantly enhanced the activities. In contrast, analogs with polar atoms (N, O) in the ring decreased the inhibitory potency to micromolar range (8-49, 8-50). These SARs are consistent with previous results obtained for urea derivatives.10
In summary, we have successfully identified a series of potent non-urea sEH inhibitors via high throughput screens. Improved potency was sought through SAR-guided modification. Compound 8-42 with an IC50 of 7.9nm represents the most potent non-urea sEH inhibitor identified in this study. Physical and pharmacokinetic properties of these promising compounds are under investigation.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the NIH MLSCN Grant.
Footnotes
Publisher's Disclaimer: This is a PDF file of an unedited manuscript that has been accepted for publication. As a service to our customers we are providing this early version of the manuscript. The manuscript will undergo copyediting, typesetting, and review of the resulting proof before it is published in its final citable form. Please note that during the production process errors may be discovered which could affect the content, and all legal disclaimers that apply to the journal pertain.
References and notes
- 1.Smith KR, Pinkerton KE, Watanabe T, Pedersen TL, Ma SJ, Hammock BD. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 2005;102:2186. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0409591102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Schmelzer KR, Kubala L, Newman JW, Kim IH, Eiserich JP, Hammock BD. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 2005;102:9772. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0503279102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Chiamvimonvat N, Ho CM, Tsai HJ, Hammock BD. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2007;50:225. doi: 10.1097/FJC.0b013e3181506445. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Kim IH, Tsai HJ, Nishi K, Kasagami T, Morisseau C, Hammock BD. J Med Chem. 2007;502:5217. doi: 10.1021/jm070705c. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Wolf NM, Morisseau C, Jones PD, Hock B, Hammock BD. Anal Biochem. 2006;335:71. doi: 10.1016/j.ab.2006.04.045. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.See the screen results published in Pubchem (AID:1026).
- 7.Jones PD, Tsai HJ, Do ZN, Morisseau C, Hammock BD. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2006;16:5212. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2006.07.009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Analytical data for the representative compounds: 8-42: 1H NMR (300 MHz, CDCl3) δ 6.94 (s, 2H), 5.38 (br, 1H), 3.92-3.89 (m, 1H), 3.62-3.57(m, 2H), 2.83-2.63(t, 2H), 2.61 (s, 6H), 2.30(s, 3H), 2.17-2.10 (m, 1H), 1.87-1.83 (m, 4H), 1.74-1.35 (m, 12H); 13C NMR (75 MHz, CD3OD) δ 172.9, 142.9, 140.6, 132.1, 131.6, 50.6, 44.0,43.1, 35.4, 28.5, 28.3, 24.5, 23.1, 21.3; ESI-MS(M+ + H): 407.2. 8-47 1H NMR (300 MHz, CDCl3) δ 6.94 (s, 2H), 5.48 (br, 1H), 3.60 (d, 2H), 3.07(t, 2H), 2.81(t, 2H), 2.61 (s, 6H), 2.30(s, 3H), 2.20-2.05 (m, 1H), 1.88-1.84 (m, 2H), 1.77-1.64 (m, 6H); 1.50-1.38 (m, 1H); 1.35-1.05 (m, 4H); 0.95-0.82 (m, 2H); 13C NMR (75 MHz, CD3OD) δ 174.2, 142.9, 140.7, 132.1, 131.5, 45.9, 44.0, 43.2, 38.2, 31.1, 28.6, 26.7, 26.1, 23.2, 21.3; ESI-MS(M+ + H): 407.3.
- 9.Argiriadi MA, Morisseau C, Goodrow MH, Dowdy DL, Hammock BD, Christianson DW. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:15265. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M000278200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Kim IH, Heirtzler FR, Morisseau C, Nishi K, Tsai HJ, Hammock BD. J Med Chem. 2005;48:3621. doi: 10.1021/jm0500929. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]