Abstract
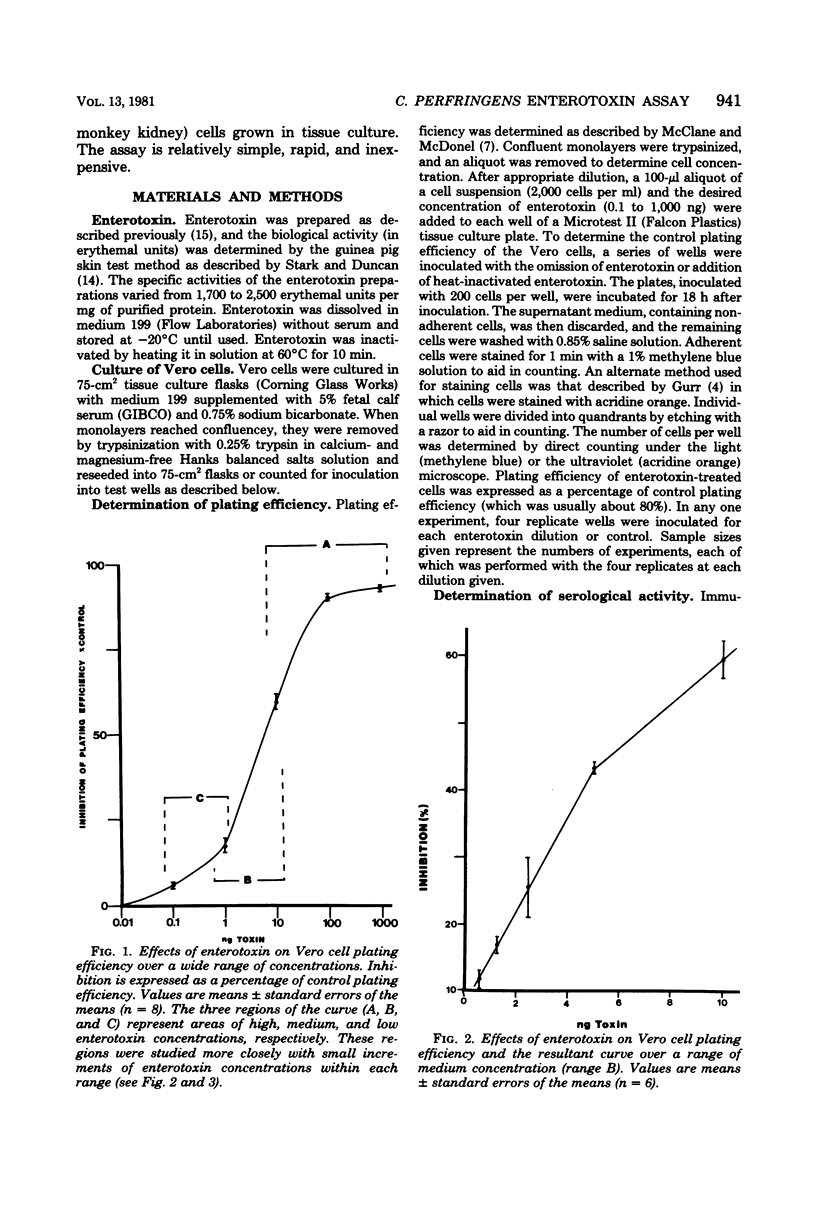
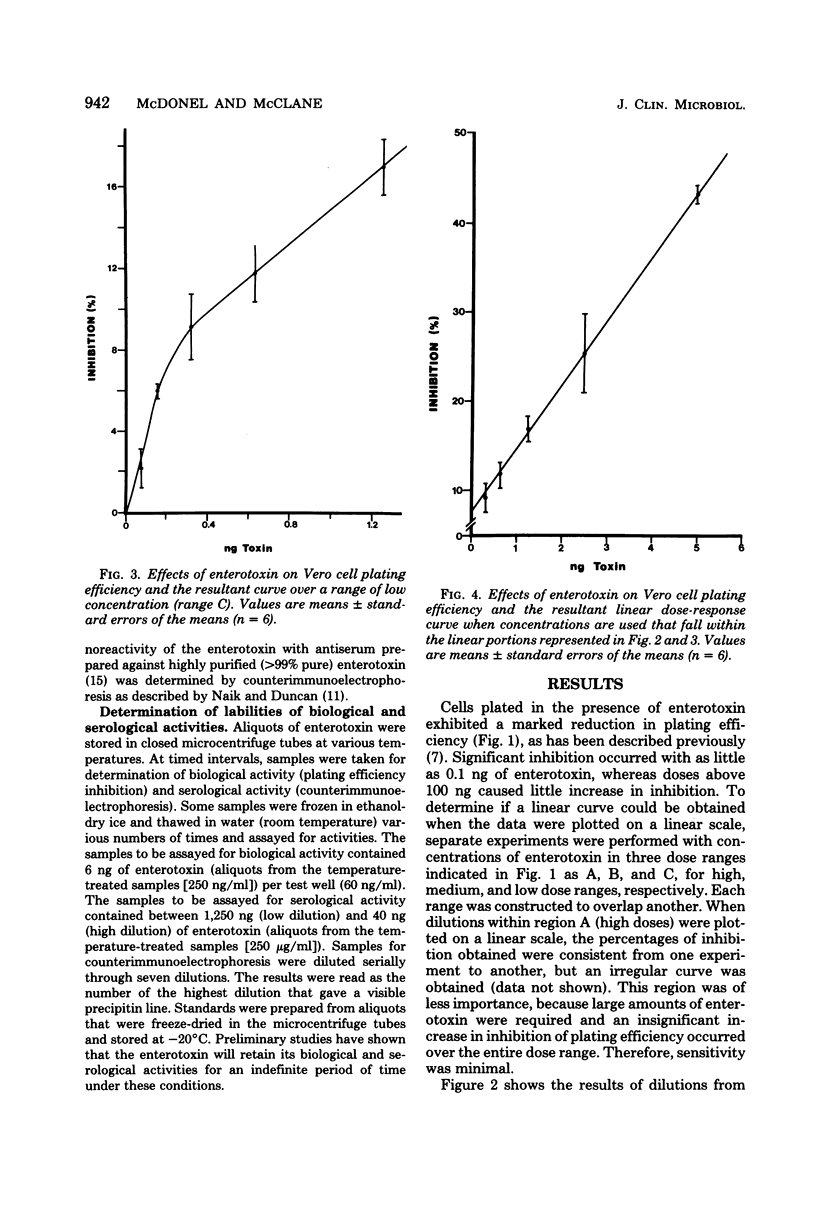
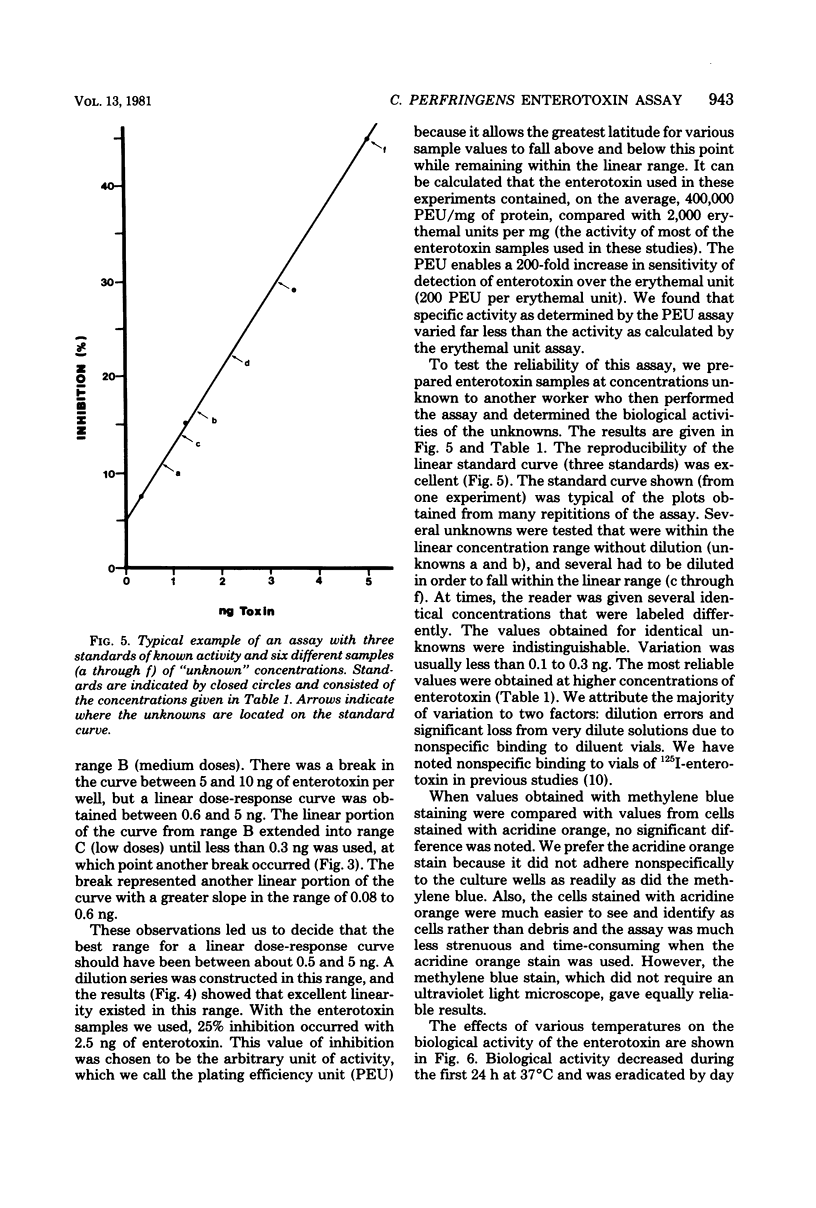
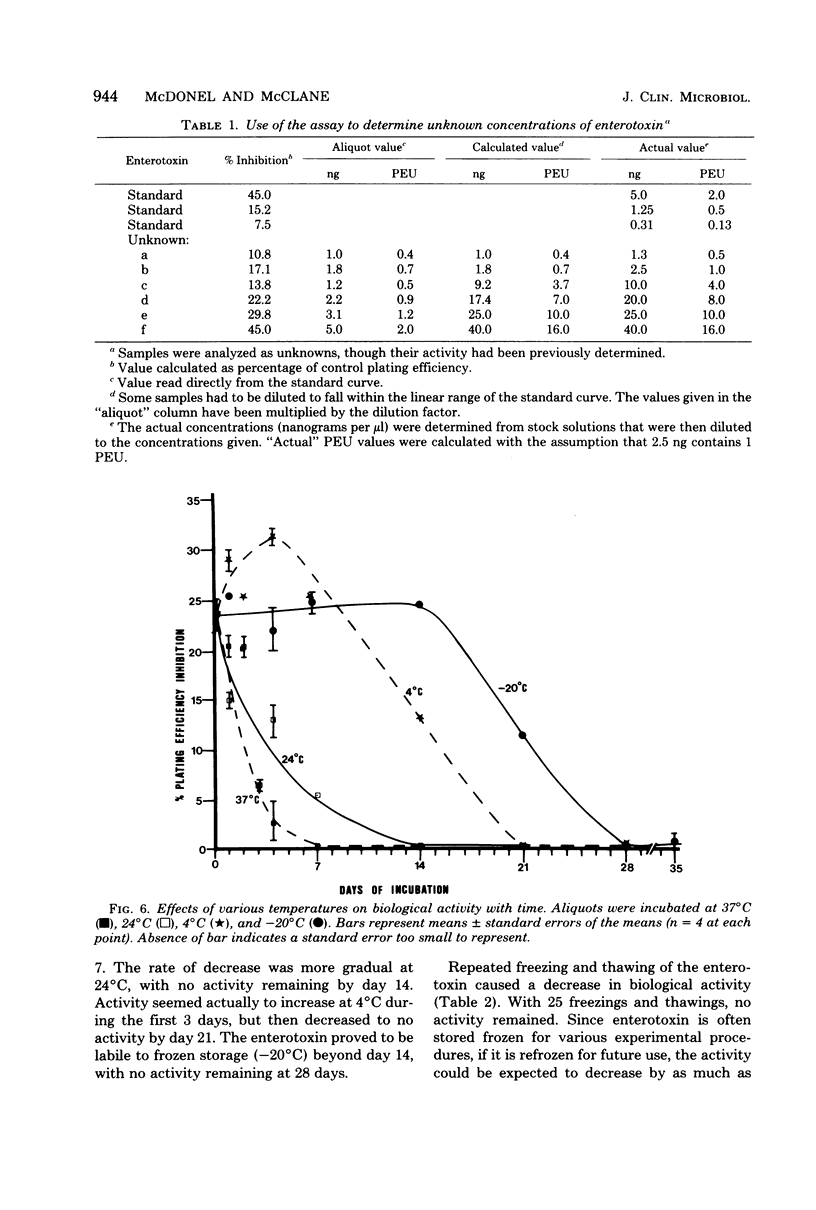
A highly sensitive and reproducible biological assay for Clostridium perfringens enterotoxin is described that uses Vero (African green monkey kidney) cells grown in tissue cultures. Very small doses of the enterotoxin inhibited the plating efficiency of the cells. This inhibition of plating efficiency could be used to detect as little as 0.1 ng (1 ng/ml) of enterotoxin, and a linear dose-response curve was obtained with 0.5 to 5 ng (5 to 50 ng/ml). A nonlinear, but reproducible, curve was obtained with a dose range from 0.1 to 100 ng (1 to 1,000 ng/ml). A new unit of biological activity, called the plating efficiency unit, was defined as that amount of enterotoxin that caused a 25% inhibition of the plating of 200 cells inoculated into 100 microliters of medium in a microwell culture system. One milligram of highly purified enterotoxin contained about 400,000 plating efficiency units. Additional studies demonstrated that the biological and serological activities of the enterotoxin molecule were not equally labile.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Duncan C. L., Somers E. B. Quantitation of Clostridium perfringens type A enterotoxin by electroimmunodiffusion. Appl Microbiol. 1972 Nov;24(5):801–804. doi: 10.1128/am.24.5.801-804.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duncan C. L., Strong D. H. Ileal loop fluid accumulation and production of diarrhea in rabbits by cell-free products of Clostridium perfringens. J Bacteriol. 1969 Oct;100(1):86–94. doi: 10.1128/jb.100.1.86-94.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Genigeorgis C., Sakaguchi G., Riemann H. Assay methods for Clostridium perfringens type A enterotoxin. Appl Microbiol. 1973 Jul;26(1):111–115. doi: 10.1128/am.26.1.111-115.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hauschild A. H., Hilsheimer R. Purification and characteristics of the enterotoxin of Clostridium perfringens type A. Can J Microbiol. 1971 Nov;17(11):1425–1433. doi: 10.1139/m71-227. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hauschild A. H., Hilsheimer R., Rogers C. G. Rapid detection of Clostridium perfringens enterotoxin by a modified ligated intestinal loop technique in rabbits. Can J Microbiol. 1971 Nov;17(11):1475–1476. doi: 10.1139/m71-235. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClane B. A., McDonel J. L. The effects of Clostridium perfringens enterotoxin on morphology, viability, and macromolecular synthesis in Vero cells. J Cell Physiol. 1979 May;99(2):191–200. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040990205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonel J. L. Binding of Clostridium perfringens [125I]enterotoxin to rabbit intestinal cells. Biochemistry. 1980 Oct 14;19(21):4801–4807. doi: 10.1021/bi00562a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonel J. L. Clostridium perfringens toxins (type A, B, C, D, E). Pharmacol Ther. 1980;10(3):617–655. doi: 10.1016/0163-7258(80)90031-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonel J. L. The molecular mode of action of Clostridium perfringens enterotoxin. Am J Clin Nutr. 1979 Jan;32(1):210–218. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/32.1.210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naik H. S., Duncan C. L. Rapid detection and quantitation of Clostridium perfringens enterostoxin by counterimmunoelectrophoresis. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1977 Aug;34(2):125–128. doi: 10.1128/aem.34.2.125-128.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niilo L. Response of ligated intestinal loops in chickens to the enterotoxin of Clostridium perfringens. Appl Microbiol. 1974 Nov;28(5):889–891. doi: 10.1128/am.28.5.889-891.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilo L. Measurement of biological activities of purified and crude enterotoxin of Clostridium perfringens. Infect Immun. 1975 Aug;12(2):440–442. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.2.440-442.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stark R. L., Duncan C. L. Biological characteristics of Clostridium perfringens type A enterotoxin. Infect Immun. 1971 Aug;4(2):89–96. doi: 10.1128/iai.4.2.89-96.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stark R. L., Duncan C. L. Purification and biochemical properties of Clostridium perfringens type A enterotoxin. Infect Immun. 1972 Nov;6(5):662–673. doi: 10.1128/iai.6.5.662-673.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uemura T., Sakaguchi G., Riemann H. P. In vitro production of Clostridium perfringens enterotoxin and its detection by reversed passive hemagglutination. Appl Microbiol. 1973 Sep;26(3):381–385. doi: 10.1128/am.26.3.381-385.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


