Abstract
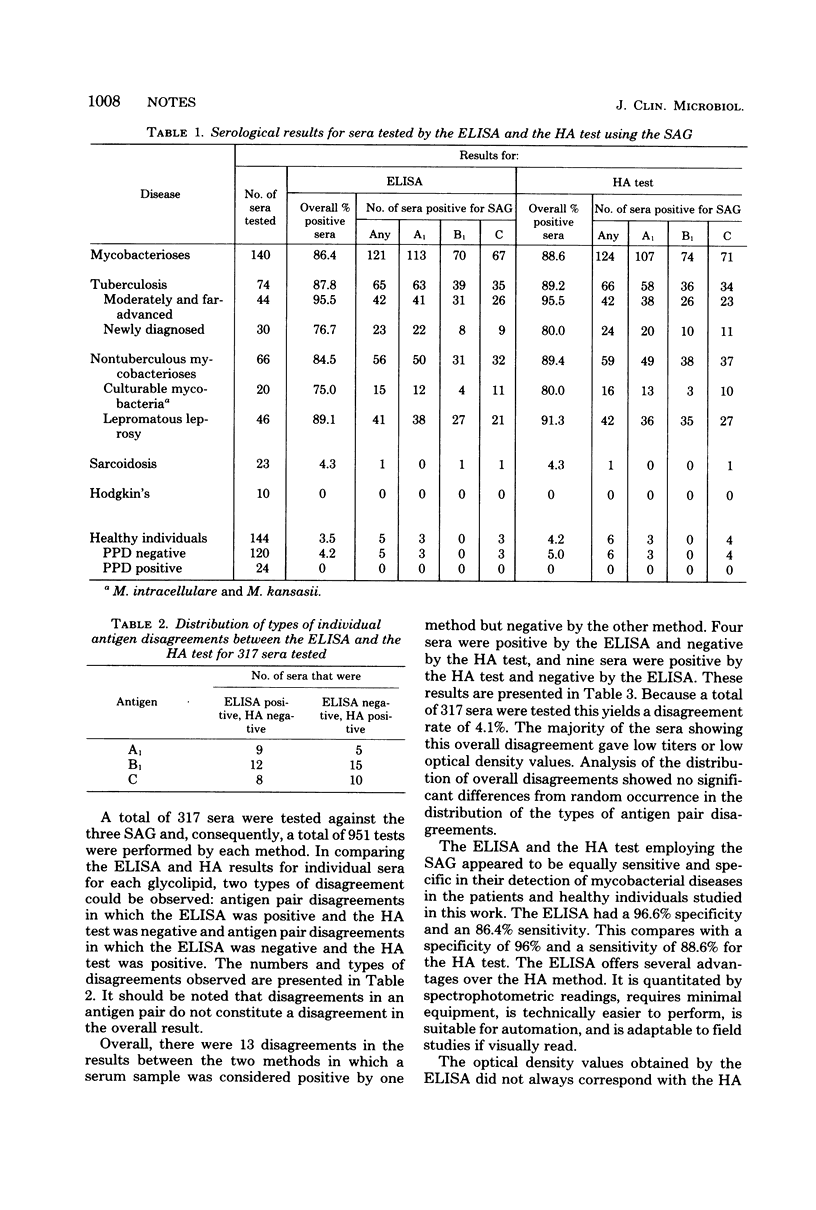
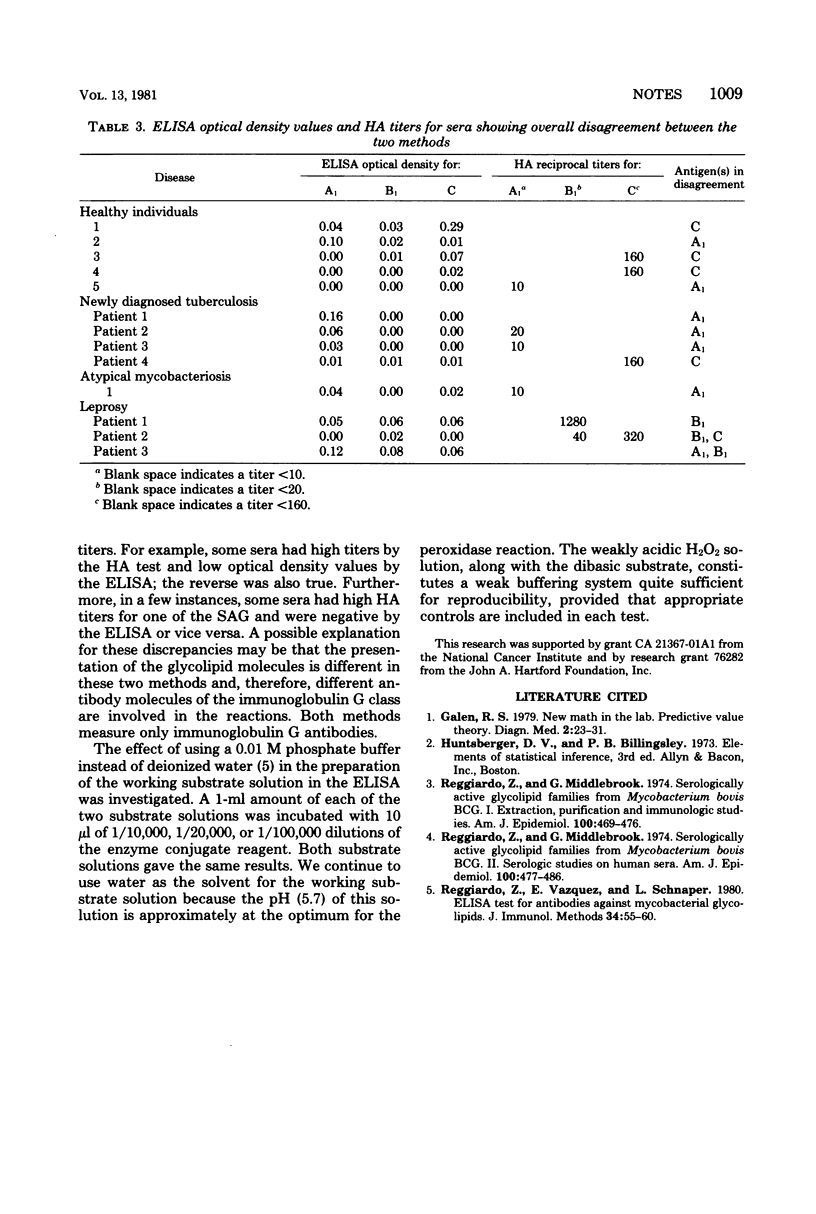
Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay and hemagglutination methods were compared using mycobacterial glycolipids as antigens. Both methods were found to have equivalent specificity and sensitivity in detecting mycobacterial diseases. Both tests had 96% specificity; the sensitivity of the enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay was 86%, and that of the hemagglutination test was 88.6%.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Reggiardo Z., Middlebrook G. Serologically active glycolipid families from Mycobacterium bovis BCG. I. Extraction, purification and immunologic studies. Am J Epidemiol. 1974 Dec;100(6):469–476. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a112059. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reggiardo Z., Middlebrook G. Serologically active glycolipid families from Mycobacterium bovis BCG. II. Serologic studies on human sera. Am J Epidemiol. 1974 Dec;100(6):477–486. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a112060. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reggiardo Z., Vazquez E., Schnaper L. ELISA tests for antibodies against mycobacterial glycolipids. J Immunol Methods. 1980;34(1):55–60. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(80)90224-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


