Abstract
Manganese(III)-mediated oxidative transformations of dearomatized phloroglucinol (1,3,5-trihydroxybenzene) derivatives are reported. A number of cyclization modes have been observed, including polycyclization to afford bicyclo[2.2.2]octadiones via a formal oxidative radical [4+2] cycloaddition.
Oxidative transformations involving an enolized carbonyl moiety have significantly attracted the attention of synthetic chemists. Metal ions such as Mn(III), Cu(II), Fe(III), and Ce(IV) are well known for their potential to extract electrons from electron-rich enols and enolates generally resulting in the formation of an electrophilic α-carbonyl radical. This general reactivity has found numerous synthetic applications. Examples include Mn(III)-mediated oxidative free radical cyclizations,1 Mn(III)-mediated cycloadditions,2 α-acetoxylation3 and arylation,1b, 4 and Fe(III)- or Cu(II)-mediated enolate hetero-5 and homocoupling.6 Some of these methods have found use in the synthesis of complex natural product targets and medicinal agents.7 Mn(III)-based oxidative radical cyclizations of carbonyl compounds onto unactivated olefins, extensively studied by Snider and others, 1, 8 are particularly attractive for their potential to rapidly generate molecular complexity.
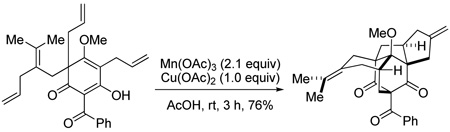
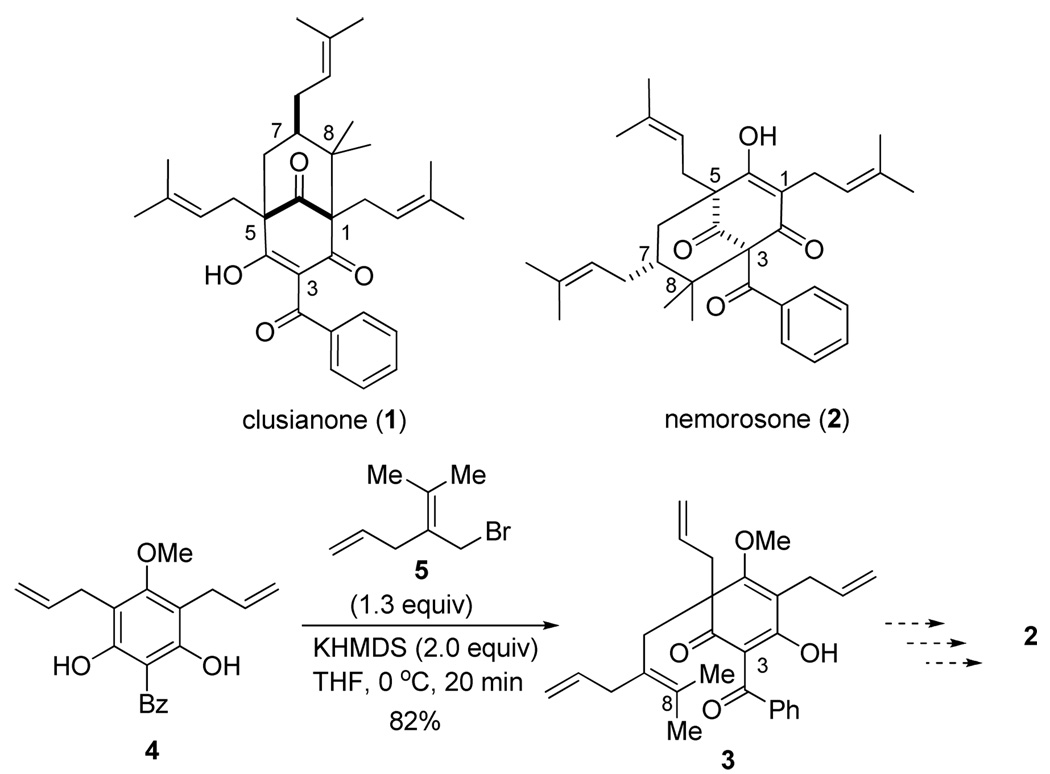
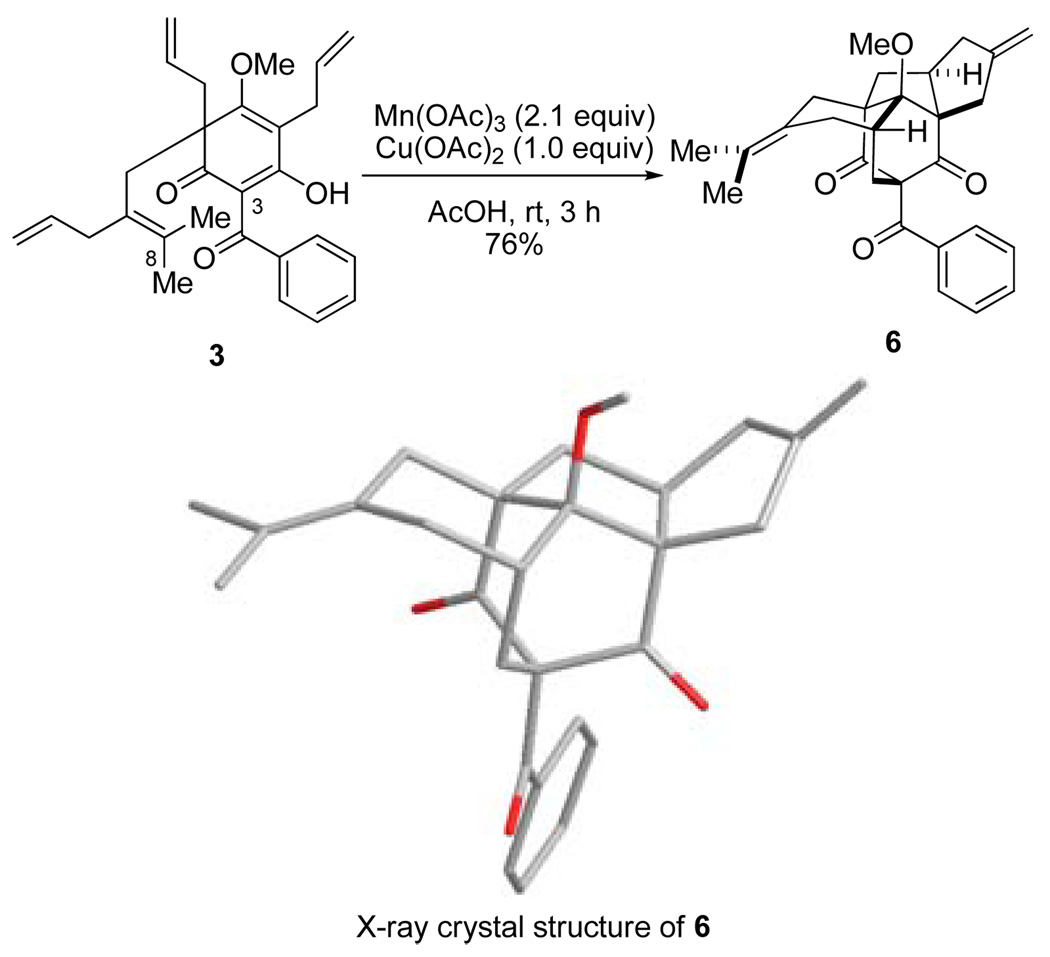
Our laboratory has a continuing interest in dearomatization of electron-rich aromatic compounds in the synthesis of bioactive natural products. For example, we have developed synthetic approaches to polyprenylated acylphloroglucinol natural products9 via alkylative dearomatization/annulation of phloroglucinol (1,3,5-trihydroxybenzene) derivatives. Along these lines, we have reported the synthesis of (±)-clusianone (1)10 employing a Michael addition/elimination/Michael addition cascade for rapid assembly of the bicyclo[3.3.1]nonane core.11 In studies aimed at developing a related approach to the regioisomeric natural product nemorosone (2),12 tetraene precursor 3 was prepared via alkylative dearomatization of 4 with allylic bromide 5 (Scheme 1).13 With the aim of effecting the desired C3–C8 bond formation (nemorosone numbering) via an oxidative generation of a radical at C3 and subsequent cyclization onto the tetrasubstituted olefin,14 we examined the reactivity of 3 in the presence of metal oxidants. It was serendipitously found that treatment of 3 with Mn(OAc)3 (2.1 equiv), Cu(OAc)2 (1.0 equiv), in AcOH at rt led to formation of the bridged pentacyclic compound 6 in 76% yield as a single isolable product (Scheme 2). The structure of 6 was unambiguously confirmed by X-ray crystallography.13
Scheme 1.
Scheme 2.
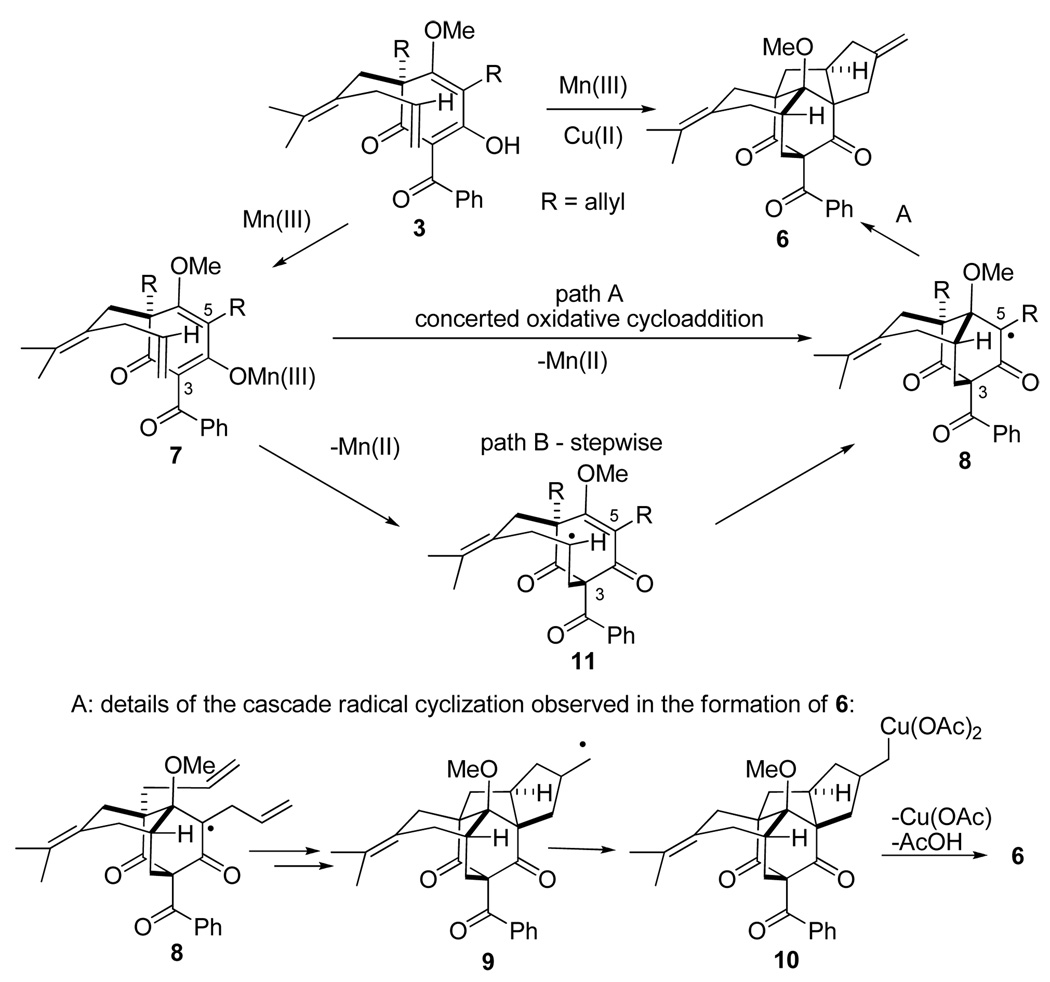
A proposed mechanism rationalizing the formation of 6 is outlined in Scheme 3. Formation of Mn(III)-enolate 7 is likely a facile and reversible process as 3 already exists in the enol form.15 Next, an overall [4+2] cycloaddition may occur leading to bicyclo[2.2.2]octadione 8 and a radical at C5. A cascade of two 5-exo radical cyclizations of intermediate 8 via the sequence outlined in Scheme 3 then results in cyclopentanemethyl radical 9 which reacts with Cu(II) to give a Cu(III) intermediate 10.16 Finally, loss of AcOH and Cu(OAc) affords polycycle 6. The most intriguing aspect of this cascade cyclization is the initial [4+2]-cycloaddition event which may be envisioned to occur in a concerted manner (path A) or a stepwise cascade radical cyclization (path B). The latter would proceed via an 8-endo cyclization to intermediate 11. Early studies by Snider have shown a similar preference for 8-endo cyclization in acyclic acetoacetate systems.17,1e While oxidative conditions have been used to promote formal [4+2] cycloadditions,18 to our knowledge this is the first example of a Mn(III)/Cu(II)-mediated [4+2] cycloaddition process. Moreover, the central bicyclo[2.2.2]octanone core is present in numerous bioactive natural products.19 These considerations prompted further studies on this transformation.
Scheme 3.
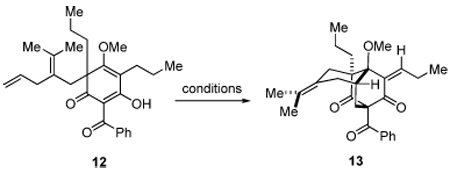
To examine the unique cycloaddition event without interference from subsequent tandem radical cyclization, we prepared precursor 12 bearing n-propyl groups on the phloroglucinol core. Treatment of 12 under identical reaction conditions (Mn(OAc)3 (2.1 equiv), Cu(OAc)2 (1 equiv), AcOH, rt) led to formation of the bridged tricyclic enone 13 in 66% yield as a 5 : 1 mixture of Z and E isomers (Table 1, entry 1). Employment of one equivalent of Mn(OAc)3 led to incomplete reaction (entry 2). Omission of Cu(OAc)2 led to slow decomposition of the starting material (entry 3), thus suggesting that Cu(II) may be required in the terminating oxidative elimination step. It was found that Cu(II) alone does not promote the cycloaddition (entry 4). Attempts to use a catalytic amount of Mn(OAc)3 in the absence of Cu(II) provided only trace amounts of product 13 (entry 5). It was also found that the reaction was not compatible with nonprotic solvents (THF, MeCN) in accordance with previous observations made by Snider and coworkers.1e A limited number of other metal oxidants were also tested. Use of Ce(NH4)2(NO3)6 in CH3CN resulted in a complex mixture of products,20 whereas PhI(OAc)2 as an oxidant resulted in no reaction (entries 8 and 9).
Table 1.
Conditions for oxidative cycloaddition of 12.
 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| entry | oxidant (equiv)a | solvent | time (h) | % yield |
| 1 | Mn(OAc)3 (2.1) | AcOH | 4 | 66b |
| Cu(OAc)2 (1.0) | ||||
| 2 | Mn(OAc)3 (1.0) | AcOH | 6 | 31d |
| Cu(OAc)2 (1.0) | ||||
| 3 | Mn(OAc)3 (2.1) | AcOH | 16 | tracec |
| 4 | Cu(OAc)2 (1.0) | AcOH | 16 | --d |
| 5 | Mn(OAc)3 (0.1) | AcOH | 16 | traced |
| 6 | Mn(OAc)3 (2.1) | THF | 16 | --c |
| Cu(OAc)2 (1.0) | ||||
| 7 | Mn(OAc)3 (2.1) | MeCN | 16 | --c |
| Cu(OAc)2 (1.0) | ||||
| 8 | Ce(NH4)2(NO3)6 (2.0) | MeCN | 3 | --e |
| 9 | PhI(OAc)2 (1.2) | MeCN | 16 | NRd |
All reactions were carried out at ambient temperature except when noted; Mn(OAc)3·2H2O, and Cu(OAc)2·H2O were used;
Isolated as a 5:1 mixture of olefin isomers (1H NMR);
Slow decomposition of the starting material occurred.
Starting material was recovered unreacted.
Reaction performed at −20 °C and resulted in a complex mixture of products.
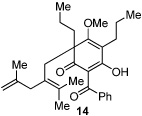
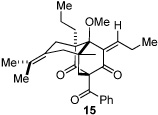
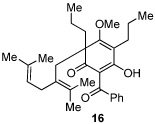
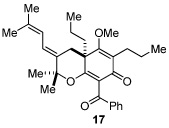
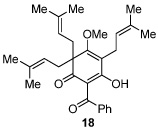
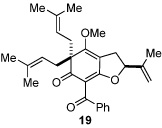
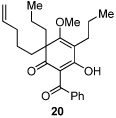
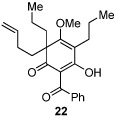
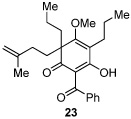
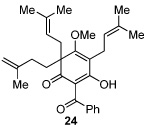
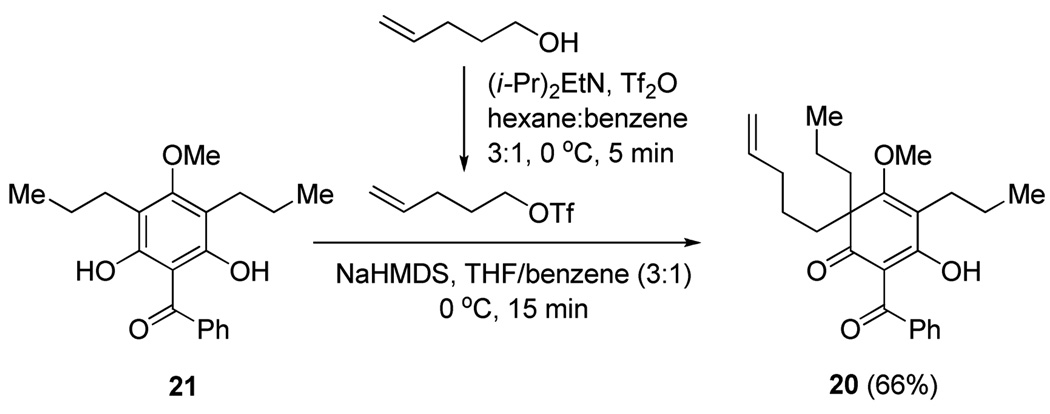
Next, we examined the scope of the oxidative [4+2] cycloaddition on a series of phloroglucinol substrates (Table 2). Oxidation of 2,2-disubstituted alkene substrate 14 (entry 1) resulted in clean conversion to cycloadduct 15 in 82% yield (>10 : 1 mixture of Z / E isomers). When a terminally disubstituted olefin 16 was employed (entry 2), the cycloaddition pathway was replaced by O-cyclization onto the proximal tetrasubstituted olefin resulting in diene 17. A related 5-exo O-cyclization was observed with the triprenylated phloroglucinol derivative 18 affording dihydrofuran 19 in 76% yield (entry 3). It was reasoned that the unique cycloaddition reactivity observed in substrates 3, 12, and 14 may be facilitated by conformational constraints imposed by the tetrasubstituted olefin in the tether placing the terminal alkene close to the reactive enol. To access substrate 20 that does not contain a constraining element, a protocol for alkylative dearomatization of phloroglucinol derivative 21 with the freshly prepared triflate of 4-penten-1-ol was developed (Scheme 4).21 This procedure was used to prepare three additional non-allylic derivatives (22–24, Table 2).13
Table 2.
Scope of the Mn(III)-mediated cycloaddition
Reaction conditions: Mn(OAc)3·2H2O (2.1 equiv), Cu(OAc)2·H2O (1.0 equiv), AcOH, rt, 4 h.
Reaction performed at 65 °C for 15 min.
Reaction performed at 35 °C for 4 h.
dr = 4:1 (major diastereomer shown).
Scheme 4.
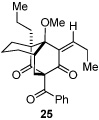
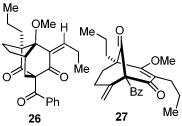
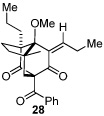
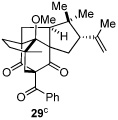
As expected, precursor 20 reacted much slower at rt (~20% yield of 25 after 16h at rt); however, only mild heating at 35 °C led to the production of cycloadduct 25 in 72% yield (Table 2, entry 4).22 Reducing the tether length by one carbon as in 22 resulted in only 23% isolated yield of cycloaddition product 26. The major product of this reaction was bicyclo[3.3.1]nonane 27 (60%) resulting from a 6-exo cyclization onto the olefin (entry 5).14 However, by using a 2,2-disubstituted olefin, the cycloaddition mode of reactivity was fully restored as substrate 23 afforded bicyclo[2.2.2]octadione 28 as a single product in 69% yield (entry 6). Similar reactivity was observed using diprenylated substrate 24 leading to a cascade reaction to afford pentacycle 29 in 74% yield as a 3 : 1 mixture of epimers (entry 7).13 The bicyclo[3.3.0]octane portion of 29 resembles the acylphloroglucinol natural products ialibinones A–D.23
In conclusion, we have examined the reactivity of a number of dearomatized acylphloroglucinol derivatives under Mn(III)/Cu(II)-mediated oxidative radical conditions. It is evident that a number of modes of cyclization are possible (cycloaddition, O-cyclization, C-cyclization) and that the reaction outcome is strongly influenced by the substitution pattern of the olefin and the tether. A novel mode of oxidative [4+2] cycloaddition was observed leading to a rapid increase of molecular complexity via cascade radical cyclizations. Further studies aimed at extending the scope and utility of this transformation are ongoing and will be reported in future publications.
Supplementary Material
Detailed experimental procedures and spectral data for all compounds. X-ray crystal structure coordinates and files in CIF format. This material is available free of charge via the Internet at http://pubs.acs.org.
Acknowledgment
Financial support from the NIH (GM073855), Eisai, Merck, and Wyeth is gratefully acknowledged. We thank Prof. Barry Snider (Brandeis University), Ji Qi, and Qiang Zhang (Boston University) for helpful discussions and Dr. Emil Lobkovsky (Cornell University) for x-ray crystallographic analysis.
References
- 1.(a) Snider BB, Patricia JJ, Kates SA. J. Org. Chem. 1988;53:2137. [Google Scholar]; (b) Kates SA, Dombroski MA, Snider BB. J. Org. Chem. 1990;55:2425. [Google Scholar]; (c) Snider BB, McCarthy BA. J. Org. Chem. 1993;58:6217. [Google Scholar]; (d) Snider BB. Chem. Rev. 1996;96:339. doi: 10.1021/cr950026m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (e) Cole BM, Han L, Snider BB. J. Org. Chem. 1996;61:7832. doi: 10.1021/jo961199u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.(a) Melikyan GG. Synthesis. 1993:833. [Google Scholar]; (b) Mellor JM, Mohammed S. Tetrahedron. 1993;49:7557. [Google Scholar]; (c) Snider BB, Han L, Xie C. J. Org. Chem. 1997;62:6978. [Google Scholar]; (d) Chowdhury FA, Nishino H, Kurosawa K. Tetrahedron Lett. 1998;39:7931. [Google Scholar]; (e) Tsai A-I, Lin C-H, Chuang C-P. Heterocycles. 2005;65:2381. [Google Scholar]
- 3.(a) Williams GJ, Hunter NR. Can. J. Chem. 1976;54:3830. [Google Scholar]; (b) Dunlap NK, Sabol MR, Watt DS. Tetrahedron Lett. 1984;25:5839. [Google Scholar]; (c) Gross RS, Kawada K, Kim M, Watt DS. Synth. Commun. 1989;19:1127. [Google Scholar]; (d) Tanyeli C, Sezen B, Iyigun C, Elmali O. Tetrahedron Lett. 2001;42:6397. [Google Scholar]
- 4.Bhowmik DR, Venkateswaran RV. Tetrahedron Lett. 1999;40:7439. [Google Scholar]
- 5.(a) Baran PS, DeMartino MP. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2006;45:7083. doi: 10.1002/anie.200603024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (b) DeMartino MP, Chen K, Baran PS. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008;130:11546. doi: 10.1021/ja804159y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.(a) Rathke MW, Lindert A. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1971;93:4605. [Google Scholar]; (b) Ito Y, Konoike T, Saegusa T. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1975;97:2912. [Google Scholar]; (c) Frazier RH, Jr, Harlow RL. J. Org. Chem. 1980;45:5408–5411. [Google Scholar]
- 7.(a) Pettus TRR, Inoue M, Chen XT, Danishefsky SJ. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2000;122:6160. [Google Scholar]; (b) Snider BB, Mohan R, Kates SA. J. Org. Chem. 1985;50:3659. [Google Scholar]; (c) Paquette LA, Schaefer AG, Springer JP. Tetrahedron. 1987;43:5567. [Google Scholar]; (d) Nicolaou KC, Gray DLF. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004;126:607. doi: 10.1021/ja030497n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (e) Baran PS, Richter JM, Lin DW. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2005;44:609. doi: 10.1002/anie.200462048. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.(a) Corey EJ, Kang MC. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1984;106:5384. [Google Scholar]; (b) Ernst AB, Fristad WE. Tetrahedron Lett. 1985;26:3761. [Google Scholar]; (c) Yang D, Ye X-Y, Gu S, Xu M. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1999;121:5579. [Google Scholar]
- 9.Ciochina R, Grossman RB. Chem. Rev. 2006;106:3963. doi: 10.1021/cr0500582. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Mccandlish LE, Hanson JC, Stout GH. Acta Cryst. 1976;B32:1793. [Google Scholar]
- 11.Qi J, Porco JA., Jr J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007;129:12682. doi: 10.1021/ja0762339. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Cuesta-Rubio O, Velez-Castro H, Frontana-Uribe BA, Cardenas J. Phytochemistry. 2001;57:279. doi: 10.1016/s0031-9422(00)00510-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.See Supporting Information for complete experimental details.
- 14.For previous use of Mn(III)-based oxidative cyclization towards phloroglucinol natural products, see:Kraus GA, Dneprovskaia E, Nguyen TH, Jeon I. Tetrahedron. 2003;59:8975.
- 15.In the 1H NMR spectra of dearomatized benzoylphloroglucinol derivatives such as 3, the enolic hydrogen appears in the far downfield region (16–18 ppm) suggesting complete enolization. The compound exists as a mixture of two enol tautomers. See references 1a and 1d for a discussion on the mechanistic details of Mn(III)-based oxidations of 1,3-dicarbonyl compounds.
- 16.(a) Kochi JK. In: Free Radicals. Chapter 11. Kochi JK, editor. Vol. 1. New York: Wiley; 1973. [Google Scholar]; (b) Kochi JK. Acc. Chem. Res. 1974;7:351. [Google Scholar]
- 17.Snider BB, Merrit JE. Tetrahedron. 1991;47:8663. [Google Scholar]
- 18.(a) Yueh W, Bauld NLJ. Phys. Org. Chem. 1996;9:529. [Google Scholar]; (b) Gao D, Bauld NL. J. Org. Chem. 2000;65:6276. doi: 10.1021/jo005530s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (c) Zhou Y, Jia X, Li R, Liu Z, Liu Z, Wu L. Tetrahedron Lett. 2005;45:8937. [Google Scholar]
- 19.(a) Carman RM, Lambert LK, Robinson WT, Van Dongen JMAM. Aust. J. Chem. 1986;39:1843. [Google Scholar]; (b) Bringmann G, Lang G, Gulder TAM, Tsuruta H, Mühlbacher J, Maksimenka K, Steffens S, Schaumann K, Stöhr R, Wiese J, Imhoff JF, Perović-Ottstadt S, Boreiko O, Müller WEG. Tetrahedron. 2005;61:7252. [Google Scholar]; (c) Chien S-C, Chang J-Y, Kuo C-C, Hsieh C-C, Yang N-S, Kuo Y-H. Tetrahedron Lett. 2007;48:1567. [Google Scholar]
- 20.These products appear to result from multiple cyclization modes onto the tetrasubstituted olefin (O vs C, 6-endo vs 5-exo).
- 21.Attempts to use non-allylic bromides led to low reactivity mainly resulting in alkylation of the phenolic oxygens. The alkyl triflate was prepared using a modified literature procedure:Bashore CG, Vetelino MG, Wirtz MC, Brooks PR, Frost HN, McDermott RE, Whritenour DC, Ragan JA, Rutherford JL, Makowski TW, Brenek SJ, Coe JW. Org. Lett. 2006;8:5947. doi: 10.1021/ol0623062.
- 22.Enones 25, 26, and 28 were isolated as a single (Z) isomer (1H NMR).
- 23.Winkelmann K, Heilmann J, Zerbe O, Rali T, Sticher O. J. Nat. Prod. 2000;63:104. doi: 10.1021/np990417m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Detailed experimental procedures and spectral data for all compounds. X-ray crystal structure coordinates and files in CIF format. This material is available free of charge via the Internet at http://pubs.acs.org.