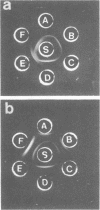
Abstract
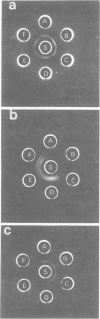
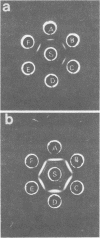
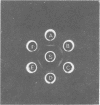
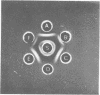
The serological identification of Propionibacterium acnes, P. granulosum, and P. avidum, using trichloroacetic acid extracts, is described. With antisera prepared against reference strains, the method has been tested on 142 strains recently isolated from human skin. All except two of the strains could be identified serologically, and there was excellent agreement between the serological results and the fermentation pattern of the strains. Two serological types of P. acnes and two of P. avidum were identified, but only one of P. granulosum.
Full text
PDF

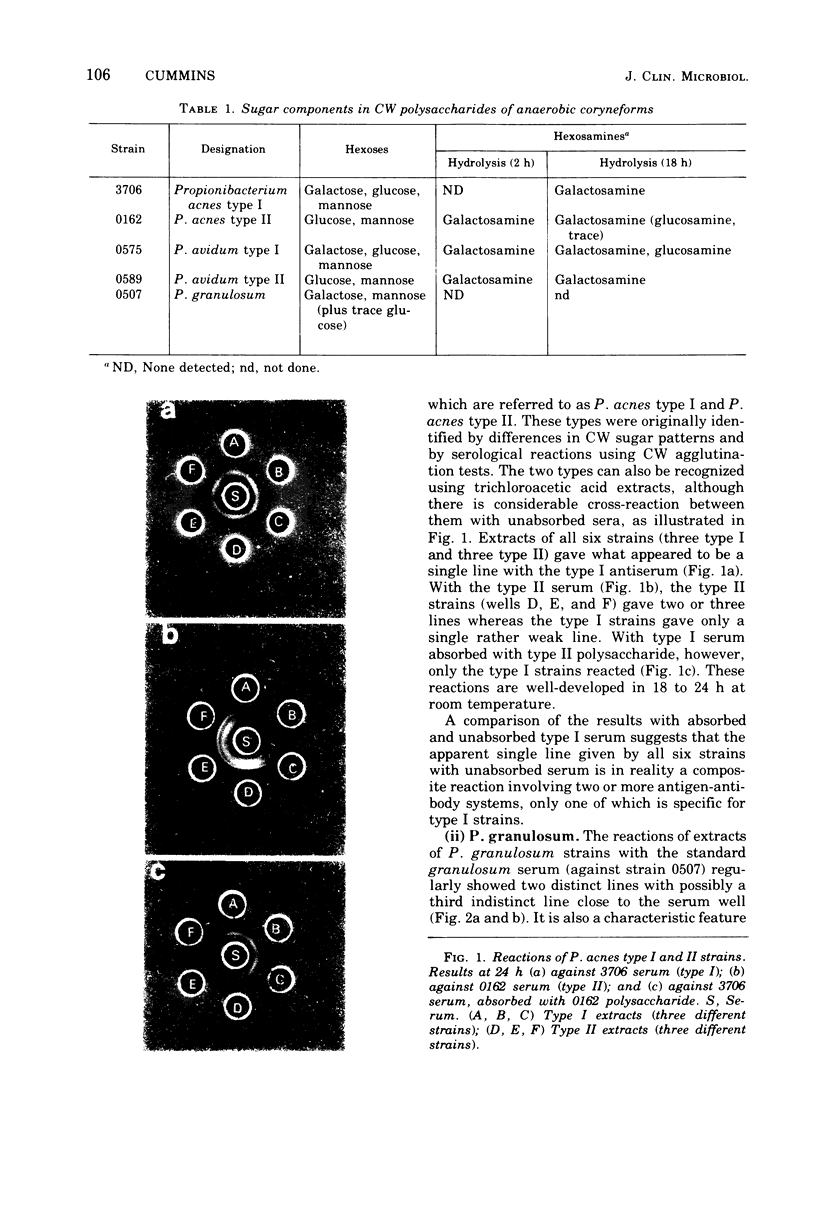
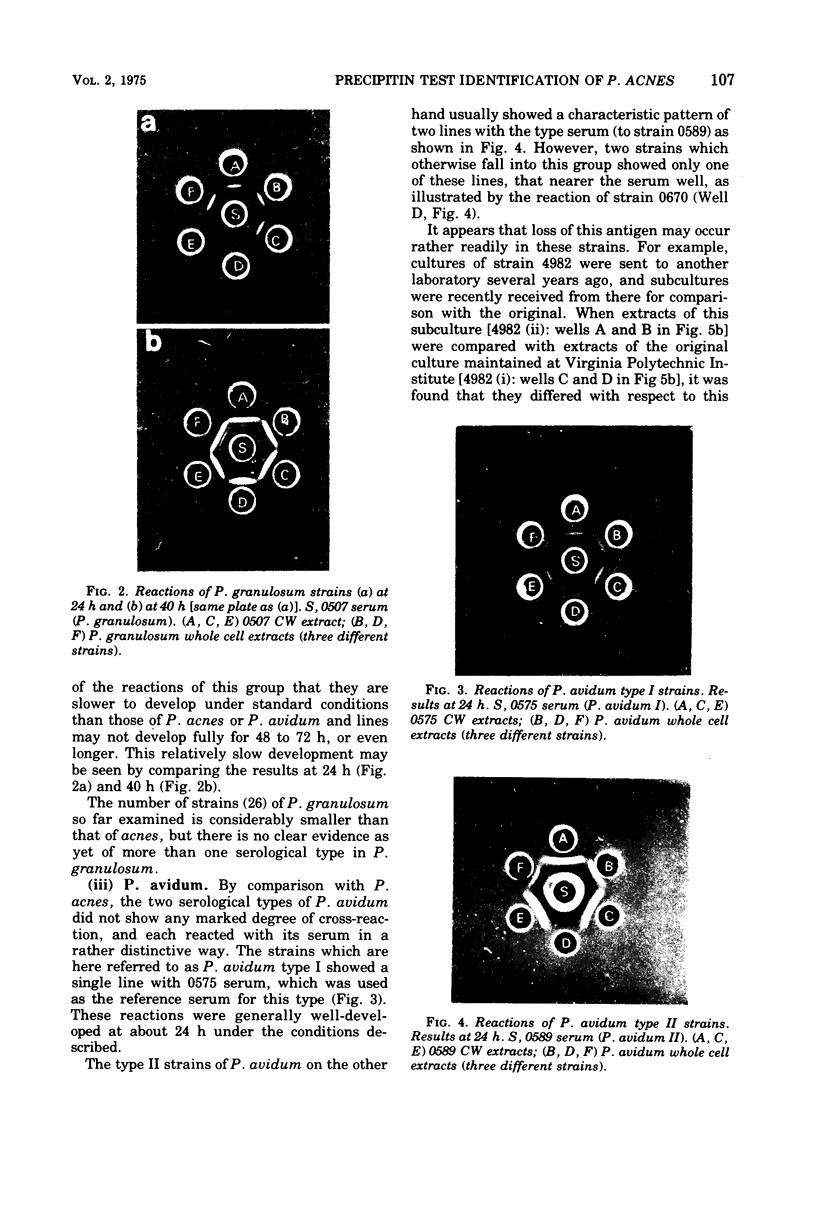

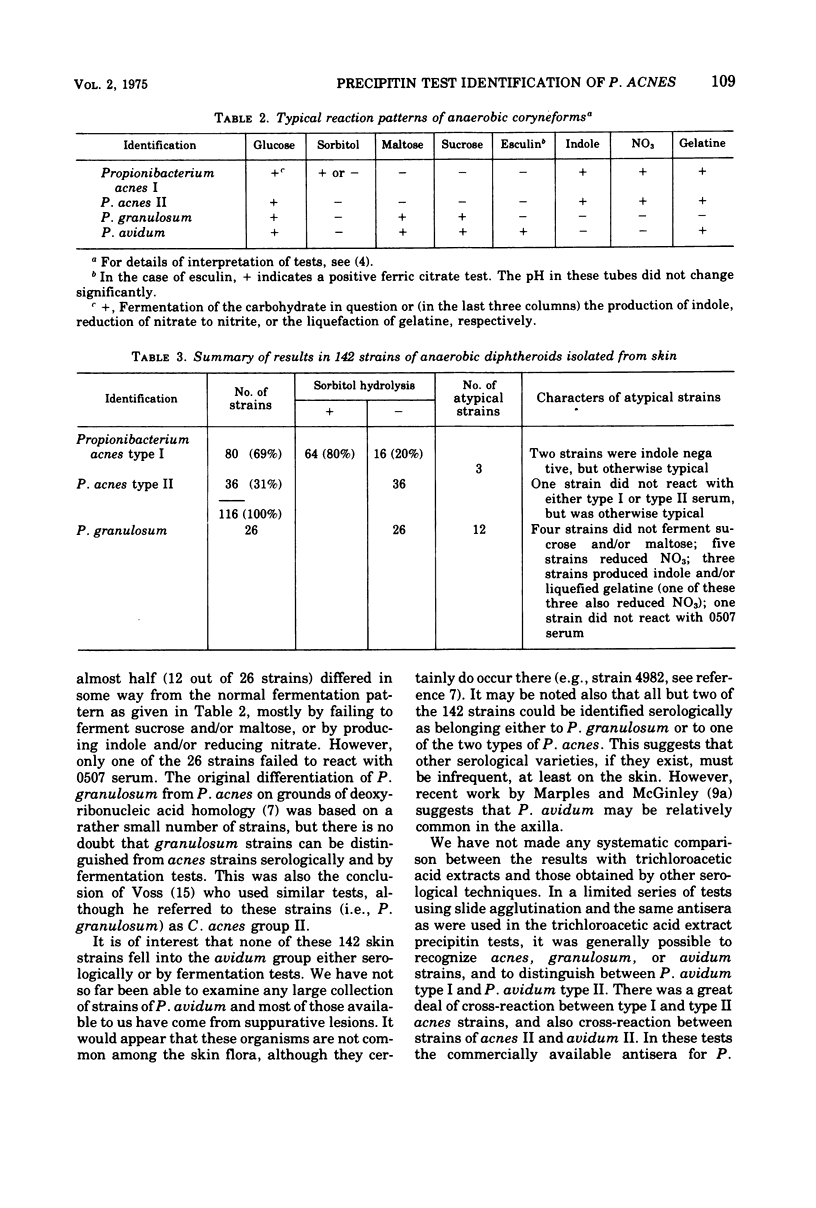

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- CAILLE B., TOUCAS M. [Antigenic study of Corynebacterium acnes by the passive hemagglutination test. Antigens in common with other Corynebacteria]. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1960 Feb;98:276–281. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cummins C. S., Johnson J. L. Corynebacterium parvum: a synonym for Propionibacterium acnes? J Gen Microbiol. 1974 Feb;80(2):433–442. doi: 10.1099/00221287-80-2-433. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FLORMAN A. L., SCOMA J. L. A latex agglutination test for anaerobic diphtheroids. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1960 Aug-Sep;104:683–685. doi: 10.3181/00379727-104-25951. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmberg K., Forsum U. Identification of Actinomyces, Arachnia, Bacterionema, Rothia, and Propionibacterium species by defined immunofluorescence. Appl Microbiol. 1973 May;25(5):834–843. doi: 10.1128/am.25.5.834-843.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson J. L., Cummins C. S. Cell wall composition and deoxyribonucleic acid similarities among the anaerobic coryneforms, classical propionibacteria, and strains of Arachnia propionica. J Bacteriol. 1972 Mar;109(3):1047–1066. doi: 10.1128/jb.109.3.1047-1066.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LINZENMEIER G. Etude sérologique des corynébactéries anaérobies par la methode des agglutinines. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1954 Nov;87(5):572–579. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marples R. R., McGinley K. J. Corynebacterium acnes and other anaerobic diphtheroids from human skin. J Med Microbiol. 1974 Aug;7(3):349–357. doi: 10.1099/00222615-7-3-349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pulverer G., Ko H. L. Fermentative and serological studies on Propionibacterium acnes. Appl Microbiol. 1973 Feb;25(2):222–229. doi: 10.1128/am.25.2.222-229.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ray L. F., Kellum R. E. Corynebacterium acnes from human skin. Identification by morphologic, cultural, biochemical, serological, and chromatographic methods. Arch Dermatol. 1970 Jan;101(1):36–40. doi: 10.1001/archderm.101.1.36. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TREVELYAN W. E., HARRISON J. S. Studies on yeast metabolism. I. Fractionation and microdetermination of cell carbohydrates. Biochem J. 1952 Jan;50(3):298–303. doi: 10.1042/bj0500298. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TREVELYAN W. E., PROCTER D. P., HARRISON J. S. Detection of sugars on paper chromatograms. Nature. 1950 Sep 9;166(4219):444–445. doi: 10.1038/166444b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voss J. G. Differentiation of two groups of Corynebacterium acnes. J Bacteriol. 1970 Feb;101(2):392–397. doi: 10.1128/jb.101.2.392-397.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]