Abstract
TGFβ1 is one of the most potent endogenous immune modulators of inflammation. The molecular mechanism of its anti-inflammatory effect on the activation of the transcription factor NF-kB has been well studied, however, the potential effects of TGFβ1 on other pro-inflammatory signaling pathways is less clear. In this study, using the well-established lipopolysaccharide (LPS) and the 1-methyl-4-phenylpyridinium (MPP+)-mediated models of Parkinson’s disease (PD), we demonstrate TGFβ1 exerts significant neuroprotection in both models via its anti-inflammatory properties. The neuroprotective effects of TGFβ1 are mainly attributed to its ability to inhibit the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) from microglia during their activation or reactivation. Moreover, we demonstrate that TGFβ1 inhibited LPS-induced NADPH oxidase (PHOX) subunit p47phox translocation from the cytosol to the membrane in microglia within 10 min. Mechanistic studies show that TGFβ1 fails to protect dopaminergic neurons in cultures from PHOX knockout mice, and significantly reduced LPS-induced translocation of the PHOX cytosolic subunits p47phox to the cell membrane. In addition, LPS-induced ERK phosphorylation and subsequent serine345 (Ser345) phosphorylation on p47phox were significantly inhibited by TGFβ1 pretreatment. Taken together, our results show that TGFβ1 exerted potent anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective properties, either through the prevention of the direct activation of microglia by LPS, or indirectly through the inhibition of reactive microgliosis elicited by MPP+. The molecular mechanisms of TGFβ1-mediated anti-inflammatory properties is through the inhibition of PHOX activity by preventing the ERK-dependent phosphorylation of Ser345 on p47phox in microlgia to reduce oxidase activities induced by LPS.
Keywords: Monocytes/Macrophages, Neuroimmunology, Inflammation
Introduction
Substantial evidence now demonstrates that microlgia-mediated inflammatory processes play an important role in the pathogenesis of several neurodegenerative diseases, including Parkinson’s disease (PD)3, Alzheimer’s disease, multiple sclerosis and the AIDS dementia complex (1–3). Microglia are the resident mononuclear phagocyte population within the central nervous system (CNS), and these cells share many phenotypical and functional characteristics with macrophages, suggesting that microglia participate in innate immune responses in the brain. While activation of microglia serves an important protective function in immune surveillance by removing foreign microorganisms (4), over-activation of microglia followed by over-production of pro-inflammatory factors have been shown to result in neuronal death in the brain (5, 6). The midbrain region that encompasses the substantia nigra is particularly rich in microglia (7), and therefore activation of nigral microglia and release of these pro-inflammatory neurotoxic factors may be crucial components of the degenerative process of dopaminergic (DA) neurons in PD. Since these pro-inflammatory neurotoxic factors also exhibit immunoregulatory functions necessary for normal immune responses, the microglial response to inflammatory stimuli must be tightly regulated to avoid over-activation and disastrous neurotoxic consequences (2).
TGFβ. is a pleiotropic cytokine that plays a critical role in control of cell growth, differentiation, inflammation, cell chemotaxis, apoptosis and hematopoiesis. Numerous in vitro studies have shown TGFβ can protect neurons from cell death induced by glutamate excitotoxicity (8), chemical hypoxia (9), apoptosis (10) and oxidative injury (10). In vivo studies have shown that TGFβ suppresses the progression of EAE (11), and that recombinant TGFβ delivered intracerebrally or via virus vectors protects animals against brain injury induced by ischemic (12), excitotoxic (9), and oxidative stress (13). Although TGFβ has been strongly implicated as a neuroprotective factor, it has also been reported that TGFβ can trigger neuronal cell death under certain conditions (14, 15). In addition, the molecular mechanism underlying its neuroprotection has not been clearly elucidated. While several reports indicated TGFβ has direct protective effects on neurons, other studies reported the neuroprotective effect of TGFβ is mediated through glia cells,such as astrocytes or microglia (16, 17). Further assessment of the functional contribution of TGFβ critically depends on the elucidation of downstream secondary signaling mechanisms, which might offer interesting targets for the development of pharmacological drugs for the treatment of both acute and chronic CNS pathologies.
Increasing evidence has shown that oxidative stress plays a very important role in PD (18, 19), and that anti-inflammatories that inhibit the oxidative stress response can be neuroprotective (20–22). The primary mediator of the oxidative stress response in microglial cells is the enzyme NADPH oxidase (PHOX), and upon LPS stimulation, microglia cells are known to produce ROS via PHOX activation (23). PHOX is a multi-component enzyme consisting of a membrane-associated cytochrome b558 (composed of two subunits: gp91phox and p22phox) and the cytosolic components: p47phox, p67phox, p40phox and a small GTPase rac2 (24). Previous studies have shown that activation of PHOX activity requires p47phox phosphorylation, a protein that has an important role in translocation of cytosolic components to cytochrome b558, as well as in the assembly and activation of NADPH oxidase (25). Previous reports have demonstrated that TGFβ1 can regulate ROS production in hepatocytes and microglia (26–29). However, the mechanism by which TGFβ1 inhibits ROS production in microglial cells, and its role in regulating the interplay between microglia and neurons in chronic CNS inflammation, remains to be determined.
The main purpose of this study was to elucidate the molecular mechanism underlying TGFβ1-elicited neuroprotection. Using primary rat mesencephalic neuron-glia cultures, we show that TGFβ1 has significant protective effects on both LPS and MPP+-induced DA neurotoxicity through its inhibition of microglia activation and reactivation. We found that TGFβ1 is acting to inhibit PHOX activity by inhibiting the translocation of the p47phox subunit of the NADPH oxidase enzyme to the cellular membrane, resulting in the loss of superoxide production by activated microglia and the inhibition of a wide array of pro-inflammatory mediators produced by activated microglia. The mechanism of action of TGFβ1 is due to the inhibition of ERK phosphorylation, resulting in the loss of p47phox phosphorylation at serine345 (Ser345). These results offer new insights into our understanding of the action of TGFβ1 on microglia, and on the etiology and eventual therapeutic treatment of neurodegenerative diseases such as PD.
Materials and Methods
Animals
NADPH oxidase-deficient (gp91phox−/−) and wild-type C57BL/6J (gp91phox+/+) mice were obtained from the Jackson Laboratory (Bar Harbor, ME). The PHOX−/− mutation is maintained in the C57BL/6 background; thus C57BL/6 mice were used as control animals. Breeding of the mice was performed to achieve timed pregnancy with the accuracy of ± 0.5 days. Timed-pregnant Fisher F344 rats were obtained from Charles River Laboratories (Raleigh, NC). Housing and breeding of the animals were performed in strict accordance with the National Institutes of Health guidelines.
Reagents
The recombinant human TGFβ1 was obtained from R&D system (Minneapolis, MN). LPS (E.coli strain O111:B4) was purchased from Calbiochem (San Diego, CA). Cell culture reagents were obtained from Invitrogen (Carlsbad, CA). [3H]-DA (30 Ci/mmol) was obtained from Perkin-Elmer Life Sciences (Boston, MA), and the monoclonal antibody against the CR3 complement receptor (OX-42) was purchased from Chemicon International (Temecula, CA). The polyclonal anti-tyrosine hydroxylase antibody was a generous gift from Dr. John Reinhard (GlaxoSmithKline, Research Triangle Park, NC). The Vectastain ABC kit and biotinylated secondary antibodies were purchased from Vector Laboratories (Burlingame, CA). The fluorescence probe Dichlorodihydro-fluorescein Diacetate (DCFH-DA) was obtained from Calbiochem (La Jolla, CA). Rabbit anti-p47phox was purchased from Upstate (Lake Placid, NY). FITC-conjugated goat anti-rabbit IgG was obtained from Jackson ImmunoResearch Laboratories. Rabbit anti-GAPDH was obtained from Abcam (Cambridge, MA). Mouse anti-gp91phox was purchased from BD Transduction Laboratories (San Jose, CA). U0126 was purchased from Biomol (Plymouth Meeting, PA).
Microglial cell line
The rat microglia HAPI cell line was a generous gift from Dr. James R. Connor (30). Briefly, cells were maintained at 37°C in DMEM supplemented with 10% FBS, 50 U/ml penicillin, and 50 µg/ml streptomycin in a humidified incubator with 5% CO2 and 95% air. The HAPI cell was derived from rat primary microglia-enriched cultures and retains the phenotypic and morphological characteristics of microglia, including phagocytic activity, expression of the receptor for isolectin B4 from Griffonia simplicifolia, as well as the specific microglial markers OX-42 (complement 3 receptor) and glucose transport protein 5. Gene expression of TNF-α and inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) can be induced by treatment with LPS.
Primary mesencephalic neuron-glia cultures
Neuron-glia cultures were prepared from the ventral mesencephalic tissues of embryonic day 14–15 rats or day 13–14 mice, as described previously (31, 32). Briefly, dissociated cells were seeded at 1 × 105 /well and 5 × 105 /well in poly-D-lysine-coated 96-well and 24-well plates, respectively. Cells were maintained at 37°C in a humidified atmosphere of 5% CO2 and 95% air, in MEM containing 10% FBS, 10% horse serum, 1 g/L glucose, 2 mM L-glutamine, 1 mM sodium pyruvate, 100 µM nonessential amino acids, 50 U/ml penicillin and 50 µg/ml streptomycin. Seven-day-old cultures were used for drug treatments. At the time of treatment, immunocytochemical analysis indicated that the rat neuron-glia cultures were made up of 11% microglia, 48% astrocytes, 41% neurons, and 1% tyrosine hydroxylase immunoreacitve (TH-IR) neurons. The composition of the neuron-glia cultures of NADPH oxidase-deficient mice was very similar to that of the wild-type mice, which consist of 12% microglia, 48% astrocytes, 40% neurons, and 1% TH-IR neurons.
Primary mesencephalic neuron-enriched cultures
Midbrain neuron-enriched cultures were established as described previously (21). Briefly, 24 h after seeding, cytosine β-D-arabinocide was added to a final concentration of 10 µM to suppress glial proliferation. Three days later, the media was removed and replaced with maintenance medium. Cells were used for drug treatments 7 days after initial seeding. Routinely, the 7-day-old neuron-enriched cultures, which normally contain less than 0.1% microglia, and less than 3–5% astrocytes, were used for treatment. Among the neuronal population (Neu-N immunoreactive neurons), 2.7–3.9% were dopaminergic neurons (TH-IR positive neurons).
Primary midbrain neuron-astroglia cocultures
Rat primary neuron-astroglia cocultures were obtained by suppressing microglial proliferation with 1.5 mM LME 24 h after seeding the cells, as described previously (21) . Three days later cultures were changed back to maintenance medium and used for treatment 7 days after initial seeding. The cultures stained with F4/80 antibody showed less than 0.1% microglia.
Primary microglia-enriched cultures
Rat microglia-enriched cultures with a purity of > 98%, were prepared from whole brains of 1-day-old Fischer 344 rat pups as described previously (33). For superoxide assays, 105 cells were grown overnight in 96-well culture plates before use.
[3H]-DA uptake assay
[3H]-DA uptake assays were performed as described (33). Briefly, cells were incubated for 20 min at 37°C with 1 µM [3H]-DA in Krebs-Ringer buffer (16 mM sodium phosphate, 119 mM NaCl, 4.7 mM KCl, 1.8 mM CaCl2, 1.2mM MgSO4, 1.3 mM EDTA, and 5.6 mM glucose; pH 7.4). Cells were washed with ice-cold Krebs-Ringer buffer three times, after which the cells were collected in 1N NaOH. Radioactivity was determined by liquid scintillation counting. Nonspecific DA uptake observed in the presence of mazindol (10 µM) was subtracted.
Immunocytochemistry
Immunostaining was performed as previously described (32). Briefly, formaldehyde (3.7%)-fixed cultures were treated with 1% hydrogen peroxide followed by sequential incubation with blocking solution, after which the cells were incubated overnight at 4°C with antibodies against TH (1:20,000). Cells were incubated with biotinylated secondary antibody for 2 h followed by incubation with ABC reagents for 40 min. Color was developed with 3,3’-diaminobenzidine. For morphological analysis, the images were recorded with an inverted microscope (Nikon, Tokyo, Japan) connected to a charge-coupled device camera (DAGE-MTI, Michigan City, IN) operated with the MetaMorph software (Universal Imaging Corporation, Downingtown, PA). For visual counting of TH-IR neurons, nine representative areas per well of the 24-well plate were counted under the microscope at 100 × magnification by three individuals. The average of these scores was reported.
Superoxide assay
The production of superoxide was determined by measuring the superoxide dismutase (SOD)-inhibitable reduction of the tetrazolium salt WST-1 (34, 35). Neuron-glia or microglia-enriched cultures in 96-well culture plates were washed twice with HBSS without phenol red. Cultures were then incubated at 37°C for 30 min with vehicle control (water) or TGFβl in HBSS (50 µl/well). Then, 50 µl of HBSS with and without SOD (50 U/ml, final concentration) was added to each well along with 50 µl of WST-1 (1 mM) in HBSS, and 50 µl of vehicle or LPS (10 ng/ml). To measure superoxide production induced by MPP+, seven day-old mesencephalic neuron-glia cultures grown in 96-well plates were treated with TGFβ1 in the presence and absence of MPP+, or vehicle alone in 150 µl of phenol red-free treatment medium. Four days after treatment, 50 µl of HBSS with and without SOD (50 U/ml, final concentration) were added to each well along with 50 µl of WST-1 (1 mM) in HBSS. Fifteen minutes later, absorbance at 450 nm was read with a SpectraMax Plus microplate spectrophotometer (Molecular Devices Corp, Sunnyvale, CA). The difference in absorbance observed in the presence and absence of SOD was considered to be the amount of superoxide produced, and results were expressed as the percentage of vehicle-treated control cultures.
Intracellular ROS assay
Intracellular ROS were determined by using a 2′ ,7′-dichlorodi-hydrofluorescein (DCFH-DA) assay as described previously with minor modifications (36). DCFH-DA enters cells passively and is deacetylated by esterase to nonfluorescent DCFH. DCFH reacts with ROS to form DCF; the fluorescent product DCFH-DA was dissolved in methanol at 10 mM and was diluted 500-fold in HBSS to give DCFH-DA at 20 µM. The cells were exposed to DCFH-DA for 1 h and then treated with HBSS containing the corresponding concentrations of LPS for 2 h. The fluorescence was read immediately at wavelengths of 485 nm for excitation and 530 nm for emission using a SpectraMax Gemini XS fluorescence microplate reader (Molecular Devices). The experimental value minus the value of the control group was interpreted as the increase in intracellular ROS.
Nitrite and tumor necrosis factor (TNFa assays)
The production of Nitric Oxide (NO) was determined by measuring the accumulated levels of nitrite in the supernatant with Griess reagent and the release of TNFα was measured with a rat TNFα unknownsymbol5 enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay kit from R and D System (Minneapolis, MN, USA), as described (21).
Confocal microscopy
HAPI cells seeded in dish at 5 × 104 cells/well were treated with LPS for 10 min in the presence and absence of TGFβl pretreatment for 1 h. Cells were fixed with 3.7% paraformaldehyde in PBS for 10 min. After washing with PBS, cells were incubated with rabbit polyclonal antibody against p47phox (0.5 µg/ml). Cells were then washed and incubated with FITC-conjugated goat anti-rabbit antibody. Focal planes spaced at 0.4-µm intervals were imaged with a Zeiss 510 laser scanning confocal microscope (63 × PlanApo 1.4 numerical aperture objective) equipped with LSM510 digital imaging software.
Membrane fractionation and western blot analysis
Membrane fractionation was performed as described (37). HAPI cells were lysed in hypotonic lysis buffer (1 mM EGTA, 1 mM EDTA, 10 mM β-glycerophosphate, 10 mM NaF, 1 mM sodium orthovanadate, 2mM MgCl2, 10 mM DTT, 1 mM PMSF, and 10 ug/ml each leupeptin, aprotinin, and pepstatin A), incubated on ice for 30 min, and then subjected to Dounce homogenization (20~25 stokes, tight pestle A). The lysates were loaded onto sucrose in lysis buffer (final 0.5 M) and centrifuged at 1600 × g for 15 min, the supernatant above the sucrose gradient was centrifugation at 150,000 × g for 30 min. The pellets solubilized in 1% NP-40 hypotonic lysis buffer were used as membranous fraction. Equal amounts of protein (20 µg per lane) were separated by 4~12% Bis-Tris Nu-PAGE gel and transferred to polyvinylidene difluoride membranes (Novex, San Diego, CA). Membranes were blocked with 5% nonfat milk and incubated with rabbit anti-p47phox antibody (1: 2000 dilution) or mouse anti-gp91phox (1:2000 dilution) for 1 h at 25°C. Horse radish peroxidase-linked anti-rabbit or mouse IgG (1:3000 dilution) for 1 h at 25°C, ECL+Plus reagents (Amersham Biosciences Inc., Piscataway, NJ) were used as a detection system. For detection the phosphorylation of MAPK, membranes were blocked with 5% nonfat milk, washed three times followed by incubation with either anti-phospho-ERK1/2 Ab, anti-ERK1/2 Ab, anti-phospho-p38 Ab, anti-p38 Ab, anti-phospho-JNK Ab or anti-JNK Ab at 1:1000 dilution (Cell Signaling Technology, Danvers, MA) overnight at 4°C. Anti-rabbit horse radish peroxidase-linked secondary antibody (1:2000 dilution) was incubated for 1h at 25°C. The same detection system as above was used.
Statistical Analysis
The data were presented as the means ± SE. For multiple comparisons of groups, two-way or three-way ANOVA was used. Statistical significance between groups was assessed by paired Student’s t test, followed by Bonferroni correction using the JMP program (SAS Institute, Cary, NC, USA). A value of P < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Results
TGFβ1 is neuroprotective against LPS- and MPP+-induced DA neurotoxicity
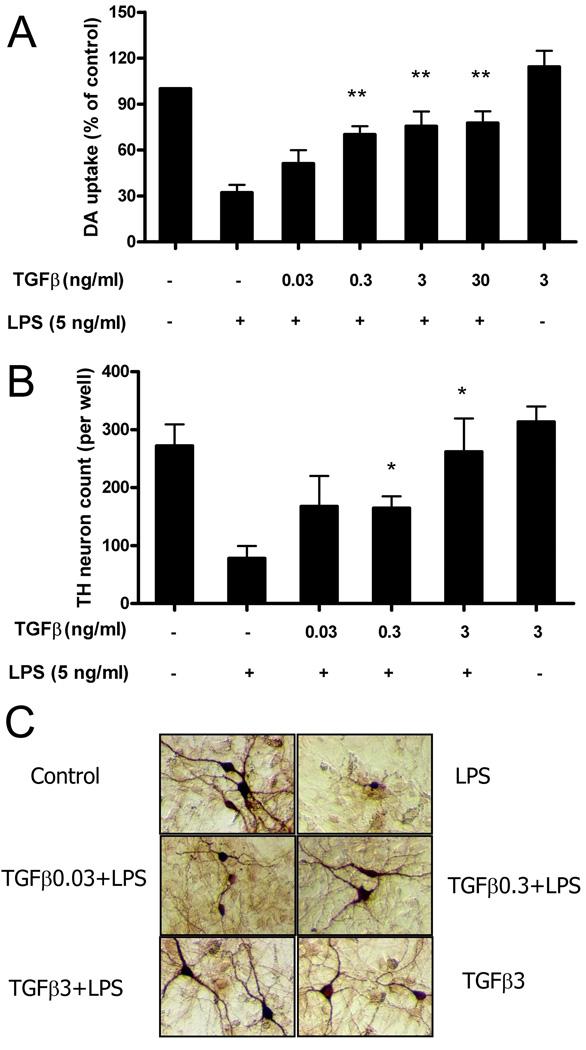
We first sought to determine if LPS-induced inflammation by glial cells leading to destruction of DA neurons could be inhibited by the anti-inflammatory cytokine TGFβ1. Mesencephalic neuron–glia cultures were pretreated with TGFβ1 for 1 h and then stimulated with LPS for 7 days. The degeneration of DA neurons was then determined by [3H]-DA uptake assay and numeration of the TH-IR neurons. The [3H]-DA uptake assay showed that LPS treatment reduced the capacity of the cultures to take up DA by approximately 70% and this LPS-induced inhibition was prevented by a dose-dependent pretreatment with TGFβ1 (Fig. 1A). While addition of 0.03 ng/ml TGFβ1 showed slight but insignificant neuroprotection, addition of 0.3, 3 or 30 ng/ml of TGFβ1 to cultures shows that the LPS-mediated decrease in DA uptake was significantly restored. Concentrations above 3 ng/ml of TGFβ1 did not show any additional increase in neuroprotection (Fig. 1A). Consistent with previous report, TGFβ1 alone at 3 ng/ml show a slight but significant neurotrophic effect as measured by DA uptake in these cultures, likely through the activation of astrocytes (17). A similar protective effect was observed with TGFβ1 when counting the number of DA neurons after immunostaining (Fig. 1B). Thus, LPS-induced loss of DA neurons was prevented by TGFβ1 pretreatment, morphological inspection revealed that LPS treatment not only decreased the number of DA neurons, but also caused a loss of neuronal processes, and these characteristics were also reversed by low dose TGFβ1 pretreatment (Fig. 1C).
FIGURE 1.
TGFβ1 protects DA neurons against LPS-induced toxicity. Rat primary mesencephalic neuron-glia cultures were seeded in a 24-well culture plate at 5×105 , then pretreated with various concentrations of TGFβ1 for 1 h before the addition of 5 ng/ml LPS. Seven days later, the LPS-induced DA neurotoxicity was quantified by the [3H]-DA uptake assay (A); the immunocytochemical analysis, including TH-IR neuron counts (B); and the representative pictures of immunostaining (C). Results were expressed as a percentage of the vehicle-treated control cultures and were the means ± SE. from three independent experiments in triplicate. *P<0.05, **P<0.01 compared with the LPS-treated cultures.
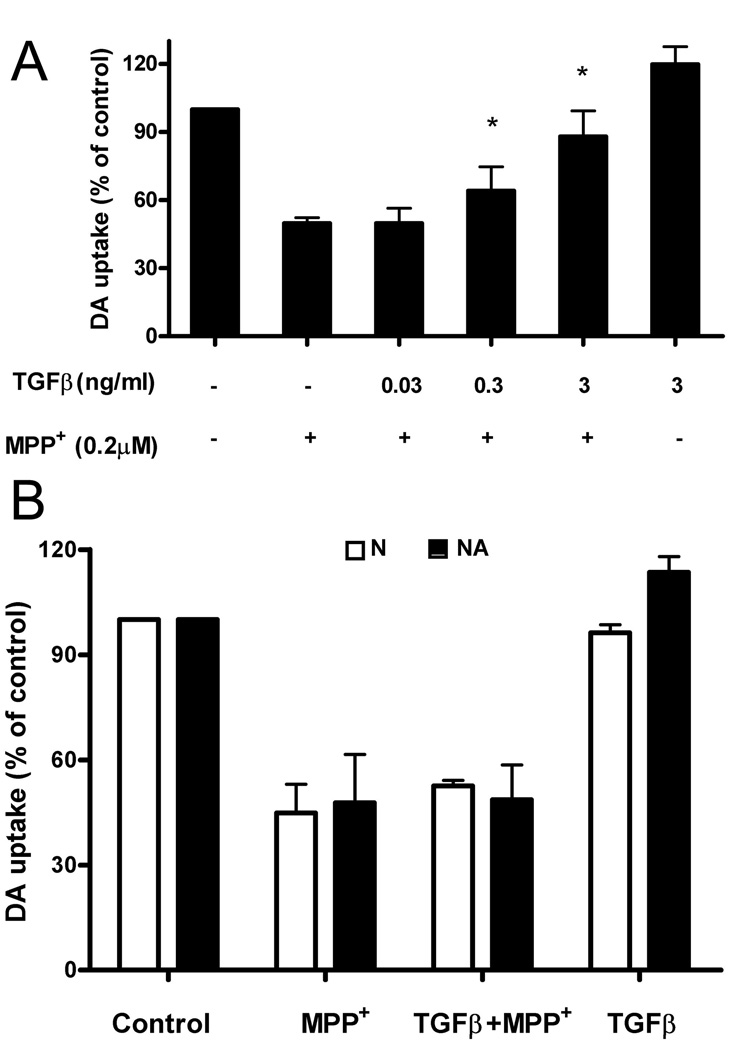
To investigate whether TGFβ1 mediates its protective function by inhibiting LPS-induced inflammatory response by glial cells, we treated neuron-glia cultures with 1-methyl-4-phenylpyridinium (MPP+), the active metabolite of MPTP, which, unlike LPS; is known to kill DA neurons directly. Our previous work has shown that neuronal death induced by MPP+ is the result of both direct cytotoxic effects on DA neurons by MPP+, as well as by reactive microgliosis induced by toxic factors released by dying neurons (22, 38, 39). Following treatment with 0.2 µM MPP+ for 7 days, DA uptake was reduced to 50% in neuron-glia cultures (Fig. 2A). These results show that TGFβ1 significantly protects DA neurons from MPP+-mediated toxicity (Fig. 2A).
FIGURE 2.
TGFβ1 protects DA neurons against MPP+-induced toxicity in neuron-glia cultures. Different doses of TGFβl were added to the neuron-glia cultures (A), or neuron-enriched cultures (B: open bars) and neuron-astrocyte cultures (B: closed bars) for 1 h prior to the addition of 0.2 µM MPP+ treatment. The [3H]-DA uptake measurements were performed 7 days following MPP+ treatment. Results were expressed as a percentage of the vehicle-treated control cultures and were the means ± SE from 3 independent experiments in triplicate. *P<0.05 compared with the MPP+ -treated cultures.
To further understand how TGFβl protects DA neurons from the cytopathic effects of MPP+, we treated cultures of rat midbrain lacking all glial cells (N, neuron enriched cultures) or cultures containing neurons and astrocytes but not microglia (NA, neuron-astrocyte enriched cultures) and measured DA neurons uptake 7 days after treatment. DA uptake was reduced to about 40% in these neuron-enriched cultures (Fig. 2B). However, TGFβl was not capable of protecting DA neurons from MPP+-induced toxicity. These results demonstrate that microglia, not neurons or astroglia, serve as the target of TGFβl-mediated neuroprotection against MPP+-induced toxicity, and that TGFβl is capable of inhibiting this reactive microgliosis.
TGFβ l inhibits the expression of ROS and other pro-inflammatory factors by activated microglia
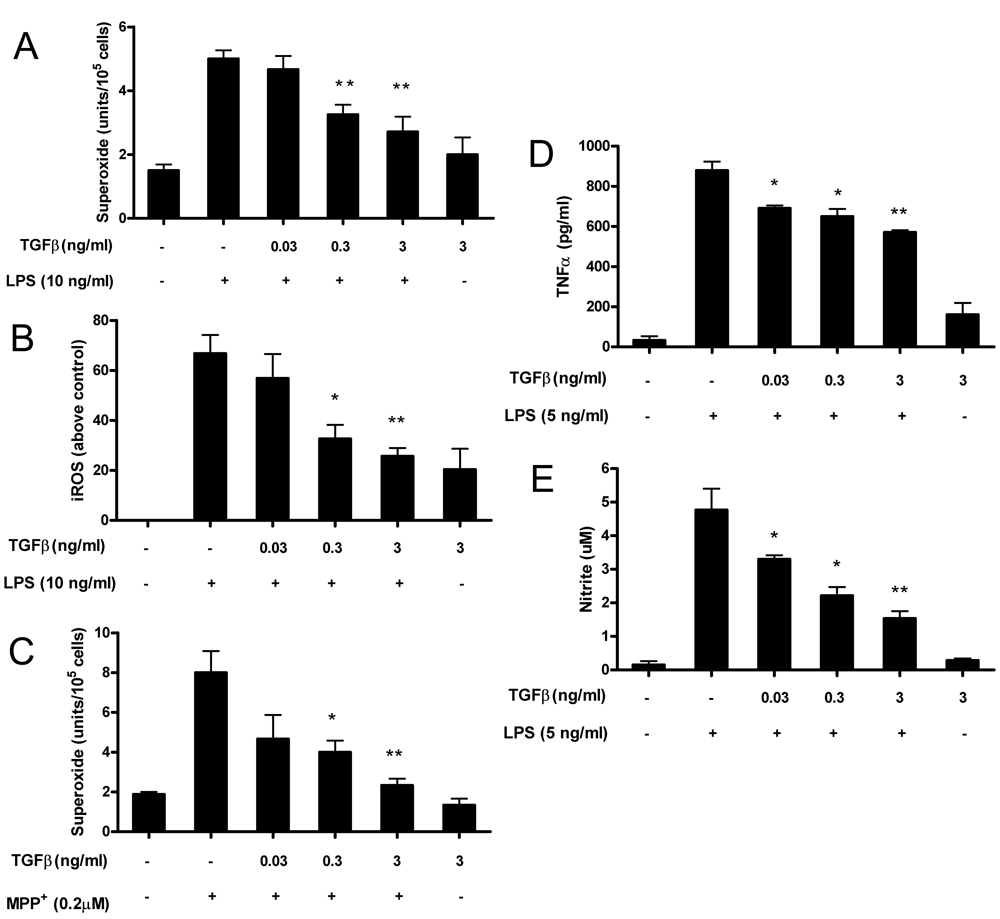
Over-activation of microglia through the direct effects of LPS on microglia or by reactive microgliosis via the death of neurons produce an array of pro-inflammatory mediators, including ROS, which is the pivotal product mediating inflammation-related neurotoxicity (23, 40). To test the effect of TGFβl on the generation of ROS by microglia, primary cells were pretreated with TGFβl, then exposed to either LPS or MPP+. TGFβl significantly reduced LPS-mediated extracellular superoxide production (Fig. 3A) and intracellular ROS concentrations (Fig. 3B). Likewise, treatment of cultures with TGFβl significantly inhibited the MPP+-induced superoxide production resulting from reactive microgliosis (Fig. 3C). Taken together, these results demonstrated that TGFβl can inhibit ROS free radical production by microglia induced either directly by LPS stimulation or indirectly by MPP+ -mediated reactive microgliosis.
FIGURE 3.
TGFβl inhibits ROS production and pro-inflammatory factors by activated microglia. Microglia-enriched cultures were seeded at a density of 1×105 /well. Cells were pretreated with different concentrations of TGFβl for 30 min followed by the addition of LPS (10 ng/ml). The production of ROS included extracellular superoxide (A) and iROS (B). Extracellular superoxide was measured as SOD-inhibitable reduction of WST-1, and iROS was determined by probe DCFH-DA. Primary rat mesencephalic neuron-glia cultures were pretreated for 1 h with vehicle or TGFβl before treatment with 0.2 µM of MPP+ .Two and 4 days after MPP+ treatment, TGFβl was added again to the TGFβ1-treated cultures. On day 4, the release of superoxide was determined as described above (C). TGFβ’s effect on LPS-induced production of TNFα and nitrite were shown in Fig.3D and Fig. 3E. Results were expressed as mean ± SE from three to seven independent experiments in triplicate. *P<0.05, **P<0.01 compared with the LPS-treated cultures.
We also investigated the effect of TGFβl on other inflammatory markers by measuring pro-inflammatory mediators in microglia enriched cultures stimulated with LPS. We used LPS to activate microglia since reactive microgliosis induced by MPP+ does not result in measurable NO or pro-inflammatory cytokine production in neuron-glia mixed cultures. TGFβl at as low as 0.03 ng/ml significantly inhibited LPS-induced production of TNFα and NO, as shown in Fig. 3D and Fig. 3E. However, no neuroprotection of DA neurons was seen at this dose, suggesting that the major source of neurotoxicity in these cultures was not through TNFα or NO-mediated toxicity but rather through the production of ROS.
PHOX plays an important role in TGFβl-mediated protection against LPS-induced neurodegeneration
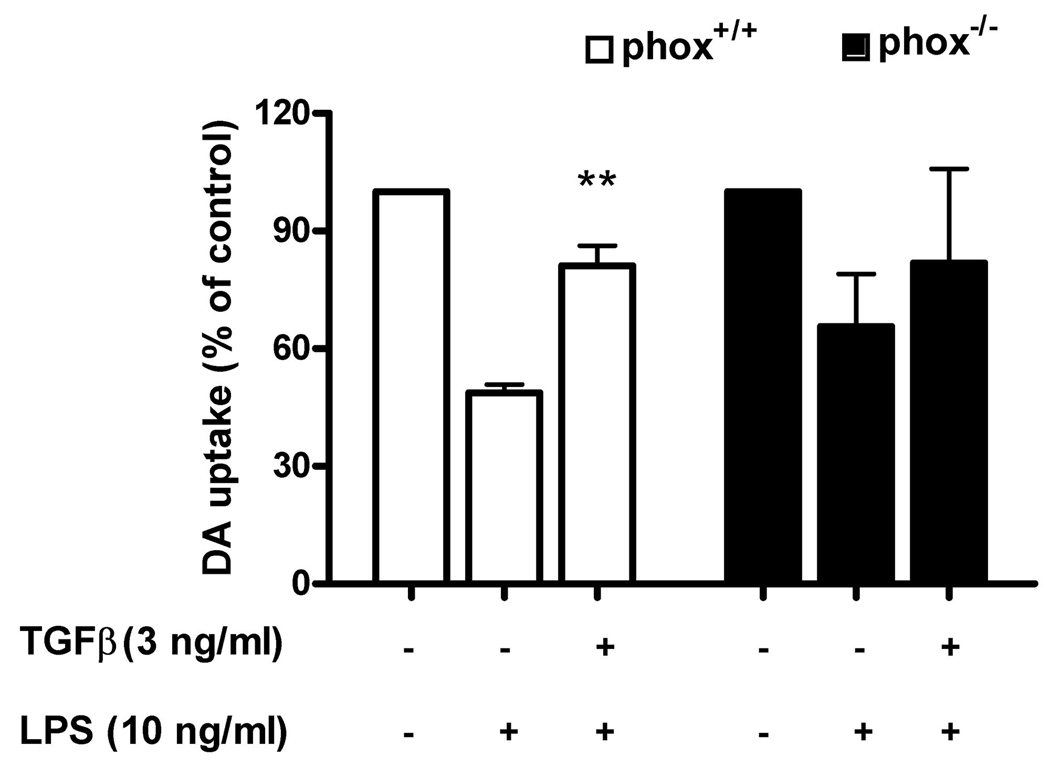
The results mentioned above indicate that TGFβl significantly reduced both LPS and MPP+-induced production of superoxide. To further investigate the role of ROS in TGFβl-elicited neuroprotection, we used neuron-glia cells from mice deficient in gp91, the catalytic subunit of PHOX, which is the key enzyme required for the production of ROS. Neuron-glia cultures were prepared from PHOX−/− knockout and PHOX+/+ wild-type mice and, as shown in Fig. 4, LPS treatment of neuron-glia cultures prepared from PHOX+/+ mice substantially reduced [3H]-DA uptake. Similarly, TGFβl significantly attenuated the decrease in [3H]-DA uptake (Fig. 4). In contrast, a three-way ANOVA analysis showed significant differences between wild type and knockout mouse (p= 0.0213). While LPS treatment also showed a significant albeit smaller reduction in [3 H]-DA uptake capacity in PHOX−/− mice, paired Student’s t test, followed by Bonferroni correction results indicated that TGFβl failed to show any protective effect on DA neurons from these mice (p=0.36). These results demonstrate that PHOX plays a key role in TGFβl-mediated neuroprotection.
FIGURE 4.
Microglia NADPH oxidase is the target of TGFβ1 inhibition in LPS-induced neurotoxicity. PHOX+/+ and PHOX–/– mice neuron-glia cultures were pretreated with vehicle or TGFβ1 for 1 h followed by LPS treatment. Neurotoxicity was assessed by DA uptake. Results are expressed as % of the control culture, and are the means ± SE of 3 individual experiments in triplicate in each experiment. **P < 0.01 compared with LPS treated culture.
TGFβl inhibits LPS-induced translocation of the cytosolic subunits p47phox of PHOX to the cellular membrane
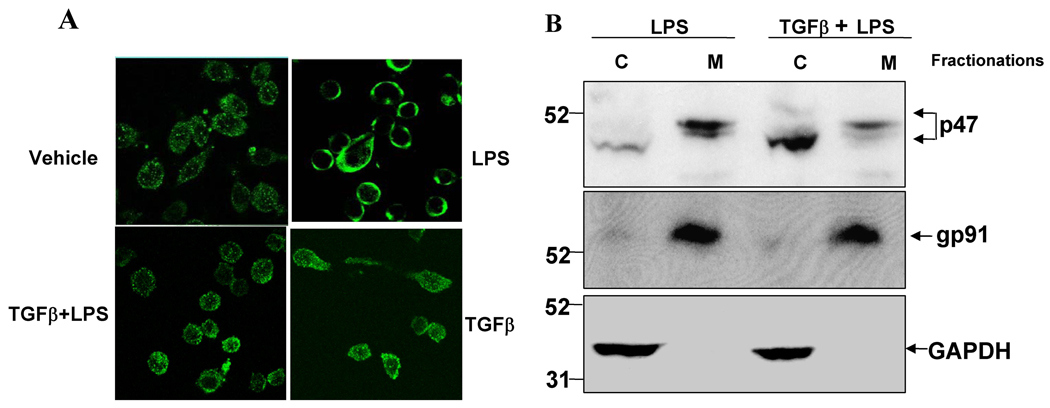
It has previously been shown that activation of the PHOX enzyme requires that the cytosolic component p47phox is phosphorylated, and subsequently translocated along with the p67phox component to the plasma membrane, where they associate with cytochrome b558 to assemble into an active enzyme complex (24). Since TGFβl showed potent effects on extracellular ROS production, we sought to determine if TGFβl inhibits PHOX activation by preventing the phosphorylation and translocation of the PHOX cytoplasmic subunit p47phox from cytosol to membrane in the microglial cell line HAPI following LPS stimulation. Using confocal light scanning microscopy, we observed that LPS initiated the translocation of cytosolic p47 phox , and that with in 10 min after LPS stimulation the majority of the p47phox-FITC fluorescence signal was found clustered on the membrane (Fig. 5A, panel II). The addition of TGFβ1 at 3 ng/ml significantly prevented the translocation of p47phox (Fig. 5A, panel III). In cells treated with vehicle (Fig. 5A, panel I) or TGFβ1 alone (Fig. 5A, panel IV), p47phox were found localized mainly in the cytosol. Consistent with the results of the confocal study, western blot assay clearly showed the majority of p47phox in the cellular membrane fraction of HAPI cells within 10 min after LPS treatment, while following TGFβ1 pretreatment we see p47phox remaining mostly within the cytosolic fraction. In contrast, the level of gp91 found in cellular membrane fraction was unaltered by TGFβ1 treatment (Fig. 5B). Therefore, it is likely that TGFβ1-mediated inhibition of superoxide production by LPS is primarily through the inhibition of p47phox translocation to the cellular membrane.
FIGURE 5.
Effects of TGFβ1 on cytosolic p47phoxprotein translocation. (A): HAPI cells seeded in dish at 5 × 104 cells/well were treated with LPS for 10 min in the absence or presence of TGFβ1 pretreatment for 1 h. Cells were fixed with 3.7% paraformaldehyde in PBS for 10 min. After washing with PBS, cells were incubated with rabbit polyclonal antibody against p47phox . Cells were then washed and incubated with FITC-conjugated goat anti-rabbit antibodies. Focal planes spaced at 0.4-µm intervals were imaged with a Zeiss 510 laser scanning confocal microscope (63 × PlanApo 1.4 numerical aperture objective) equipped with LSM510 digital imaging software. Three adjacent focal planes were averaged using Metamorph software. The signal of p47phox (FITC-p47phox ; green) are shown. (B): HAPI cells were pretreated with vehicle or TGFβ1 (3 ng/ml) for 1 h, followed by LPS treatment for 10 min. Subcellular fractions were isolated to perform western blot analysis. c: cytosolic extract; m: membrane extract. GAPDH is as an internal cytosolic control, gp91phox as an internal membrane control. Each experiment has been performed three times.
TGFβ1 suppresses LPS-induced ERK-regulated p47phox phosphorylation
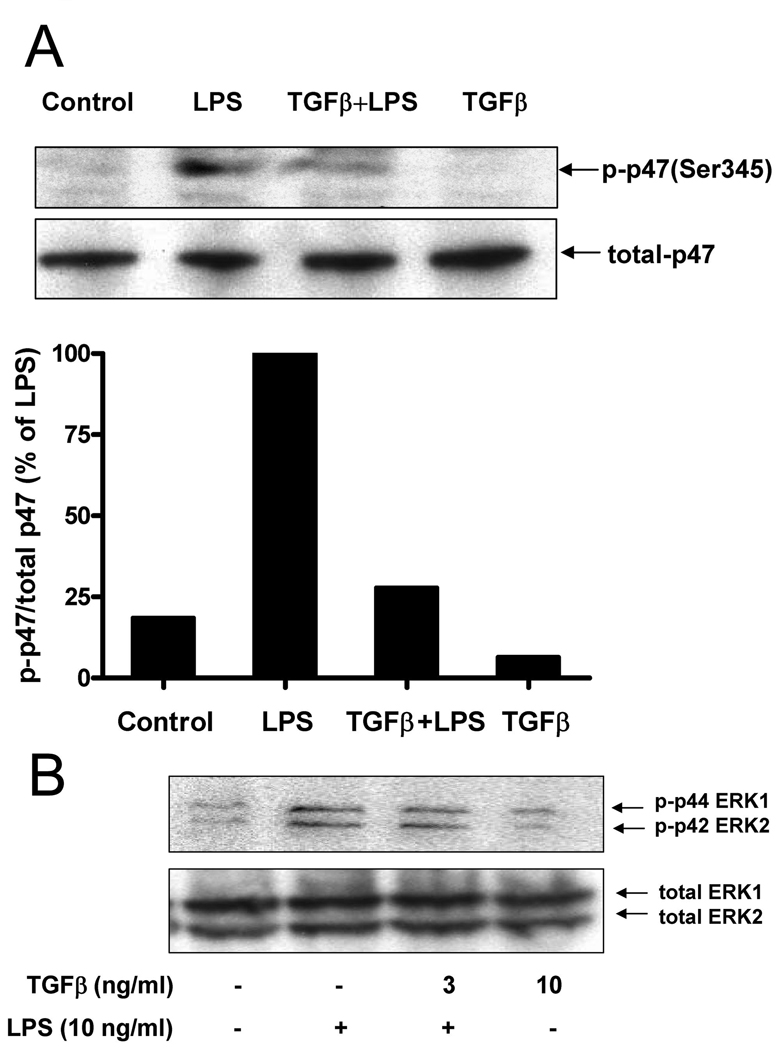
Phosphorylation of p47phox is one of the key intracellular events associated with NADPH oxidase activation, and Ser345 phosphorylation of p47phox by the MAP-kinase protein ERK plays a critical role in the potentiation of NADPH oxidase activation by pro-inflammatory agents (41). Therefore, we first examined the levels of LPS-induced p47phox phosphorylation using the anti–phospho-Ser345–p47phox antibody. Enriched microglial cells were incubated with LPS for 10 min, and the levels of phosphorylation of Ser345 in p47phox were analyzed by western blot assay. In the absence of LPS, weak basal phosphorylation of p47phox was detected, and significant phosphorylation of p47phox was observed 10 min following LPS stimulation. LPS-induced phosphorylation of p47phox was significantly inhibited by TGFβ1 pretreatment (Fig. 6A). These data suggest that the TGFβ1 inhibits Ser345 phosphorylation on p47phox in microlgia to reduce oxidase activities induced by LPS. Furthermore, we determined if TGFβ1 mediated the inhibition of Ser345 phosphorylation on p47phox through the inhibition of ERK. TGFβ1 pretreatment significantly inhibited LPS-induced ERK1 and ERK2 phosphorylation five minutes after LPS stimulation (Fig. 6B). These data suggest that TGFβ1 inhibits LPS-induced ROS production in microglia by inhibiting the phosphorylation of ERK1/2 and the subsequent phosphorylation of p47phox at Ser345,which in turn resulted in the reduction in translocation of p47phox to the cellular membrane.
FIGURE 6.
Western blot analysis of p47phoxand ERK phosphorylation. Enriched microglial cells were treated with LPS (10 ng/ml) in the presence or absence of TGFβ1 (3 ng/ml) for 10 min, cells were then harvested, proteins were analyzed by SDS-PAGE and immunoblotting with anti-phospho-Ser345–p47phox Ab (p-p47-Ser345) or anti-p47phoxAb.The Western blots from different experiments were scanned, phosphorylated, total p47phoxwas quantified by densitometry, and the intensity of phosphorylated p47phoxwas corrected for the amount of p47phox(A); The levels of phosphorylated ERK relative to total ERK were determined by western blot using specific antibodies against phosphorylated or total ERK, respectively (B). Representative western blots for Ser345– p47phox, and ERK1/2 phosphorylation are shown from 3 independent experiments.
ERK1/2 activation is required for LPS-induced DA neurotoxicity, microglial superoxide production and p47phox translocation
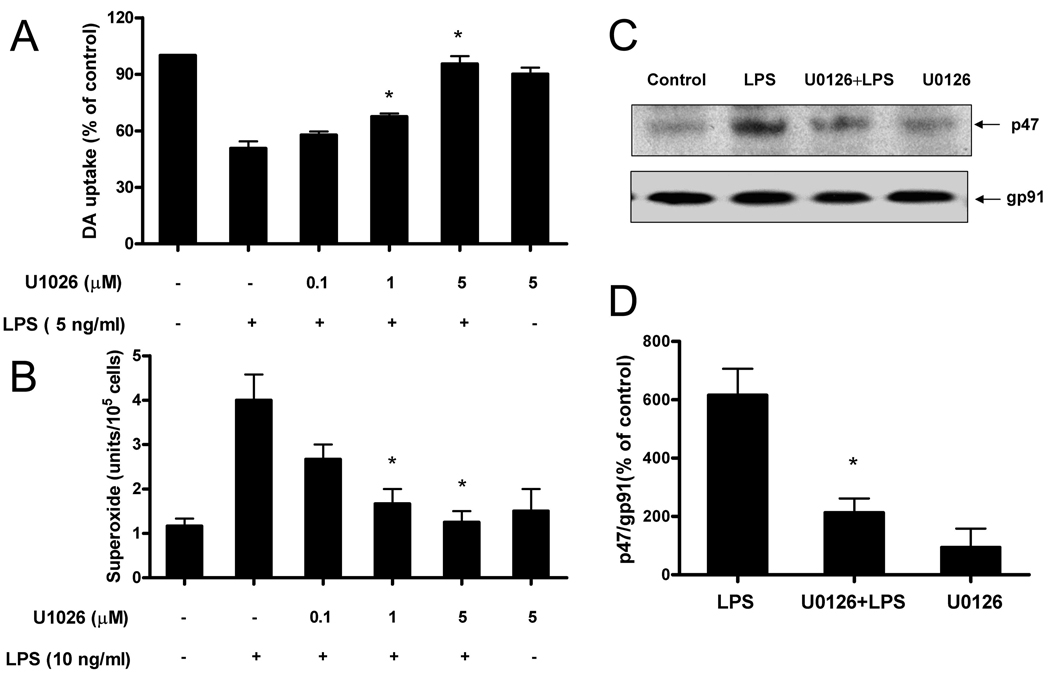
Since TGFβ1 significantly inhibited LPS-induced ERK phosphorylation, we further tested the role of ERK on LPS-induced DA neurotoxicity, microglial superoxide production, and p47phox translocation using the specific ERK inhibitor U0126. Mesencephalic neuron–glia cultures were pretreated with U0126 for 30 min and then stimulated with LPS for 7 days. The [3H]-DA uptake assay showed that LPS treatment reduced the capacity of the cultures to take up DA to approximately 50% of the vehicle control and this LPS-induced reduction was prevented by U0126 pretreatment in a dose-dependent manner (Fig. 7A). At 1 and 5 µM U0126, the LPS-induced decrease in DA uptake was significantly restored, while U0126 alone at 5 µM did not affect DA uptake levels.
FIGURE 7.
ERK1/2 activation is required for LPS-induced DA neurotoxicity, microglial superoxide production and p47phoxtranslocation. Rat primary mesencephalic neuron-glia cultures were seeded in a 24-well culture plate at 5×105, then pretreated with various concentrations of U0126 for 30 min before the addition of 5 ng/ml LPS. Seven days later, LPS-induced DA neurotoxicity was quantified by the [3H]-DA uptake assay (A); Microglia-enriched cultures were seeded at a density of 1×105/well. Cells were pretreated with different concentrations of U0126 for 30 min followed by the addition of LPS (10 ng/ml). The production of extracellular superoxide was measured as SOD-inhibitable reduction of WST-1 (B). HAPI cells were pretreated with U0126 (5 µM) or vehicle for 30 min, followed by LPS (10 ng/ml) treatment for 10 min. Cellular membrane fractions were isolated for western blot analysis using antibodies against either p47phoxor gp91phoxas described in material and methods (C). ImageJ software was used to quantitate the intensity of the p47phoxand gp91phoxbands in western blot, and the results given in figure D represents the percentage difference of the ratio of p47phoxcompared with gp91phoxnormalized to the vehicle-treated control (D). Each experiment has been performed three times. Results in A, B, and D were expressed as mean ± SE from three independent experiments in triplicate. *P<0.05, compared with the LPS-treated cultures, while the results in C show the results of 1 representative western blots.
Consistent with the neuroprotection data, U0126 at 1 and 5 µM, significantly attenuated the LPS-induced superoxide production in microglia (Fig. 7B). Further, we stimulated rat HAPI microglia cells with LPS, isolated the membrane fraction, and ran western blot analysis to measure p47phox translocation. We found that while the majority of p47phox was located in the cellular membrane fraction of stimulated HAPI cells, pretreatment of stimulated HAPI cells with U0126 prevented the translocation of p47phox to the cellular membrane, but rather it remained mostly within the cytosolic fraction. In contrast, the level of gp91 found in cellular membrane fraction was unaltered by U0126 treatment (Fig. 7C). Quantitatively analyzing the intensity of the p47phox and gp91phox bands in western blot, we found a significant inhibitory effect of U0126 on LPS-induced p47phox translocation (Fig. 7D). These results suggest that ERK phosphorylation is required for LPS-induced p47phox phosphorylation, its translocation to the cellular membrane, and ultimately for cellular ROS production resulting in the toxicity of DA-producing neurons.
Discussion
Inflammation-induced degeneration of DA neurons in mesencephalic neuron-glia cultures is a useful in vitro model for studying the mechanism and identifying the potential therapeutic application in PD (2). Using the well-characterized models of LPS and MPP+-induced neurodegeneration, we sought to identify the mechanism by which TGFβ1, a major anti-inflammatory cytokine, mediates the neuroprotection of inflammation-induced neurotoxicity in vitro. Our results showed that TGFβ1 exerted potent effects in inhibiting LPS and MPP+-induced inflammation and neuronal destruction through the inhibition of oxidative stress responses in microglial cells. Three salient features of this protective role of TGFβ1 were observed in this study: 1) TGFβ1 exerts potent anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective effects through the inhibition of both direct microglial activation by LPS, and reactive microgliosis elicited by MPP+ ; 2) TGFβ1 decreases NADPH oxidase-mediated superoxide production mainly through the inhibition of p47phox translocation to the cellular membrane, a novel site of action for the neuroprotective effect of TGF β1; and 3) The inhibition of p47phox translocation is mediated through the inhibition of PHOX subunit p47phox phosphorylation at Ser345 via suppression of the ERK signaling pathway.
Our results showed that TGFβ1 has protective effects in both the LPS and the MPP+ model of PD even though the target of these two agents is different. LPS leads to the direct activation of microglia, which results in death of DA neurons through the production of inflammatory mediators. Reports from our laboratory and others have shown that MPP+ can cause reactive microgliosis, and that oxidative stress is involved in MPP/MPP+-induced neurotoxicity (19, 40, 44). Even though MPP+ directly damages DA neurons, we show that TGFβ1 still provides significant neuroprotective effects through the inhibition of reactive microgliosis in neuron-glia cultures. However, when microglial cells are removed, TGFβ1 can no longer show any protective effects on DA neurons, suggesting that TGFβ1 does not work directly on DA-neurons, but rather indirectly by inhibiting activated microglia which contribute to additional neurotoxicity by producing toxic inflammatory mediators. Based on our current evidence, we propose that the anti-inflammatory effect of TGFβl is capable of inhibiting both LPS-induced microglial activation and MPP+-induced reactive microgliosis, and its ultimate result is to suppress the inflammation that mediates chronic neurodegeneration in PD.
Our studies indicated that TGFβl functions in neuroprotection by inhibiting the initial events in the inflammatory response, the activation of oxidative stress response, and the subsequent production of inflammatory mediators TNFα and NO. It has been shown that DA neurons in the substantia nigra are uniquely vulnerable to oxidative stress due to lower antioxidant capacity, increased accumulation of iron, high content of dopamine auto-oxidative metabolites and high density of microglia in the substantia nigra (7, 45, 46). The fact that TGFβl significantly inhibits the production of superoxide induced by LPS within a few minutes after stimulation, led us to examine this factor in greater details by using PHOX-deficient mice. The findings that TGFβl could significantly lessen the LPS-induced DA uptake reduction in cells from wild-type mice, but has no significant protective effect on cells from PHOX−/− mice (Fig. 4) strongly support the contention that the protective effect of TGFβl is most likely mediated through the inhibition of PHOX activity.
While our rat primary midbrain cultures consist of a variety of different types of cells, it is clear that the primary source of LPS-induced ROS in these cultures is the microglial cell. This notion was supported by our previous reports, which indicated that LPS fails to produce extracellular superoxide in neuron-glia cultures devoid of microglial cells, or in cultures of enriched microglia prepared from PHOX−/− mice (23). Thus, these findings indicate that PHOX is the key enzyme involved in superoxide production in these cultures. Activation of PHOX in microglia not only increases the production of superoxide, but indirectly increases the intracellular ROS concentration, possibly through the conversion of superoxide to H2O2, which is membrane permeable. Increase of intracellular ROS can intensify the activation of NF-κB, which leads to higher TNFα production (2, 23). In addition, it was reported that PHOX inhibitors prevented LPS/IFNγ-induced degradation of IκBα, and thus, inhibited the activation of NF-κB (47). However, the ability to activate NF-κB-dependent genes such as TNFα in PHOX−/− cells suggests that PHOX plays an important but not exclusive role in regulating inflammation in microglial cells. These data are consistent with the notion that inhibition of NF-κB activity by TGFβ1 may be mediated at least in part through its inhibition of PHOX, and that PHOX is the major target of the anti-inflammatory activity and neuroprotective effects of TGFβ1.
It is known that translocation of the cytosolic components p47phox, p67phox, p40 phox, and rac2 to the plasma membrane is required for the activation of PHOX (25). The phosphorylation of Ser345 of p47phox by pro-inflammatory agents enhances this translocation event (41). While investigating the mechanism by which TGFβ1 inhibits PHOX activity, we found that TGFβ1 significantly inhibits this LPS-induced p47phox phosphorylation at Ser345, resulting in the inhibition of p47phox translocation. As Ser345 is located in the MAPK consensus sequence, we investigated whether TGFβ1 inhibited components of the MAPK signaling pathway, and our results indicate that TGFβ1 shows significant inhibitory effect on LPS-induced ERK phosphorylation, but not p38 or JNK (data not shown).Furthermore, a specific Erk inhibitor, U0126, showed strong inhibitory effects against LPS-induced neurodegeneration, superoxide production and p47phox translocation, suggesting a central role for ERK in these effects (Fig.7). These findings, coupled with our previous findings on the role of ERK in PHOX activation (22), strongly suggests it is ERK that regulates p47phox phosphorylation and is the crucial target for TGFβ1-mediated inhibition of PHOX activation. Previously, we have shown that ERK is a crucial mediator of GM-CSF-induced activation of Ser345 on p47phox in neutrophils (41), and it appears that ERK also plays a central in the LPS-induced phosphorylation of Ser345 on p47phox in microglial cells. Taken together, we suggest that TGFβ1 inhibits LPS-induced ROS production in microglia by inhibiting p47phox phosphorylation and translocation, which is regulated by ERK signaling pathway.
These results suggest a central role for microglia in the pathogenesis of PD, and that by limiting their pro-inflammatory response with anti-inflammatory mediators TGFβ1 we can significantly inhibit the neurotoxicity associated with this disease. In addition, we have previously shown that IL-10 also has similarly potent neuroprotective properties (48), and the combination of both TGFβ1 and IL-10 might even act in concert to regulate chronic inflammation in the brain. It has recently been shown that regulatory T cells (Treg cells), a significant source of both IL-10 and TGFβ1, show strong therapeutic efficacy in the treatment of neuroinflammation (49). It is yet to be determined the exact role TGFβ1 plays in the physiological regulation of chronic CNS inflammation in PD, and how TGFβ1 may synergize with other anti-inflammatory mediators to regulate microglia-mediated neurotoxicity. In addition, the level of the immune response in the brain necessary to effectively control infections without resulting in neuropathology is yet to be understood. Consequently, much work remains to determine if TGFβ1, either therapeutically delivered or produced in the CNS, can play an important anti-inflammatory role by limiting the activation of microglia and promoting a well-regulated immune response that is lacking during the pathophysiology of CNS disorders.
Acknowledgments
We thank Dr. Salvador Nares at UNC for his helpful suggestions for this paper.
This work was supported by NIH grant DE-13079 from the National Institute for Dental and Craniofacial Research, and was also supported in part by the Intramural Research Program of the NIH/NIEHS.
Footnotes
Disclosures
The authors have no financial conflict of interest.
Abbreviations used in this paper: 1-methyl-4-phenylpyridinium (MPP+); dopaminergic (DA); Parkinson’s disease (PD); reactive oxygen species (ROS); inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS); tyrosine hydroxylase-immunoreactive (TH-IR); nitritc oxide (NO); prostaglandin E2 (PGE2); NADPH oxidase (PHOX); dichlorodihydrofluorescein Diacetate (DCFH-DA); superoxide dismutase (SOD); tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNFα); lipopolysaccharide (LPS); mitogen activated protein kinase (MAPK); intracellular ROS (iROS); serine 345 (Ser 345).
Reference
- 1.McGeer PL, S I, Boyes BE, McGeer EG. Reactive microglia are positive for HLA-DR in the substantia nigra of Parkinson's and Alzheimer's disease brains. Neurology. 1988;38:1285–1291. doi: 10.1212/wnl.38.8.1285. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Liu B, Hong JS. Role of microglia in inflammation-mediated neurodegenerative diseases: mechanisms and strategies for therapeutic intervention. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2003;304:1–7. doi: 10.1124/jpet.102.035048. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Rosi S, Ramirez-Amaya V, Vazdarjanova A, Worley PF, Barnes CA, Wenk GL. Neuroinflammation alters the hippocampal pattern of behaviorally induced Arc expression. J Neurosci. 2005;25:723–731. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4469-04.2005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Aloisi F. The role of microglia and astrocytes in CNS immune surveillance and immunopathology. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 1999;468:123–133. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4615-4685-6_10. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.McGuire SO, Ling ZD, Lipton JW, Sortwell CE, Collier TJ, Carvey PM. Tumor necrosis factor alpha is toxic to embryonic mesencephalic dopamine neurons. Exp Neurol. 2001;169:219–230. doi: 10.1006/exnr.2001.7688. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Sriram K, Matheson JM, Benkovic SA, Miller DB, Luster MI, O'Callaghan JP. Mice deficient in TNF receptors are protected against dopaminergic neurotoxicity: implications for Parkinson's disease. Faseb J. 2002;16:1474–1476. doi: 10.1096/fj.02-0216fje. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Kim WG, Mohney RP, Wilson B, Jeohn GH, Liu B, Hong JS. Regional difference in susceptibility to lipopolysaccharide-induced neurotoxicity in the rat brain: role of microglia. J Neurosci. 2000;20:6309–6316. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.20-16-06309.2000. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Zhu Y, Yang GY, Ahlemeyer B, Pang L, Che XM, Culmsee C, Klumpp S, Krieglstein J. Transforming growth factor-beta 1 increases bad phosphorylation and protects neurons against damage. J Neurosci. 2002;22:3898–3909. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.22-10-03898.2002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Ruocco A, Nicole O, Docagne F, Ali C, Chazalviel L, Komesli S, Yablonsky F, Roussel S, MacKenzie ET, Vivien D, Buisson A. A transforming growth factor-beta antagonist unmasks the neuroprotective role of this endogenous cytokine in excitotoxic and ischemic brain injury. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 1999;19:1345–1353. doi: 10.1097/00004647-199912000-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Prehn JH, Bindokas VP, Marcuccilli CJ, Krajewski S, Reed JC, Miller RJ. Regulation of neuronal Bcl2 protein expression and calcium homeostasis by transforming growth factor type beta confers wide-ranging protection on rat hippocampal neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994;91:12599–12603. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.26.12599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Szczepanik M, Tutaj M, Bryniarski K, Dittel BN. Epicutaneously induced TGF-beta-dependent tolerance inhibits experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J Neuroimmunol. 2005;164:105–114. doi: 10.1016/j.jneuroim.2005.04.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Unsicker K, Krieglstein K. TGF-betas and their roles in the regulation of neuron survival. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2002;513:353–374. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4615-0123-7_13. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Henrich-Noack P, Prehn JH, Krieglstein J. TGF-beta 1 protects hippocampal neurons against degeneration caused by transient global ischemia. Dose-response relationship and potential neuroprotective mechanisms. Stroke. 1996;27:1609–1614. doi: 10.1161/01.str.27.9.1609. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Dunker N, Schuster N, Krieglstein K. TGF-beta modulates programmed cell death in the retina of the developing chick embryo. Development. 2001;128:1933–1942. doi: 10.1242/dev.128.11.1933. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Krieglstein K, Richter S, Farkas L, Schuster N, Dunker N, Oppenheim RW, Unsicker K. Reduction of endogenous transforming growth factors beta prevents ontogenetic neuron death. Nat Neurosci. 2000;3:1085–1090. doi: 10.1038/80598. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Basu A, Krady JK, Enterline JR, Levison SW. Transforming growth factor beta1 prevents IL-1beta-induced microglial activation, whereas TNFalpha- and IL-6-stimulated activation are not antagonized. Glia. 2002;40:109–120. doi: 10.1002/glia.10118. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Buisson A, Nicole O, Docagne F, Sartelet H, Mackenzie ET, Vivien D. Up-regulation of a serine protease inhibitor in astrocytes mediates the neuroprotective activity of transforming growth factor beta1. Faseb J. 1998;12:1683–1691. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Smith AD, Zigmond MJ. Can the brain be protected through exercise? Lessons from an animal model of parkinsonism. Exp Neurol. 2003;184:31–39. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2003.08.017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Jackson-Lewis V, Smeyne RJ. MPTP and SNpc DA neuronal vulnerability: role of dopamine, superoxide and nitric oxide in neurotoxicity. Minireview. Neurotox Res. 2005;7:193–202. doi: 10.1007/BF03036449. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Liu Y, Qin L, Li G, Zhang W, An L, Liu B, Hong JS. Dextromethorphan Protects Dopamanergic Neurons against Inflammation-Mediated Degeneration through Inhibition of Microglial Activation. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2003;305:1–7. doi: 10.1124/jpet.102.043166. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Qian L, Block ML, Wei SJ, Lin CF, Reece J, Pang H, Wilson B, Hong JS, Flood PM. Interleukin-10 protects lipopolysaccharide-induced neurotoxicity in primary midbrain cultures by inhibiting the function of NADPH oxidase. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2006;319:44–52. doi: 10.1124/jpet.106.106351. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Qian L, Tan KS, Wei SJ, Wu HM, Xu Z, Wilson B, Lu RB, Hong JS, Flood PM. Microglia-Mediated Neurotoxicity Is Inhibited by Morphine through an Opioid Receptor-Independent Reduction of NADPH Oxidase Activity. J Immunol. 2007;179:1198–1209. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.179.2.1198. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Qin L, Liu Y, Wang T, Wei SJ, Block ML, Wilson B, Liu B, Hong JS. NADPH oxidase mediates lipopolysaccharide-induced neurotoxicity and proinflammatory gene expression in activated microglia. J Biol Chem. 2004;279:1415–1421. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M307657200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Liva SM, Kahn MA, Dopp JM, de Vellis J. Signal transduction pathways induced by GM-CSF in microglia: significance in the control of proliferation. Glia. 1999;26:344–352. doi: 10.1002/(sici)1098-1136(199906)26:4<344::aid-glia8>3.0.co;2-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Groemping Y, Rittinger K. Activation and assembly of the NADPH oxidase: a structural perspective. Biochem J. 2005;386:401–416. doi: 10.1042/BJ20041835. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Carmona-Cuenca I, Herrera B, Ventura JJ, Roncero C, Fernandez M, Fabregat I. EGF blocks NADPH oxidase activation by TGF-beta in fetal rat hepatocytes, impairing oxidative stress, and cell death. J Cell Physiol. 2006;207:322–330. doi: 10.1002/jcp.20568. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Zhuge J, Cederbaum AI. Increased toxicity by transforming growth factor-beta 1 in liver cells overexpressing CYP2E1. Free Radic Biol Med. 2006;41:1100–1112. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2006.06.017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Suzumura A, Sawada M, Yamamoto H, Marunouchi T. Transforming growth factor-beta suppresses activation and proliferation of microglia in vitro. J Immunol. 1993;151:2150–2158. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Herrera-Molina R, Bernhardi Rvon. Transforming growth factor-beta 1 produced by hippocampal cells modulates microglial reactivity in culture. Neurobiol Dis. 2005;19:229–236. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2005.01.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Cheepsunthorn P, Radov L, Menzies S, Reid J, Connor JR. Characterization of a novel brain-derived microglial cell line isolated from neonatal rat brain. Glia. 2001;35:53–62. doi: 10.1002/glia.1070. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Liu B, Du L, Hong JS. Naloxone protects rat dopaminergic neurons against inflammatory damage through inhibition of microglia activation and superoxide generation. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2000;293:607–617. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Gao HM, Jiang J, Wilson B, Zhang W, Hong JS, Liu B. Microglial activation-mediated delayed and progressive degeneration of rat nigral dopaminergic neurons: relevance to Parkinson's disease. J Neurochem. 2002;81:1285–1297. doi: 10.1046/j.1471-4159.2002.00928.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Liu B, Du L, Kong LY, Hudson PM, Wilson BC, Chang RC, Abel HH, Hong JS. Reduction by naloxone of lipopolysaccharide-induced neurotoxicity in mouse cortical neuron-glia co-cultures. Neuroscience. 2000;97:749–756. doi: 10.1016/s0306-4522(00)00057-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Peskin AV, Winterbourn CC. A microtiter plate assay for superoxide dismutase using a water-soluble tetrazolium salt (WST-1) Clin Chim Acta. 2000;293:157–166. doi: 10.1016/s0009-8981(99)00246-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Tan AS, Berridge MV. Superoxide produced by activated neutrophils efficiently reduces the tetrazolium salt, WST-1 to produce a soluble formazan: a simple colorimetric assay for measuring respiratory burst activation and for screening anti-inflammatory agents. J Immunol Methods. 2000;238:59–68. doi: 10.1016/s0022-1759(00)00156-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Liu J, Shen HM, Ong CN. Role of intracellular thiol depletion, mitochondrial dysfunction and reactive oxygen species in Salvia miltiorrhiza-induced apoptosis in human hepatoma HepG2 cells. Life Sci. 2001;69:1833–1850. doi: 10.1016/s0024-3205(01)01267-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Yuan ZM, Huang Y, Kraeft SK, Chen LB, Kharbanda S, Kufe D. Interaction of cyclin-dependent kinase 2 and the Lyn tyrosine kinase in cells treated with 1-beta-D-arabinofuranosylcytosine. Oncogene. 1996;13:939–946. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Block ML, Hong JS. Microglia and inflammation-mediated neurodegeneration: Multiple triggers with a common mechanism. Prog Neurobiol. 2005;76:77–98. doi: 10.1016/j.pneurobio.2005.06.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Qian L, Xu Z, Zhang W, Wilson B, Hong JS, Flood PM. Sinomenine, a natural dextrorotatory morphinan analog, is anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective through inhibition of microglial NADPH oxidase. J Neuroinflammation. 2007;4:23–36. doi: 10.1186/1742-2094-4-23. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Gao HM, Liu B, Zhang W, Hong JS. Critical role of microglial NADPH oxidase-derived free radicals in the in vitro MPTP model of Parkinson's disease. Faseb J. 2003;17:1954–1956. doi: 10.1096/fj.03-0109fje. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Dang PM, Stensballe A, Boussetta T, Raad H, Dewas C, Kroviarski Y, Hayem G, Jensen ON, Gougerot-Pocidalo MA, El-Benna J. A specific p47phox -serine phosphorylated by convergent MAPKs mediates neutrophil NADPH oxidase priming at inflammatory sites. J Clin Invest. 2006;116:2033–2043. doi: 10.1172/JCI27544. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Boche D, Cunningham C, Gauldie J, Perry VH. Transforming growth factor-beta 1-mediated neuroprotection against excitotoxic injury in vivo. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2003;23:1174–1182. doi: 10.1097/01.WCB.0000090080.64176.44. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Dhandapani KM, Brann DW. Transforming growth factor-beta: a neuroprotective factor in cerebral ischemia. Cell Biochem Biophys. 2003;39:13–22. doi: 10.1385/CBB:39:1:13. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Wu DC, Teismann P, Tieu K, Vila M, Jackson-Lewis V, Ischiropoulos H, Przedborski S. NADPH oxidase mediates oxidative stress in the 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine model of Parkinson's disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003;100:6145–6150. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0937239100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Jenner P. Oxidative mechanisms in nigral cell death in Parkinson's disease. Mov Disord. 1998;13 Suppl 1:24–34. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Greenamyre JT, MacKenzie G, Peng TI, Stephans SE. Mitochondrial dysfunction in Parkinson's disease. Biochem Soc Symp. 1999;66:85–97. doi: 10.1042/bss0660085. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Pawate S, Shen Q, Fan F, Bhat NR. Redox regulation of glial inflammatory response to lipopolysaccharide and interferongamma. J Neurosci Res. 2004;77:540–551. doi: 10.1002/jnr.20180. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Qian L, Hong JS, Flood PM. Role of microglia in inflammation-mediated degeneration of dopaminergic neurons: neuroprotective effect of interleukin 10. J Neural Transm. 2006 Suppl:367–371. doi: 10.1007/978-3-211-45295-0_56. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Liu Y, Teige I, Birnir B, Issazadeh-Navikas S. Neuron-mediated generation of regulatory T cells from encephalitogenic T cells suppresses EAE. Nat Med. 2006;12:518–525. doi: 10.1038/nm1402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]