Abstract
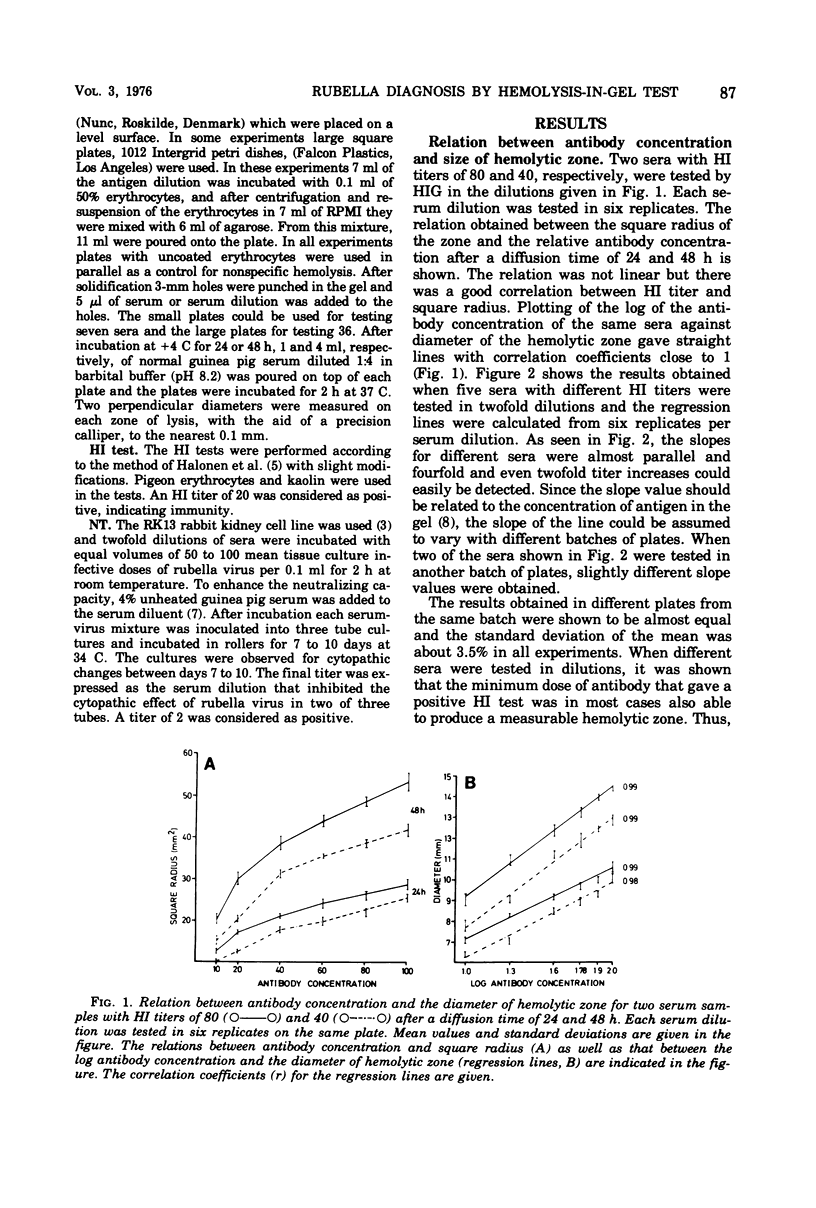
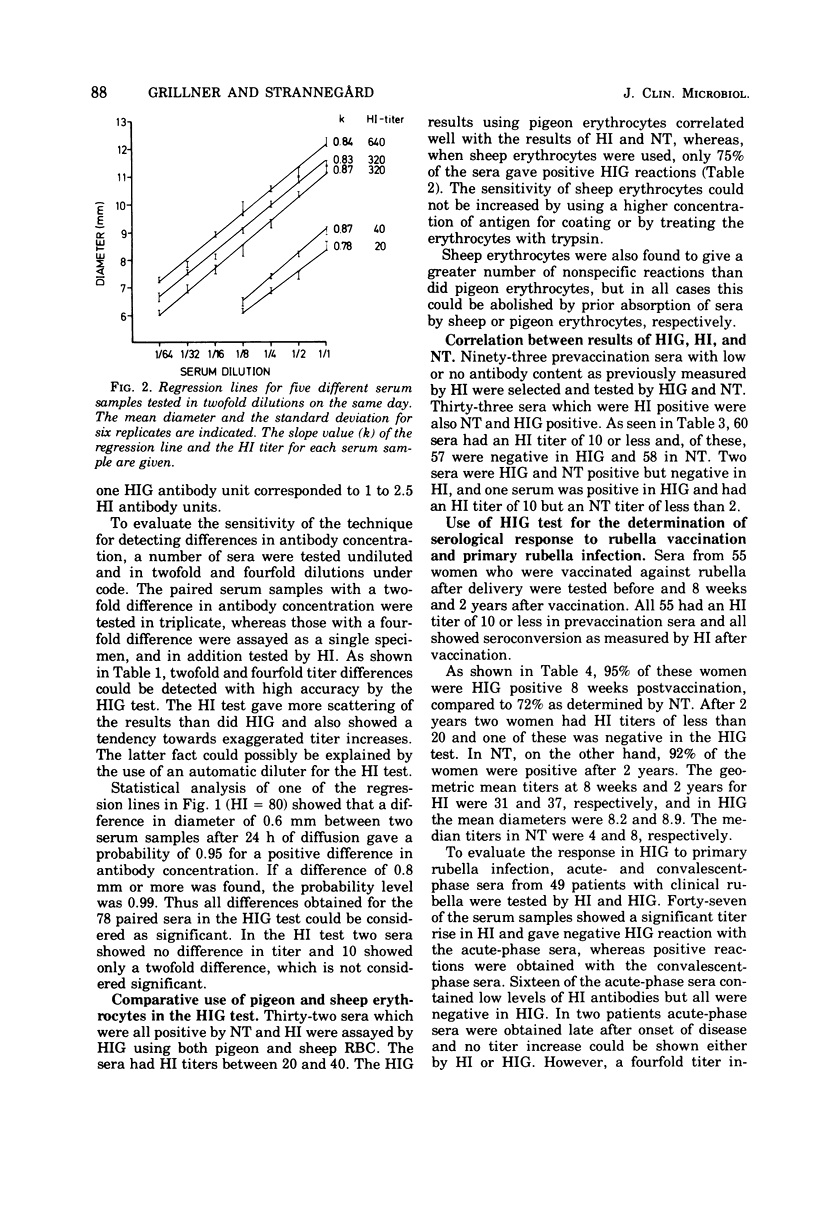
The hemolysis-in-gel method for detection of antibodies to rubella virus gave results which correlated well with results of hemagglutination inhibition and neutralization tests. With a diffusion time of 24 or 48 h, a linear correlation was obtained between the logarithm of antibody concentration and the diameter of the hemolytic zone. Fourfold, and even twofold, differences in serum antibody concentrations were shown to give statistically significant differences in hemolytic zone diameters. It could therefore be concluded that the hemolysis-in-gel test is well suited for the serological diagnosis of primary rubella infection, as well as of reinfection. The sensitivity of the hemolysis-in-gel test was comparable to that of the hemagglutination inhibition test. Pigeon erythrocytes were superior to sheep erythrocytes for use in the test. Studies of the antibody response after natural rubella infection or vaccination showed that the appearance and persistence of antibodies measured by hemolysis in gel is similar to that of hemagglutination inhibition antibodies.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Eilard T., Strannegård O. Rubella reinfection in pregnancy followed by transmission to the fetus. J Infect Dis. 1974 May;129(5):594–596. doi: 10.1093/infdis/129.5.594. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FAHEY J. L., MCKELVEY E. M. QUANTITATIVE DETERMINATION OF SERUM IMMUNOGLOBULINS IN ANTIBODY-AGAR PLATES. J Immunol. 1965 Jan;94:84–90. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furesz J., Moreau P., Yarosh W. A micro tissue culture test for the titration and neutralization of rubella virus. Can J Microbiol. 1969 Jan;15(1):67–71. doi: 10.1139/m69-011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grillner L. Neutralizing antibodies after rubella vaccination of newly delivered women: a comparison between three vaccines. Scand J Infect Dis. 1975;7(3):169–172. doi: 10.3109/inf.1975.7.issue-3.03. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halonen P. E., Ryan J. M., Stewart J. A. Rubella hemagglutinin prepared with alkaline extraction of virus grown in suspension culture of BHK-21 cells. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1967 May;125(1):162–167. doi: 10.3181/00379727-125-32038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horstmann D. M., Liebhaber H., Le Bouvier G. L., Rosenberg D. A., Halstead S. B. Rubella: reinfection of vaccinated and naturally immune persons exposed in an epidemic. N Engl J Med. 1970 Oct 8;283(15):771–778. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197010082831501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leerhoy J. Rubella virus neutralization in heated sera. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1968;73(2):275–282. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mancini G., Carbonara A. O., Heremans J. F. Immunochemical quantitation of antigens by single radial immunodiffusion. Immunochemistry. 1965 Sep;2(3):235–254. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(65)90004-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quirin E. P., Nelson D. B., Inhorn S. L. Use of trypsin-modified human erythrocytes in rubella hemagglutination-inhibition testing. Appl Microbiol. 1972 Sep;24(3):353–357. doi: 10.1128/am.24.3.353-357.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell S. M., McCahon D., Beare A. S. A single radial haemolysis technique for the measurement of influenza antibody. J Gen Virol. 1975 Apr;27(1):1–10. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-27-1-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skaug K., Orstavik I., Ulstrup J. C. Application of the passive haemolysis test for the determination of rubella virus antibodies. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B. 1975 Aug;83(4):367–372. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1975.tb00114.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strannegård O., Grillner L., Lindberg I. M. Hemolysis-in-gel test for the demonstration of antibodies to rubella virus. J Clin Microbiol. 1975 Jun;1(6):491–494. doi: 10.1128/jcm.1.6.491-494.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


