Abstract
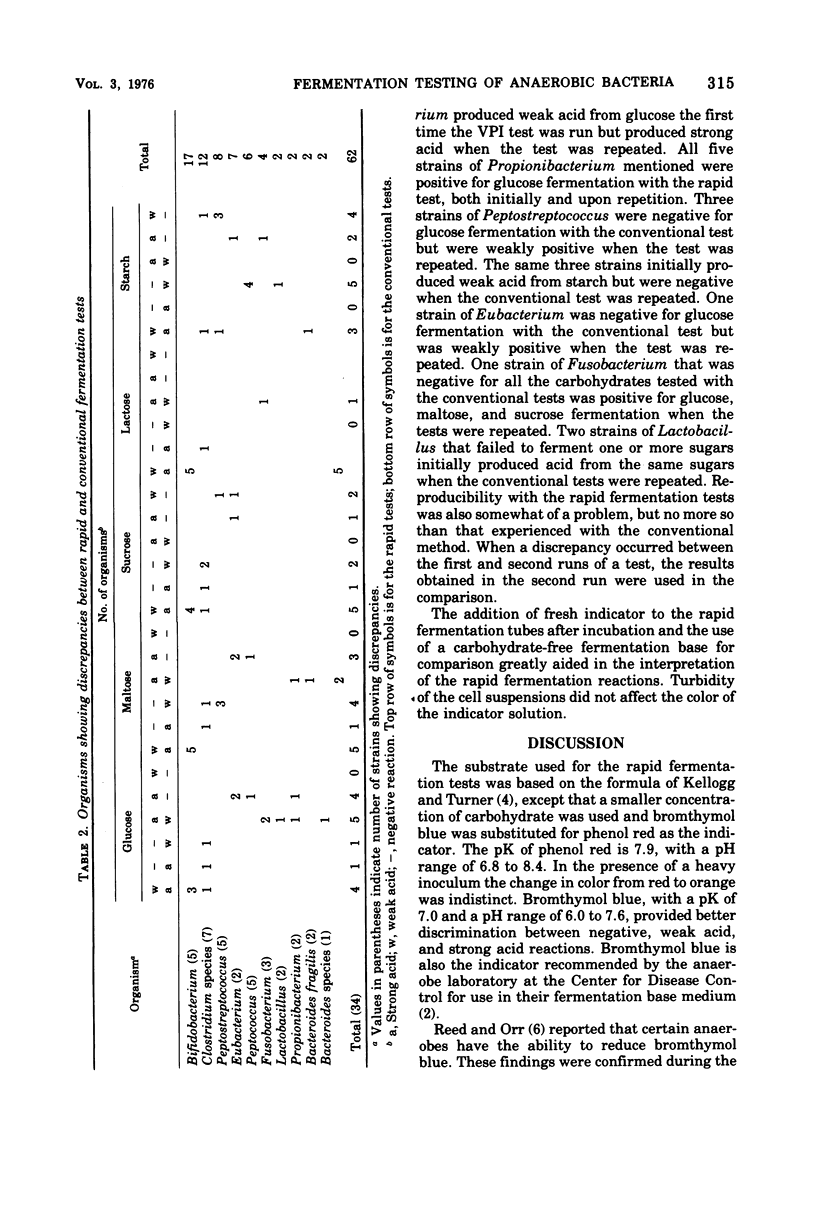
Rapid tests for glucose, maltose, lactose, sucrose, and starch fermentation were performed on 112 strains of anaerobic bacteria. The tests were incubated under aerobic conditions, and results were read within 4 h. An overall correlation of 89% was achieved between the rapid tests and the Virginia Polytechnic Institute method.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brown W. J. Modification of the rapid fermentation test for Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Appl Microbiol. 1974 Jun;27(6):1027–1030. doi: 10.1128/am.27.6.1027-1030.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kellogg D. S., Jr, Turner E. M. Rapid fermentation confirmation of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Appl Microbiol. 1973 Apr;25(4):550–552. doi: 10.1128/am.25.4.550-552.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore H. B., Sutter V. L., Finegold S. M. Comparison of three procedures for biochemical testing of anaerobic bacteria. J Clin Microbiol. 1975 Jan;1(1):15–24. doi: 10.1128/jcm.1.1.15-24.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreckenberger P. C., Blazevic D. J. Rapid methods for biochemical testing of anaerobic bacteria. Appl Microbiol. 1974 Nov;28(5):759–762. doi: 10.1128/am.28.5.759-762.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starr S. E., Thompson F. S., Dowell V. R., Jr, Balows A. Micromethod system for identification of anaerobic bacteria. Appl Microbiol. 1973 May;25(5):713–717. doi: 10.1128/am.25.5.713-717.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



